Abstract
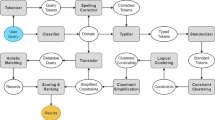
Document indexing is considered as a crucial phase in the information retrieval field because textual information is constantly increasing. With this accumulation of documents, the satisfaction of user needs becomes more and more complex. For these reasons, several information retrieval systems have been designed in order to respond to user requests. The main contribution of the current work resides in the suggestion of a novel hybrid approach for biomedical document indexing. We improve the estimation of the correspondence between a document and a given concept using two methods: vector space model (VSM) and description logics (DL). VSM performs partial matching between documents and external resource terms. DL allows representing knowledge in a relevant manner for better matching. The proposed contribution reduces the limitation of exact matching. It serves to index documents by exploiting medical subject headings (MeSH) thesaurus services with approximate matching. The latter partially matches document terms with biomedical vocabularies to extract other morphological variants in that resource. It also generates irrelevant concepts. The filtering step solves this problem and grants the selection of the most important concepts by exploiting the knowledge provided by MeSH. The experiments, carried out on different corpora, show encouraging results of around 25% improvement in average accuracy compared to other approaches studied in the literature.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
CNLP.Platform http://www.nlp.org.cn.
This research work is supported in part from the NSF Career grant (NSF IIS 0448023). NSF CCF 0514679 and the research grant from PA Dept of Health.
References
Abu-Salih, B., Wongthongtham, P., & Chan, K. Y. (2018a). Twitter mining for ontology-based domain discovery incorporating machine learning. Journal of Knowledge Management, 22, 949–981.
Abu-Salih, B., Wongthongtham, P., Chan, K. Y., & Zhu, D. (2018b). Credsat: Credibility ranking of users in big social data incorporating semantic analysis and temporal factor. Journal of Information Science, 45, 259–280.
Ali, M., Khalid, S., & Saleemi, M. (2019). Comprehensive stemmer for morphologically rich urdu language. The International Arab Journal of Information Technology, 16(1), 138–147.
Alotaibi, F. S., & Gupta, V. (2018). A cognitive inspired unsupervised language-independent text stemmer for information retrieval. Cognitive Systems Research, 52, 291–300.
Aravazhi, R., & Chidambaram, M. (2018). An efficient indexing mesh term description logic using in medical subject headings. Journal of Computer and Mathematical Sciences, 9(10), 1556–1567.
Aronson, A., Mork, J., Gay, C., Humphrey, S., & Rogers, W. (2004). The NLM indexing initiative’s medical text indexer. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, 11(1), 268–272.
Arroyo-Fernández, I., Méndez-Cruz, C., Sierra, G., Torres-Moreno, J., & Sidorov, G. (2019). Unsupervised sentence representations as word information series: Revisiting TF-IDF. Computer Speech and Language, 56, 107–129.
Baoli, H., Ling, C., & Xiaoxue, T. (2018). Knowledge based collection selection for distributed information retrieval. Information Processing and Management, 54(1), 116–128.
Boukhari, K., & Omri, M. N. (2015). Said: A new stemmer algorithm to indexing unstructured document. In The international conference on intelligent systems design and applications (pp. 59–63).
Boukhari, K., & Omri, M. N. (2016). Raid: Robust algorithm for stemming text document. International Journal of Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management Applications, 8(1), 235–246.
Boukhari, K., & Omri, M. N. (2017a). Information retrieval approach based on indexing text documents: Application to biomedical domain. In The 13th international conference on natural computation, fuzzy systems and knowledge discovery (ICNC-FSKD) (pp. 2213–2220).
Boukhari, K., & Omri, M. N. (2017b). Information retrieval based on description logic: Application to biomedical documents. In International conference on high performance computing and simulation (HPCS) (pp. 846–853).
Bracewell, D., Ren, F., & Kuroiwa, S. (2005). Multilingual single document keyword extraction for information retrieval. In Proceedings of natural language processing and knowledge engineering (NLP-KE) (pp. 517–522).
Chebil, W., Soualmia, L. F., & Darmoni, S. J. (2013). Biodi: A new approach to improve biomedical documents indexing. In Database and expert systems applications (pp. 78–87).
Dahak, F., Boughanem, M., & Ballaa, A. (2017). A probabilistic model to exploit user expectations in xml information retrieval. Information Processing and Management, 53(1), 87–105.
Dinh, D., & Tamine, L. (2011). Combining global and local semantic contexts for improving biomedical information retrieval. In European conference on information retrieval research (pp. 375–386).
Ferjani, F., Elloumi, S., Jaoua, A., Sahar Ahmad Ismail, S. B. Y., & Ravan, S. (2012). Formal context coverage based on isolated labels: An efficient solution for text feature extraction. Information Sciences-Informatics and Computer Science, Intelligent Systems, Applications: An International Journal, 188(1), 198–214.
Fkih, F., & Omri, M. N. (2012). Complex terminology extraction model from unstructured web text based linguistic and statistical knowledge. International Journal of Information Retrieval Research, 2(3), 1–18.
Fkih, F., & Omri, M. N. (2016a). Hybridization of an index based on concept lattice with a terminology extraction model for semantic information retrieval guided by wordnet. In International conference on hybrid intelligent systems (pp. 144–152).
Fkih, F., & Omri, M. N. (2016b). Irafca: An o(n) information retrieval algorithm based on formal concept analysis. Knowledge and Information Systems, 48(2), 465–491.
García, M. A. M., Rodríguez, R. P., & Rifón, L. A. (2018). Leveraging wikipedia knowledge to classify multilingual biomedical documents. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 88(1), 37–57.
Haarslev, V., & Moller, R. (2001). Description of the racer system and its applications. In The international workshop on description logics (pp. 132–141).
Hao, S., Shi, C., Niu, Z., & Cao, L. (2018). Concept coupling learning for improving concept lattice-based document retrieval. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 69(1), 56–75.
Happe, A., Pouliquen, B., Burgun, A., Cuggia, M., & Beux, P. L. (2003). Automatic concept extraction from spoken medical reports. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 70(2–3), 255–263.
Jiménez, S., Cucerzan, S., González, F. A., Gelbukh, A. F., & Dueñas, G. (2018). BM25-CTF: Improving TF and IDF factors in BM25 by using collection term frequencies. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems, 34(5), 2887–2899.
Jonquet, C., LePendu, P., Falconer, S., Coulet, A., Noy, N. F., Musen, M. A., et al. (2011). Ncbo resource index: Ontology-based search and mining of biomedical resources. Journal of Web Semantics, 9(3), 316–324.
Jutinico, C. J. M., Montenegro-Marin, C. E., Burgos, D., & Crespo, R. G. (2019). Natural language interface model for the evaluation of ergonomic routines in occupational health (ilena). Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 10(4), 1611–1619.
Karaa, W. B. A. (2013). A new stemmer to improve information retrieval. International Journal of Network Security and Its Applications (IJNSA), 5(4), 143–154.
Liu, Y. H., & Wacholderc, N. (2017). Evaluating the impact of mesh (medical subject headings) terms on different types of searchers. Information Processing and Management, 53(4), 851–870.
Lv, X., Guan, Y., & Deng, B. (2014). Transfer learning based clinical concept extraction on data from multiple sources. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 52(3), 55–64.
Mahedi, H. H., Sanyal, F., & Chaki, D. (2018) A novel approach to extract important keywords from documents applying latent semantic analysis. In International conference on knowledge and smart technology (KST) (pp. 1–6).
Matsuo, Y., & Ishizuka, M. (2003). Keyword extraction from a single document using word co-occurrence statistical information. In Proceedings of the sixteenth international Florida artificial intelligence research society conference (pp. 392–396).
Mukherjea, S., Gaurav Chanda, L. V. S., Sankararaman, S., Kothari, R., Batra, V. S., Bhardwaj, D. N., et al. (2004). Enhancing a biomedical information extraction system with dictionary mining and context disambiguation. IBM Journal of Research and Development, 48(5–6), 693–702.
Naouar, F., Hlaoua, L., & Omri, M. N. (2016). Collaborative information retrieval model based on fuzzy confidence network. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems, 30(4), 2119–2129.
Naouar, F., Hlaoua, L., & Omri, M. N. (2017). Information retrieval model using uncertain confidence’s network. International Journal of Information Retrieval Research, 7(2), 34–50.
Nicolas, F., Ranwez, S., Montmain, J. M., & Ranwez, V. (2015). Usi: A fast and accurate approach for conceptual document annotation. BMC Bioinformatics, 16(1), 1–10.
Radhouani, S., & Falquet, G. (2008). Description logics-based modelling for precise information retrieval. In International workshop on description logics (pp. 1–11).
Radhouani, S., Falquet, G., & Chevallet, J. P. (2008). Description logic to model a domain specific information retrieval system. In International conference on database and expert systems applications (pp. 142–149).
Ru, C., Tang, J., Li, S., Xie, S., & Wang, T. (2018). Using semantic similarity to reduce wrong labels in distant supervision for relation extraction. Information Processing and Management, 54(4), 593–608.
Ruch, P. (2006). Automatic assignment of biomedical categories: Toward a generic approach. Bioinformatics Journal, 6(22), 58–64.
Sirin, E., Parsia, B., Grau, B. C., Kalyanpur, A., & Katz, Y. (2007). Pellet: A practical owl-dl reasoner. Journal of Web Semantics, 5(2), 51–53.
Sohn, S., Kim, W., Comeau, D. C., & Wilbur, W. J. (2008). Optimal training sets for Bayesian prediction of mesh®assignment. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 15(4), 546–553.
Soldaini, L., & Goharian, N. (2016). Quickumls: A fast, unsupervised approach for medical concept extraction. In Medical information retrieval (MedIR) workshop (pp. 1–4).
Song, M. (2015). Exploring concept graphs for biomedical literature mining. In International conference on big data and smart computing (pp. 103–110).
Sun, P., Wang, L., & Xia, Q. (2017). The keyword extraction of Chinese medical web page based on WF-TF-IDF algorithm. In (pp. 193–198).
Tsarkov, D., & Horrocks, I. (2004). Efficient reasoning with range and domain constraints. Description Logic Workshop DL, 2004, 41–50.
Warren, P., Mulholland, P., Collins, T. D., & Motta, E. (2019). Improving comprehension of knowledge representation languages: A case study with description logics. International Journal of Human–Computer Studies, 122, 145–167.
Wongthongtham, P., & Salih, B. A. (2018). Ontology-based approach for identifying the credibility domain in social big data. Journal of Organizational Computing and Electronic Commerce, 28, 354–377.
You, W., Fontaine, D., & Barthès, J. P. (2013). An automatic keyphrase extraction system for scientific documents. Knowledge and Information Systems, 34(3), 691–724.
Yuan, L. (2018). Supporting relevance feedback with concept learning for semantic information retrieval in large owl knowledge base. In: Knowledge management and acquisition for intelligent systems (pp. 61–75).
Zhang, C., Wang, H., Liu, Y., Wu, D., Liao, Y., & Wang, B. (2008). Automatic keyword extraction from documents using conditional random fields. Journal of Computational Information Systems, 4(3), 1169–1180.
Zhou, X., Zhang, X., & Hu, X. (2006). Maxmatcher: Biological concept extraction using approximate dictionary lookup. In Pacific RIM international conference on artificial intelligence (pp. 1145–1149).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boukhari, K., Omri, M.N. Approximate matching-based unsupervised document indexing approach: application to biomedical domain. Scientometrics 124, 903–924 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03474-w
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03474-w