Abstract
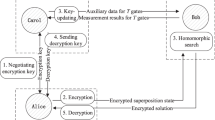
Quantum information processing protocols have great advantages over their classical counterparts, especially on cryptography. Homomorphic encryption (HE) schemes enable processing encrypted data without decrypting them. In this paper, we study a quantum version of the HE scheme (iacr-ePrint/2019/1023) and improve it with flexible parties. Furthermore, we propose a threshold quantum secret scheme since multiparty cryptosystem is more practical due to its flexibility. These two schemes only require sequential decryption of quantum states. As a result, both schemes are information theoretically secure, perfectly correct and support homomorphism in a fully compact and non-interactive way. Finally, they are tested and verified on the IBM Q Experience platform.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., DiVincenzo, D.P.: Quantum information and computation. Nature 404(6775), 247 (2000)
Einstein, A., Podolsky, B., Rosen, N.: Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be considered complete? Phys. Rev. 47, 777–780 (1935)
Bell, J.S.: On the einstein podolsky rosen paradox. Physics 1(3), 195–200 (1964)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Systems and Signal Processing, pp. 175–179, New York, USA (1984)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peresand, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70(13), 1895–1899 (1993)
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 124–134. IEEE (1994)
Grover, L.K.: Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a haystack. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79(2), 325 (1997)
Hillery, M., Bužek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59(3), 1829 (1999)
Crépeau, C., Gottesman, D., Smith, A.: Secure multi-party quantum computation. In: Proceedings of the Thiry-fourth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 643–652. ACM (2002)
Zeng, G., Keitel, C.H.: Arbitrated quantum-signature scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65(4), 042312 (2002)
Deng, F.-G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.-S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042317 (2003)
Zhang, K.J., Zhang, L., Song, T.T., Yang, Y.H.: A potential application in quantum networks-deterministic quantum operation sharing schemes with bell states. Scie. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 59(6), 660302 (2016)
Zhang, K., Zhang, X., Jia, H., Zhang, L.: A new n-party quantum secret sharing model based on multiparty entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(3), 81 (2019)
Zhang, C., Razavi, M., Sun, Z., Situ, H.: Improvements on secure multi-party quantum summation based on quantum fourier transform. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(11), 336 (2019)
Zhang, C., Razavi, M., Sun, Z., Huang, Q., Situ, H.: Multi-party quantum summation based on quantum teleportation. Entropy 21(7), 719 (2019)
Gentry, C., Boneh, D.: A Fully Homomorphic Encryption Scheme. Stanford University, Stanford (2009)
Acar, A., Aksu, H., Uluagac, A.S., Conti, M.: A survey on homomorphic encryption schemes: theory and implementation. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 51(4), 79 (2018)
Martins, P., Sousa, L., Mariano, A.: A survey on fully homomorphic encryption: an engineering perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 50(6), 83 (2018)
Rohde, P.P., Fitzsimons, J.F., Gilchrist, A.: Quantum walks with encrypted data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109(15), 150501 (2012)
Liang, M.: Symmetric quantum fully homomorphic encryption with perfect security. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(12), 3675–3687 (2013)
Tan, S.-H., Kettlewell, J.A., Ouyang, Y., Chen, L., Fitzsimons, J.F.: A quantum approach to homomorphic encryption. Sci. Rep. 6, 33467 (2016)
Ouyang, Y., Tan, S.-H., Fitzsimons, J.F.: Quantum homomorphic encryption from quantum codes. Phys. Rev. A 98(4), 042334 (2018)
Tan, S.-H., Ouyang, Y., Rohde, P.P.: Practical somewhat-secure quantum somewhat-homomorphic encryption with coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 97(4), 042308 (2018)
Ouyang, Y., Tan, S.-H., Fitzsimons, J., Rohde, P.P.: Homomorphic encryption of linear optics quantum computation on almost arbitrary states of light with asymptotically perfect security. Phys. Rev. Res. 2(1), 013332 (2020)
Broadbent, A., Jeffery, S.: Quantum homomorphic encryption for circuits of low t-gate complexity. In: Annual Cryptology Conference, pp. 609–629. Springer, Berlin (2015)
Dulek, Y., Schaffner, C., Speelman, F.: Quantum homomorphic encryption for polynomial-sized circuits. In: Annual International Cryptology Conference, pp. 3–32. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Alagic, G., Dulek, Y., Schaffner, C., Speelman, F.: Quantum fully homomorphic encryption with verification. In: International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, pp. 438–467. Springer, Berlin (2017)
Mahadev, U.: Classical homomorphic encryption for quantum circuits. In: 2018 IEEE 59th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS), pp. 332–338. IEEE (2018)
Brakerski, Z.: Quantum FHE (almost) as secure as classical. In: Annual International Cryptology Conference, pp. 67–95. Springer, Berlin (2018)
Yu, L., Pérez-Delgado, C.A., Fitzsimons, J.F.: Limitations on information-theoretically-secure quantum homomorphic encryption. Phys. Rev. A 90(5), 050303 (2014)
Aharonov, D., Brakerski, Z., Chung, K.-M., Green, A., Lai, C.-Y., Sattath, O.: On quantum advantage in information theoretic single-server PIR. In: Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, pp. 219–246. Springer, Berlin (2019)
Bitan, D., Dolev, S.: Randomly rotate qubits compute and reverse—it-secure non-interactive fully-compact homomorphic quantum computations over classical data using random bases. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Report 2019/1023 (2019). https://eprint.iacr.org/2019/1023
Cleve, R., Gottesman, D., Lo, H.-K.: How to share a quantum secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83(3), 648 (1999)
Ouyang, Y., Tan, S.-H., Zhao, L., Fitzsimons, J.F.: Computing on quantum shared secrets. Phys. Rev. A 96(5), 052333 (2017)
Shamir, A.: How to share a secret. Commun. ACM 22(11), 612–613 (1979)
Changbin, L., Miao, F., Hou, J., Huang, W., Xiong, Y.: A verifiable framework of entanglement-free quantum secret sharing with information-theoretical security. Quantum Inf. Process. 19(1), 24 (2020)
Ambainis, A., Mosca, M., Tapp, A., De Wolf, R.: Private quantum channels. In: Proceedings 41st Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 547–553. IEEE (2000)
Rivest, R.L., Adleman, L., Dertouzos, M.L.: On data banks and privacy homomorphisms. Founda. Sec. Comput. 4(11), 169–180 (1978)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for helpful suggestions. This work is supported by Key Research and Development Program of China 2018YFB0803400, National Natural Science Foundation of China 61572454, 61572453, 61520106007 and Anhui Initiative in Quantum Information Technologies AHY150100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, C., Miao, F., Hou, J. et al. Quantum multiparty cryptosystems based on a homomorphic random basis encryption. Quantum Inf Process 19, 293 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-02788-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-02788-1