Abstract
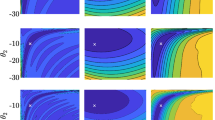
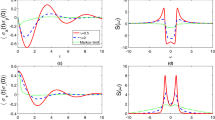
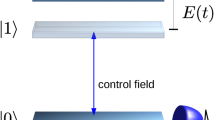
In this paper, we present a least squares approach to identifying an unknown damping rate function in a time-convolution-less master equation describing the non-Markovian dynamics of a probing single qubit. For the purpose of identification, we measure two kinds of time trace observables \(\langle \sigma _z\rangle \) and \(\langle \sigma _x\rangle \) with which the identification problem can be solved via our least squares approach. In the case of measuring the time trace observable \(\langle \sigma _x\rangle \), a data-driven method is also developed to estimate the unmeasured \(\langle \sigma _y\rangle \) such that the identification problem fits into the least squares framework. A physical example is given to show the effectiveness of our method.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertini, F., D’Alessandro, D.: Model identification for spin networks. Linear Algebra Appl. 394, 237–256 (2005)
Barata, J.C.A., Hussein, M.S.: The Moore–Penrose pseudoinverse: a tutorial review of the theory. Braz. J. Phys. 42(1), 146–165 (2012)
Bonnabel, S., Mirrahimi, M., Rouchon, P.: Observer-based Hamiltonian identification for quantum systems. Automatica 45(5), 1144–1155 (2009)
Breuer, H.P., Petruccione, F.: The Theory of Open Quantum Systems. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2002)
Burgarth, D., Maruyama, K.: Indirect Hamiltonian identification through a small gateway. New J. Phys. 11(10), 103019 (2009)
Burgarth, D., Yuasa, K.: Quantum system identification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 080502 (2012)
D’Alessandro, D.: Controllability, observability, and parameter identification of two coupled spin 1’s. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 50(7), 1054–1058 (2005)
Frey, T., Leek, P.J., Beck, M., Blais, A., Ihn, T., Ensslin, K., Wallraff, A.: Dipole coupling of a double quantum dot to a microwave resonator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 046807 (2012)
Gambetta, J., Wiseman, H.M.: State and dynamical parameter estimation for open quantum systems. Phys. Rev. A 64, 042105 (2001)
Gută, M.: Fisher information and asymptotic normality in system identification for quantum Markov chains. Phys. Rev. A 83, 062324 (2011)
Gută, M., Yamamoto, N.: System identification for passive linear quantum systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 61(4), 921–936 (2016)
Hou, S.Y., Li, H., Long, G.L.: Experimental quantum Hamiltonian identification from measurement time traces. Sci. Bull. 62(12), 863–868 (2017)
Kato, Y., Yamamoto, N.: Structure identification and state initialization of spin networks with limited access. New J. Phys. 16(2), 023024 (2014)
Le Bris, C., Mirrahimi, M., Rabitz, H., Turinici, G.: Hamiltonian identification for quantum systems: well-posedness and numerical approaches. ESAIM Control Optim. Calc. Var. 13(2), 378–395 (2007)
Mabuchi, H., Khaneja, N.: Principles and applications of control in quantum systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear 15, 647–667 (2005)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Owari, M., Maruyama, K., Takui, T., Kato, G.: Probing an untouchable environment for its identification and control. Phys. Rev. A 91, 012343 (2015)
Phan, M.Q., Rabitz, H.: Learning control of quantum-mechanical systems by laboratory identification of effective input–output maps. Chem. Phys. 217(2), 389–400 (1997)
Schirmer, S.G., Kolli, A., Oi, D.K.L.: Experimental Hamiltonian identification for controlled two-level systems. Phys. Rev. A 69, 050306 (2004)
Sone, A., Cappellaro, P.: Hamiltonian identifiability assisted by a single-probe measurement. Phys. Rev. A 95, 022335 (2017)
Wu, R.B., Li, T.F., Kofman, A.G., Zhang, J., Liu, Y.X., Pashkin, Y.A., Tsai, J.S., Nori, F.: Spectral analysis and identification of noises in quantum systems. Phys. Rev. A 87, 022324 (2013)
Xue, S., Zhang, J., Petersen, I.R.: Identification of non-Markovian environments for spin chains. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCST.2018.2879042
Xue, S.B., Zhang, J., Wu, R.B., Li, C.W., Tarn, T.J.: Quantum operation for a one-qubit system under a non-Markovian environment. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Phys. 44(15), 154016 (2011)
Xue, Z., Lin, H., Lee, T.H.: Identification of unknown parameters for a class of two-level quantum systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 58(7), 1805–1810 (2013)
Zhang, J., Sarovar, M.: Quantum Hamiltonian identification from measurement time traces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 080401 (2014)
Zhang, J., Sarovar, M.: Identification of open quantum systems from observable time traces. Phys. Rev. A 91, 052121 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61873162 and 61473199, in part by the Shanghai Pujiang Program under Grant 18PJ1405500, in part by the Suzhou Key Industry Technology Innovation Project SYG201808, in part by the Key Laboratory of System Control and Information Processing in Ministry of Education of China Scip201804. This work is also supported by the Open Research Project of the State Key Laboratory of Industrial Control Technology, Zhejiang University, China (No. ICT1900304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, S., Tan, L., Jiang, M. et al. A least squares identifier for a quantum non-Markovian environment model. Quantum Inf Process 18, 310 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2425-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2425-0