Abstract
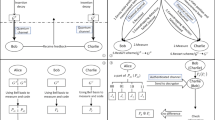
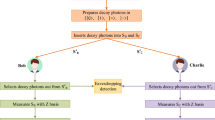
At the current stage, quantum secret sharing (QSS) protocols still face many challenges and difficulties in practical application, including the expensive cost of quantum devices and the difficulties of quantum memory technology development. In order to solve the problem of expensive quantum devices, some scholars proposed the collective detection strategy, which cuts the use of quantum devices and increases communication efficiency. However, the use of quantum memory is usually still inevitable in these QSS protocols with collective detection. In this paper, we propose a newly designed (n,n) -threshold multiparty quantum secret sharing protocol with collective detection. And in this protocol, the sender Alice will measure the agents’ qubits as soon as she receives them, avoiding the use of quantum memory. Considering the difficulties in the development of quantum memory, our protocol is more promising for practical application than the previous QSS protocol with collective detection. Additionally, we also analyze communication security and discuss measurement, the used quantum devices, and the communication efficiency of this new formalism.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum information and computation. Phys. Today 48(10), 24–30 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.881452
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: Discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science. SFCS ’94, pp. 124–134. IEEE Computer Society, USA (1994). https://doi.org/10.1109/SFCS.1994.365700
Monz, T., Nigg, D., Martinez, E.A., Brandl, M.F., Schindler, P., Rines, R., Wang, S.X., Chuang, I.L., Blatt, R.: Realization of a scalable Shor algorithm. Science 351(6277), 1068–1070 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad9480
Xu, G.-B., Jiang, D.-H.: Novel methods to construct nonlocal sets of orthogonal product states in an arbitrary bipartite high-dimensional system. Quantum Inf. Process. 20(4), 128 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03062-8
Bennett, C., Brassard, G.: Withdrawn: Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing, 560, pp. 175–179 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2011.08.039
Cleve, R., Gottesman, D., Lo, H.-K.: How to share a quantum secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 648–651 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.83.648
Quantum secret sharing: Hillery, M., Buž žek, V., Berthiaume, A. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829–1834 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.59.1829
Liu, B., Gao, F., Wen, Q.-Y.: Single-photon multiparty quantum cryptographic protocols with collective detection. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 47(11), 1383–1390 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/JQE.2011.2167743
Zhou, Y., Yu, J., Yan, Z., Jia, X., Zhang, J., Xie, C., Peng, K.: Quantum secret sharing among four players using multipartite bound entanglement of an optical field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 150502 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.150502
Chen, X.-B., Tang, X., Xu, G., Dou, Z., Chen, Y.-L., Yang, Y.-X.: Cryptanalysis of secret sharing with a single d-level quantum system. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(9), 225 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-1988-5
Xiao, L., Lu Long, G., Deng, F.-G., Pan, J.-W.: Efficient multiparty quantum-secret-sharing schemes. Phys. Rev. A 69, 052307 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.69.052307
Markham, D., Sanders, B.C.: Graph states for quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 78, 042309 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.78.042309
Lin, S., Wen, Q.-Y., Qin, S.-J., Zhu, F.-C.: Multiparty quantum secret sharing with collective eavesdropping-check. Opt. Commun. 282(22), 4455–4459 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2009.07.053
Hsu, J.-L., Chong, S.-K., Hwang, T., Tsai, C.-W.: Dynamic quantum secret sharing. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(1), 331–344 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-012-0380-0
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 3121–3124 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.68.3121
Scarani, V., Acín, A., Ribordy, G., Gisin, N.: Quantum cryptography protocols robust against photon number splitting attacks for weak laser pulse implementations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 057901 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.057901
Ma, X., Qi, B., Zhao, Y., Lo, H.-K.: Practical decoy state for quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 72, 012326 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.72.012326
Xu, F., Ma, X., Zhang, Q., Lo, H.-K., Pan, J.-W.: Secure quantum key distribution with realistic devices. Rev. Mod. Phys. 92, 025002 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.92.025002
Zhou, C., Wang, X., Zhang, Z., Yu, S., Chen, Z., Guo, H.: Rate compatible reconciliation for continuous-variable quantum key distribution using Raptor-like LDPC codes. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 64(6), 260311 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-021-1688-4
Gao, F., Qin, S.-J., Guo, F.-Z., Wen, Q.-Y.: Dense-coding attack on three-party quantum key distribution protocols. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 47(5), 630–635 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/JQE.2011.2107889
Boström, K., Felbinger, T.: Deterministic secure direct communication using entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 187902 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.187902
Wang, X.-Y., Zhao, S.-H., Dong, C., Zhu, Z.-D., Gu, W.-Y.: Orbital angular momentum-encoded measurement device independent quantum key distribution under atmospheric turbulence. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(10), 304 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2424-1
Yang, Y.-G., Wang, H.-Y., Jia, X., Zhang, H.: A Quantum Protocol for (t, n)-Threshold Identity Authentication Based on Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger States. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52(2), 524–530 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-012-1356-7
Zhang, Z., Zeng, G., Zhou, N., Xiong, J.: Quantum identity authentication based on ping-pong technique for photons. Phys. Lett. A 356(3), 199–205 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2006.03.048
Liu, B., Gao, Z., Xiao, D., Huang, W., Zhang, Z., Xu, B.: Quantum identity authentication in the counterfactual quantum key distribution protocol. Entropy (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/e21050518
Hong, C.H., Heo, J., Jang, J.G., Kwon, D.: Quantum identity authentication with single photon. Quantum Inform. Process. 16(10), 236 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1681-0
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L.: Quantum private queries. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 230502 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.230502
Yang, Y.-G., Sun, S.-J., Xu, P., Tian, J.: Flexible protocol for quantum private query based on B92 protocol. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(3), 805–813 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0692-8
Wei, C.-Y., Cai, X.-Q., Liu, B., Wang, T.-Y., Gao, F.: A generic construction of quantum-oblivious-key-transfer-based private query with ideal database security and zero failure. IEEE Trans. Comput. 67(1), 2–8 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TC.2017.2721404
Liu, B., Xia, S., Xiao, D., Huang, W., Xu, B., Li, Y.: Decoy-state method for quantum-key-distribution-based quantum private query. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 65(4), 240312 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-021-1843-7
Li, J., Li, H., Wang, N., Li, C., Hou, Y., Chen, X., Yang, Y.: A quantum key distribution protocol based on the EPR Pairs and its simulation. Mobile Netw. Appl. 26(2), 620–628 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-019-01408-2
Xue, P., Han, C., Yu, B., Lin, X.-M., Guo, G.-C.: Entanglement preparation and quantum communication with atoms in optical cavities. Phys. Rev. A 69, 052318 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.69.052318
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62171418, U19A2076, 61901425, and 61702061), Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (Grant No. cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0719), National Science Key Lab Fund project (Grant No. 6142103200105), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2020CDJQY-A018 and 2020CDJ-LHZZ-056), and Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant 019JDJQ0060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Liu, B., Huang, W. et al. Memory-free quantum secret sharing protocol with collective detection. Quantum Inf Process 22, 181 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03897-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03897-3