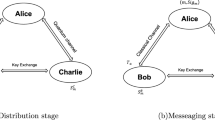
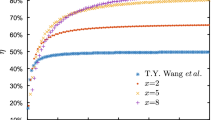
Abstract
Quantum digital signature (QDS) provides an effective method to guarantee the information-theoretical security of signature messages. Here, we propose a scheme of implementing QDS with configurable decoy states. In this scheme, the legitimate parties configure the number of decoy states to maximize the signature rate and/or simplify the experimental operation in practical scenarios. Considering different optical intrinsic errors, we investigate the performance of a typical QDS system in one and two decoy-state cases and give the corresponding guide to configure decoy states, which we expect would be valuable for researchers to design QDS systems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rivest, R.L., Shamir, A., Adleman, L.: A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Commun. ACM 21, 120–126 (1978)
Diffie, W., Hellman, M.: New directions in cryptography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 22, 644–654 (1976)
Gottesman, D., Chuang, I.: Quantum digital signatures. Preprint arXiv:quant-ph/0105032 (2001)
Dunjko, V., Wallden, P., Andersson, E.: Quantum digital signatures without quantum memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 040502 (2014)
Wallden, P., Dunjko, V., Kent, A., Andersson, E.: Quantum digital signatures with quantum-key-distribution components. Phys. Rev. A 91, 042304 (2015)
Amiri, R., Wallden, P., Kent, A., Andersson, E.: Secure quantum signatures using insecure quantum channels. Phys. Rev. A 93, 032325 (2016)
Puthoor, I.V., Amiri, R., Wallden, P., Curty, M., Andersson, E.: Measurement-device-independent quantum digital signatures. Phys. Rev. A 94, 022328 (2016)
Yin, H.L., Fu, Y., Chen, Z.B.: Practical quantum digital signature. Phys. Rev. A 93, 032316 (2016)
Collins, R.J., Donaldson, R.J., Dunjko, V., Wallden, P., Clarke, P.J., Andersson, E., Jeffers, J., Buller, G.S.: Realization of quantum digital signatures without the requirement of quantum memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 040502 (2014)
Roberts, G., Lucamarini, M., Yuan, Z., Dynes, J., Comandar, L., Sharpe, A., Shields, A., Curty, M., Puthoor, I., Andersson, E.: Experimental measurement-device-independent quantum digital signatures. Nat. Commun. 8, 1098 (2017)
An, X.B., Zhang, H., Zhang, C.M., Chen, W., Wang, S., Yin, Z.Q., Wang, Q., He, D.Y., Hao, P.L., Liu, S.F., Zhou, X.Y., Guo, G.C., Han, Z.F.: Practical quantum digital signature with a gigahertz BB84 quantum key distribution system. Opt. Lett. 44, 139–142 (2019)
Zhang, C.H., Zhou, X.Y., Ding, H.J., Zhang, C.M., Guo, G.C., Wang, Q.: Proof-of-principle demonstration of passive decoy-state quantum digital signatures over 200 km. Phys. Rev. Appl. 10, 034033 (2018)
Yin, H.L., Fu, Y., Liu, H., Tang, Q.J., Wang, J., You, L.X., Zhang, W.J., Chen, S.J., Wang, Z., Zhang, Q., Chen, T.Y., Chen, Z.B., Pan, J.W.: Experimental quantum digital signature over 102 km. Phys. Rev. A 95, 032334 (2017)
Yin, H.L., Wang, W.L., Tang, Y.L., Zhao, Q., Liu, H., Sun, X.X., Zhang, W.J., Li, H., Puthoor, I.V., You, L.X., Andersson, E., Wang, Z., Liu, Y., Jiang, X., Ma, X., Zhang, Q., Curty, M., Chen, T.Y., Pan, J.W.: Experimental measurement-device-independent quantum digital signatures over a metropolitan network. Phys. Rev. A 95, 042338 (2017)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, pp. 175–179 (1984)
Lo, H.K., Ma, X., Chen, K.: Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230504 (2005)
Wang, X.B.: Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230503 (2005)
Huttner, B., Imoto, N., Gisin, N., Mor, T.: Quantum cryptography with coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 51, 1863–1869 (1995)
Brassard, G., Lütkenhaus, N., Mor, T., Sanders, B.C.: Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1330–1333 (2000)
Rusca, D., Boaron, A., Grünenfelder, F., Martin, A., Zbinden, H.: Finite-key analysis for the 1-decoy state QKD protocol. Appl. Phys. Lett. 112, 171104 (2018)
Boaron, A., Boso, G., Rusca, D., Vulliez, C., Autebert, C., Caloz, M., Perrenoud, M., Gras, G., Bussières, F., Li, M., Nolan, D., Martin, A., Zbinden, H.: Secure quantum key distribution over 421 km of optical fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 190502 (2018)
Bacco, D., Vagniluca, I., Lio, B., Biagi, N., Frera, A., Calonico, D., Toninelli, C., Cataliotti, F., Bellini, M., Oxenløwe, L., Zavatta, A.: Field trial of a three-state quantum key distribution scheme in the Florence metropolitan area. EPJ Quantum Technol. 6, 5 (2019)
Lim, C.C.W., Curty, M., Walenta, N., Xu, F., Zbinden, H.: Concise security bounds for practical decoy-state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 89, 022307 (2014)
Serfling, R.J.: Probability inequalities for the sum in sampling without replacement. Ann. Stat. 2, 39–48 (1974)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grants 2018YFA0306400, 2017YFA0304100, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 11847215, 61705110, 11774180, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grants 2019T120446, 2018M642281, the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grant BK20170902, and the Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds under Grant 2018K185C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, CM., Zhu, Y., Chen, JJ. et al. Practical quantum digital signature with configurable decoy states. Quantum Inf Process 19, 151 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-02648-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-02648-y