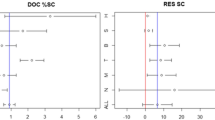
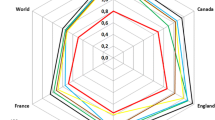
Abstract
The aim of the present work is to determine the share of country self-citations and to analyze its impact on total citations, average citation per paper, % cited publications and ranking of top ten most research productive countries over the period 1996–2015 using Scopus database. It was found that the mean and median of the country self-citation rates of these countries were 28.0 ± 3.8% and 22.9 ± 12.1% respectively and ranged from 17.8% (Canada) to 54.9% (China) over the studied period. United States (45.6%) ranked second country with % self-citation after China (54.9%). Country self-citations and/or its percentage were highly and positively correlated with total publications, total citations, cited publications and international collaboration. On the other hand, a strong negative correlation was observed between country self-citations with both average net-citation per paper and per capita publication. Also, significant impact of self-citation on total citations, average citation per paper and % cited publications was observed. China in total citations and United States in average citation per paper and % cited publications, were the most affected nations in rankings among all the studied nations. Among top 10 countries, China contains the highest share of self-citations in both average citation per paper (55.1%) and % cited publications (37.9%). Thus, self-citation has a strong impact on the top country’s scholarly performance. Some implications/recommendations were suggested to deal with country self-citation phenomenon. Shortly, excluding self-citation from calculating various citation-based bibliometric indicators will not remove the entire effect, but at least, it will produce a more reliable and real impact of each publication.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksnes, D. W. (2003). A macro study of self-citation. Scientometrics, 56(2), 235–246. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1021919228368.
Bai, X., Liu, H., Zhang, F., Ning, Z., Kong, X., Lee, I., et al. (2017). An overview on evaluating and predicting scholarly article impact. Information, 8(3), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/info8030073.
Costas, R., van Leeuwen, T. N., & Bordons, M. (2010). Self-citations at the meso and individual levels: Effects of different calculation methods. Scientometrics, 82(3), 517–537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-010-0187-7.
Della Sala, S., & Brooks, J. (2008). Multi-authors’ self-citation: A further impact factor bias? Cortex, 44(9), 1139–1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2008.07.001.
Elsevier. (2015). SciVal user guide: Elsevier Research Intelligence. Netherlands: Elsevier BV.
Fassoulaki, A., Paraskeva, A., Papilas, K., & Karabinis, G. (2000). Self-citations in six anaesthesia journals and their significance in determining the impact factor. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 84(2), 266–269. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.bja.a013418.
Ferrara, E., & Romero, A. E. (2013). Scientific impact evaluation and the effect of self-citations: Mitigating the bias by discounting the h-index. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 64(11), 2332–2339. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22976.
Foley, J. A., & Della Sala, S. (2010). The impact of self-citation. Cortex, 46(6), 802–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2010.01.004.
Fowler, J. H., & Aksnes, D. W. (2007). Does self-citation pay? Scientometrics, 72(3), 427–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-007-1777-2.
Gami, A. S., Montori, V. A., Wilczynski, N. L., & Haynes, R. B. (2004). Author self-citation in the diabetes literature. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 170(13), 1925–1927. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.1031879.
Gingras, Y., & Khelfaoui, M. (2018). Assessing the effect of the United States’ “citation advantage” on other countries’ scientific impact as measured in the Web of Science (WoS) database. Scientometrics, 114(2), 517–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2593-6.
Glänzel, W., Debackere, K., Thijs, B., & Schubert, A. (2006). A concise review on the role of author self-citations in information science, bibliometrics and science policy. Scientometrics, 67(2), 263–277. https://doi.org/10.1556/Scient.67.2006.2.8.
Glänzel, W., & Thijs, B. (2004a). Does co-authorship inflate the share of self-citations? Scientometrics, 61(3), 395–404. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SCIE.0000045117.13348.b1.
Glänzel, W., & Thijs, B. (2004b). World flash on basic research—the influence of author self-citations on bibliometric macro indicators. Scientometrics, 59(3), 281–310. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SCIE.0000018535.99885.e9.
Glänzel, W., Thijs, B., & Schlemmer, B. (2004). A bibliometric approach to the role of author self-citations in scientific communication. Scientometrics, 59(1), 63–77.
Hyland, K. (2003). Self-citation and self-reference: Credibility and promotion in academic publication. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 54(3), 251–259. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.10204.
Jaffe, K. (2011). Do countries with lower self-citation rates produce higher impact papers? Or, does humility pay? Interciencia, 36(9), 694–698.
Li, Z., & Ho, Y. S. (2008). Use of citation per publication as an indicator to evaluate contingent valuation research. Scientometrics, 75(1), 97–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-007-1838-1.
Minasny, B., Hartemink, A., & McBratney, A. (2010). Individual, country, and journal self-citation in soil science. Geoderma, 155(3–4), 434–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.12.003.
Minasny, B., McBratney, A., & Hartemink, A. (2009). Soil bibliometrics—more on self citation. Pedometron, 27, 21–24.
Persson, O., Glänzel, W., & Danell, R. (2004). Inflationary bibliometric values: The role of scientific collaboration and the need for relative indicators in evaluative studies. Scientometrics, 60(3), 421–432. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SCIE.0000034384.35498.7d.
Rad, A. E., Shahgholi, L., & Kallmes, D. (2012). Impact of self-citation on the H Index in the field of academic radiology. Academic Radiology, 19(4), 455–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2011.11.013.
Shehatta, I., & Mahmood, K. (2016). Research collaboration in Saudi Arabia 1980–2014: Bibliometric patterns and national policy to foster research quantity and quality. Libri, 66(1), 13–29. https://doi.org/10.1515/libri-2015-0095.
Swanson, E. W., Miller, D. T., Susarla, S. M., Lopez, J., Lough, D. M., May, J. W., et al. (2016). What effect does self-citation have on bibliometric measures in academic plastic surgery? Annals of Plastic Surgery, 77(3), 350–353. https://doi.org/10.1097/sap.0000000000000585.
Thijs, B., & Glänzel, W. (2006). The influence of author self-citations on bibliometric meso-indicators. The case of European universities. Scientometrics, 66(1), 71–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-006-0006-3.
Van Raan, A. F. J. (1998). The influence of international collaboration on the impact of research results. Scientometrics, 42(3), 423–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02458380.
Van Raan, A. F. J. (2008). Self-citation as an impact-reinforcing mechanism in the science system. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 59(10), 1631–1643. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.20868.
World Bank. (n.d.). http://web.worldbank.org/wbsite/external/news/art67528.htm. Accessed May 03, 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shehatta, I., Al-Rubaish, A.M. Impact of country self-citations on bibliometric indicators and ranking of most productive countries. Scientometrics 120, 775–791 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-019-03139-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-019-03139-3