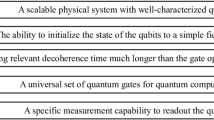
Abstract
In this paper we propose several new quantum computation algorithms as an original contribution to the domain of PageRank algorithm theory, Spectral Graph Theory and Quantum Signal Processing. We first propose an application to PageRank of the HHL quantum algorithm for linear equation systems. We then introduce one of the first Quantum-Based Algorithms to perform a directed Graph Fourier Transform with a low gate complexity. After proposing a generalized PageRank formulation, based on ideas stemming from Spectral Graph Theory, we show how our quantum directed graph Fourier Transform can be applied to compute our generalized version of the PageRank.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the repository Generalized PageRank on Gitlab: https://gitlab-research.centralesupelec.fr/theodore.chapuis-chkaiban/generalised_pagerank
References
Brin, S., Page, L.: The anatomy of a large-scale hypertextual web search engine. Comput. Netw. ISDN Syst. 30(1–7), 107–117 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-7552(98)00110-x
University, C.: Networks. https://blogs.cornell.edu/info2040/2014/11/03/more-than-just-a-web-search-algorithm-googles-pagerank-in-non-internet-contexts/
Gleich, D.F.: Pagerank beyond the web. SIAM Rev. 57(3), 321–363 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1137/140976649
Shuman, D.I., Narang, S.K., Frossard, P., Ortega, A., Vandergheynst, P.: The emerging field of signal processing on graphs: Extending high-dimensional data analysis to networks and other irregular domains. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 30(3), 83–98 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/msp.2012.2235192
Chung, F.R.K., Graham, F.C., on Recent Advances in Spectral Graph Theory, C.C., (U.S.), N.S.F., Society, A.M., of the Mathematical Sciences, C.B.: Spectral graph theory (1997)
Ricaud, B., Borgnat, P., Tremblay, N., Gonçalves, P., Vandergheynst, P.: Fourier could be a data scientist: From graph Fourier transform to signal processing on graphs. C. R. Phys. 20(5), 474–488 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crhy.2019.08.003
Sevi, H., Rilling, G., Borgnat, P.: Harmonic analysis on directed graphs and applications: from Fourier analysis to wavelets (2019)
Harrow, A.W., Hassidim, A., Lloyd, S.: Quantum algorithm for linear systems of equations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 15 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.103.150502
Garnerone, S., Zanardi, P., Lidar, D.A.: Adiabatic quantum algorithm for search engine ranking. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 23 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.108.230506
Gilyén, A., Su, Y., Low, G.H., Wiebe, N.: Quantum singular value transformation and beyond: exponential improvements for quantum matrix arithmetics. In: Proceedings of the 51st Annual ACM SIGACT Symposium on Theory of Computing (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3313276.3316366
Paparo, G.D., Martin-Delgado, M.A.: Google in a quantum network. Sci. Rep. 2, 1 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00444
Choromański, K., Matuszak, M., Jacek, M.: Scale-free graph with preferential attachment and evolving internal vertex structure. J. Stat. Phys. 151(6), 1175–1183 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-013-0749-1
Barabási, A.-L., Albert, R.: Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 286(5439), 509–512 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.286.5439.509
Albert, R., Barabási, A.-L.: Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74(1), 47–97 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/revmodphys.74.47
Meyer, C.: Matrix analysis and applied linear algebra (2000). https://doi.org/10.1137/1.9780898719512
Boldi, P., Posenato, R., Santini, M., Vigna, S.: Traps and pitfalls of topic-biased pagerank. Algorithms and Models for the Web-Graph Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 107–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-78808-9_10
Langville, A., Meyer, C.: Deeper inside pagerank. Internet Math. 1(3), 335–380 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1080/15427951.2004.10129091
Paparo, G.D., Müller, M., Comellas, F., Martin-Delgado, M.A.: Quantum google algorithm. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 129, 7 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2014-14150-y
Paparo, G.D., Müller, M., Comellas, F., Martin-Delgado, M.A.: Quantum google in a complex network. Sci. Rep. 3, 1 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02773
Sánchez-Burillo, E., Duch, J., Gómez-Gardeñes, J., Zueco, D.: Quantum navigation and ranking in complex networks. Sci. Rep. 2, 1 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00605
Loke, T., Tang, J.W., Rodriguez, J., Small, M., Wang, J.B.: Comparing classical and quantum pageranks. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 1 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1456-z
Kempe, J.: Quantum random walks: an introductory overview. Contemp. Phys. 50(1), 339–359 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/00107510902734722
Clader, B.D., Jacobs, B.C., Sprouse, C.R.: Preconditioned quantum linear system algorithm. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 25 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.110.250504
Zhao, Z., Pozas-Kerstjens, A., Rebentrost, P., Wittek, P.: Bayesian deep learning on a quantum computer. Quantum Mach. Intell. 1(1–2), 41–51 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42484-019-00004-7
Pan, J., Cao, Y., Yao, X., Li, Z., Ju, C., Chen, H., Peng, X., Kais, S., Du, J.: Experimental realization of quantum algorithm for solving linear systems of equations. Phys. Rev. A 89, 2 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/physreva.89.022313
Team, T.Q.: Solving Linear Systems of Equations using HHL. Data 100 at UC Berkeley (2021). https://qiskit.org/textbook/ch-applications/hhl_tutorial.html
Grinko, D., Gacon, J., Zoufal, C., Woerner, S.: Iterative quantum amplitude estimation. NPJ Quantum Inf. 7, 1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-021-00379-1
Brassard, G., Høyer, P., Mosca, M., Tapp, A.: Quantum amplitude amplification and estimation. Contemp. Math. Quantum Comput. Inf. 305, 53–74 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1090/conm/305/05215
Sandryhaila, A., Moura, J.M.F.: Discrete signal processing on graphs: Frequency analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(12), 3042–3054 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/tsp.2014.2321121
Sardellitti, S., Barbarossa, S., Lorenzo, P.D.: Graph fourier transform for directed graphs based on lovász extension of min-cut. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/icassp.2017.7952886
Magniez, F., Nayak, A., Roland, J., Santha, M.: Search via quantum walk. SIAM J. Comput. 40(1), 142–164 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1137/090745854
Childs, A.M., Jeffery, S., Kothari, R., Magniez, F.: A time-efficient quantum walk for 3-distinctness using nested updates (2013). https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.1302.7316
Lin, J., Bao, W.-S., Zhang, S., Li, T., Wang, X.: An improved quantum principal component analysis algorithm based on the quantum singular threshold method. Phys. Lett. A 383(24), 2862–2868 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2019.06.026
Duan, B., Yuan, J., Liu, Y., Li, D.: Efficient quantum circuit for singular-value thresholding. Phys. Rev. A 98, 1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/physreva.98.012308
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L.: Architectures for a quantum random access memory. Phys. Rev. A 78, 5 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/physreva.78.052310
Arunachalam, S., Gheorghiu, V., Jochym-O’Connor, T., Mosca, M., Srinivasan, P.V.: On the robustness of bucket brigade quantum ram. New J. Phys. 17(12), 123010 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/17/12/123010
Park, D.K., Petruccione, F., Rhee, J.-K.K.: Circuit-based quantum random access memory for classical data. Sci. Rep. 9, 1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40439-3
Szegedy, M.: Quantum speed-up of markov chain based algorithms. In: 45th Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.1109/focs.2004.53
Ortega, A., Frossard, P., Kovacevic, J., Moura, J.M.F., Vandergheynst, P.: Graph signal processing: overview, challenges, and applications. Proc. IEEE 106(5), 808–828 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/jproc.2018.2820126
Yang, H., King, I., Lyu, M.R.: Diffusionrank. In: Proceedings of the 30th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval - SIGIR 07 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1145/1277741.1277815
Baeza-Yates, R., Boldi, P., Castillo, C.: Generalizing pagerank. Proceedings of the 29th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval - SIGIR 06 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1145/1148170.1148225
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T. Chapuis-Chkaiban, as the main author, produced most of the results presented in this paper and wrote the first version of the manuscript. Z.Toffano and B.Valiron, as co-authors, have made several research suggestions—both of them contributed equally to the scientific content. Besides, Z.Toffano and B.Valiron corrected and contributed to the writing and clarification of the manuscript and made several structural improvements for the final submitted version of this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A Generalized PageRank using various Kernels
Appendix A Generalized PageRank using various Kernels
See Figs. 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 and Tables 4, 5.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chapuis-Chkaiban, T., Toffano, Z. & Valiron, B. On new PageRank computation methods using quantum computing. Quantum Inf Process 22, 138 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03856-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03856-y