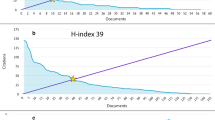
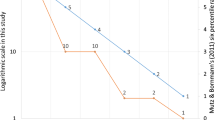
Abstract
Journal impact factors (JIF) have been an accepted indicator of ranking journals. However, there has been increasing arguments against the fairness of using the JIF as the sole ranking criteria. This resulted in the creation of many other quality metric indices such as the h-index, g-index, immediacy index, Citation Half-Life, as well as SCIMago journal rank (SJR) to name a few. All these metrics have their merits, but none include any great degree of normalization in their computations. Every citation and every publication is taken as having the same importance and therefore weight. The wealth of available data results in multiple different rankings and indexes existing. This paper proposes the use of statistical standard scores or z-scores. The calculation of the z-scores can be performed to normalize the impact factors given to different journals, the average of z-scores can be used across various criteria to create a unified relative measurement (RM) index score. We use the 2008 JCR provided by Thompson Reuters to demonstrate the differences in rankings that would be affected if the RM-index was adopted discuss the fairness that this index would provide to the journal quality ranking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, A., Altmann, J., & Hwang, J. (2010). Evaluating scholars based on their academic collaboration activities: two indices, the RC-index and the CC-index, for quantifying collaboration activities of researchers and scientific communities. Scientometrics, 83(1), 1–13.
Adler, R., Ewing, J. & Taylor, P. (2008). Citation Statistics. Retrieved February 24, 2009, from http://www.ams.org/ewing/Documents/CitationStatistics-FINAL-1.pdf.
Amin, M., & Mabe, M. (2000). Impact factor: use and abuse. Perspectives in Publishing, 1, 1–6.
Archambault, E., & Gagne, E. V. (2004). The use of bibliometrics in social sciences and humanities. Montreal: Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRCC).
Bornmann, L., Mutz, R., Neuhaus, C., & Daniel, H. D. (2008). Citation counts for research evaluation: standards of good practice for analyzing bibliometric data and presenting and interpreting results. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics, 8(1), 93–102.
Campanario, J. M., Carretero, J., Marangon, V., Molina, A., & Ros, G. (2011). Effect on the journal impact factor of the number and document type of citing records: a wide-scale study. Scientometrics, 87, 75–84.
Campbell, P. (2008). Escape from the impact factor. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics, 8(1), 5–6.
Egghe, L. (2006). Theory and practice of the g-index. Scientometrics, 69, 131–152.
Fok, D., & Franses, P. H. (2007). Modeling the diffusion of scientific publications. Journal of Econometrics, 139(2), 376–390.
Franceshet, M. (2010). Journal influence factors. Journal of Informatics, 4(3), 239–248.
Frandsen, T., Rousseau, R., & Rowlands, I. (2006). Diffusion factors. Journal of Documentation, 62(1), 58–72.
Garfield, E. (1999). Journal impact factor: a brief review. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 161(8), 979–980. http://www.cmaj.ca/cgi/content/full/161/8/979?ijkey=nr8.IXo1aXxvc 19 October.
Garfield, E. (2005). The agony and the ecstasy: the history and meaning of the journal impact factor. International Congress on Peer Review and Biomedical Publication. http://garfield.library.upenn.edu/papers/jifchicago2005.pdf. Accessed 1 May 2009.
Glanzel, W. (2006). On the h-index—a mathematical approach to a new measure of publication activity and citation impact. Scientometrics, 67(2), 315–321.
Gonzalez-Pereira, B., Guerrero-Bote, V. P., & Moya-Anegon, F. (2010). A new approach to the metric of journal scientific prestige: the SJR indicator. Journal of Informetrics, 4(3), 379–391. Accessed at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1751157710000246
Guns, R., Liu, Y. X., & Mahbuba, D. (2011). Q-measures and betweenness centrality in a collaboration network: a case study of the field of informetrics. Scientometrics, 87(1), 133–147.
Haddow, G., & Genoni, P. (2009). Australian education journals: quantitative and qualitative indicators. Australian Academic & Research Libraries, 40(2), 88–104.
Harnad, S. (2008). Validating research performance metrics against peer rankings. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics, 8(1), 103–107.
Harnad, S. & Brody, T. (2004). Comparing the impact of open access (OA) vs non-OA articles in the same journals. D-Lib Magazine, 10(6), (June 2004). Retrieved from: http://www.dlib.org/dlib/june04/harnad/06harna.html. Accessed 13 Oct 2011.
Harter, S. P. (1998). Scholarly communications and electronic journals: an impact Study. Journal of the American Society of Information Science, 49(6), 507–516.
Harzing, A.W. & Van der Wal, R. (2007). Google scholar: the democratization of citation analysis? Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics. Retrieved from: http://imechanica.org/files/gsdemo.pdf. Accessed 13 Oct 2011.
Hirsch, J. E. (2005). An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102(46), 16569–16572.
Hodge, D. R., & Lacasse, J. R. (2011). Evaluating journal quality: is the H index a better measure than impact factors. Research on Social work Practice, 21(2), 222–230.
Korn, A., Schubert, A., & Telcs, A. (2009). Lobby index in networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 388, 2221–2226.
Lee, K. P., Schotland, M., Bacchetti, Peter., & Bero, L. A. (2002). Association of journal quality indicators with methodological quality of clinical research articles. Journal of American Medical Association, 287(21), 2805–2808.
Monastersky, R. (2005). The number that’s devouring science. Chronicle of Higher Education, 52(8), A12–A17.
Pringle, J. (2004). Do open access journals have impact. Nature. Retrieved from: http://www.nature.com/nature/focus/access/debate/19.html. Accessed 13 Oct 2011.
Rowlands, I. (2002). Journal diffusion factors: a new approach to measuring research influence. Aslib Proceedings, 54(2), 77–84.
Saha, S., Saint, C., & Christakis, D. R. (2003). Impact factor: a valid measure of journal quality? Journal of Medical Librarian Association, 91(1), 42–46.
Schubert, A., Korn, A., & Telcs, A. (2009). Hirsch-type indices for characterizing networks. Scientometrics, 78(2), 375–382.
Sharma, O. (2007). Journal impact factor: an essential quality indicator. Current Science, 23(3), 141–142.
Thomson Scientific (2009). 2008 Journal Citation Report. Available: http://wokinfo.com/products_tools/analytical/jcr. Accessed on: 1 Dec 2011.
Thomson Scientific (2011a). Thompson Reuters Journal Selection Process. Available: http://thomsonreuters.com/products_services/science/free/essays/journal_selection_process. Accessed on 2 Feb 2012.
Thomson Scientific (2011b). The Thompson Reuters Impact Factor. Available: http://thomsonreuters.com/products_services/science/free/essays/impact_factor. Accessed on: 2 Feb 2012.
Todd, P. A., & Ladle, R. J. (2008). Hidden dangers of a ‘citation culture’. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics, 8(1), 13–16.
Zhao, S. X., Rousseau, R., & Ye, F. Y. (2011). h-Degree as a basic measure in weighted networks. Journal of Informetrics, 5, 668–677.
Acknowledgment
This study was made possible from consultation funding provided by the Malaysian Citation Centre, Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia addressed at the Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raj, R.G., Zainab, A.N. Relative measure index: a metric to measure the quality of journals. Scientometrics 93, 305–317 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-012-0675-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-012-0675-z