Abstract
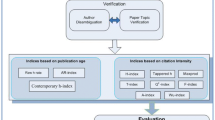
The renowned international scientific societies nominate researchers for awards based on qualitative judgments every year. Qualitative judgment uses subjective assessments based on information that is not quantifiable. The way of assessing the quality of the work has not been established or disclosed, nor do we have any qualitative evaluation criteria. We can assess the quality of the researcher's work by mapping the quantitative parameters to qualitative judgments. To date, the scientific community has presented more than 50 research assessment quantitative parameters, including publication count, citation count, h-index, and its variants. The contemporary state-of-the-art in authors ranking does not determine the best parameter that effectively maps on experts' qualitative evaluation. Moreover, these parameters have been evaluated by using same scenarios. In such scenarios, the value and effect of each parameter over the others are complicated to ascertain. Therefore, they must be assessed in inequitable scenarios. The purpose of this research is to identify the significant parameters that map on qualitative judgments of international scientific societies in Civil Engineering (CE) for award nominations. We will identify the rank of author assessment parameters, which includes published papers, citations, No of years since 1st publication, citations in h-core, authors/paper, citations/paper, citations/year, h-index, g-index, hg-index, A-index, R-index, e-index, and f-index. We have evaluated these parameters on the dataset from the discipline of Civil Engineering (CE). The data set contains 250 non-award winners and 250 award winners from prestigious scientific societies of CE. The h-index and its variants have been ranked based on their effectiveness for awardees using Logistic Regression. The award-winning researchers have less number of average authors/paper than the non-awardees. The authors/paper has achieved the highest effectiveness of 67% for awardees. Furthermore, we have also analyzed the ratio of awardees in the ranked list of 50, 100, and 150 researchers by author assessment parameters. The authors/papers have outperformed all other indices by elevating 62% and 66% of the award recipients in its ranked list of 100 and 150 researchers. In the ranked list of 50 researchers, publications elevate 54% awardees, and Authors/papers achieved the second-highest elevation score of awardees of 50%.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, N., & Kudo, M. (2005). Entropy criterion for classifier-independent feature selection. In international conference on knowledge-based and intelligent information and engineering systems (pp. 689–695). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Ain, Q. U., Riaz, H., & Afzal, M. T. (2019). Evaluation of h-index and its citation intensity based variants in the field of mathematics. Scientometrics, 119(1), 187–211.
Algamal, Z. Y., & Lee, M. H. (2019). A two-stage sparse logistic regression for optimal gene selection in high-dimensional microarray data classification. Advances in data analysis and classification, 13(3), 753–771.
Alonso, S., Cabrerizo, F. J., Herrera-Viedma, E., & Herrera, F. (2009). h-index: A review focused in its variants, computation and standardization for different scientific fields. Journal of Informetrics, 3(4), 273–289.
Alonso, S., Cabrerizo, F. J., Herrera-Viedma, E., & Herrera, F. (2010). hg-index: A new index to characterize the scientific output of researchers based on the h-and g-indices. Scientometrics, 82(2), 391–400.
Ameer, M., & Afzal, M. T. (2019). Evaluation of h-index and its qualitative and quantitative variants in Neuroscience. Scientometrics, 121, 653.
Aoun, S. G., Bendok, B. R., Rahme, R. J., Dacey, R. G., & Batjer, H. H. (2013). Standardizing the evaluation of scientific and academic performance in neurosurgery—Critical review of the “h” index and its variants. World Neurosurgery, 80(5), e85–e90.
Ayaz, S., & Afzal, M. T. (2016). Identification of conversion factor for completing-h index for the field of mathematics. Scientometrics, 109(3), 1511–1524.
Cameron, D. L. (2007). SEMEF: A taxonomy-based discovery of experts, expertise and collaboration networks. MS thesis, The University of Georgia, ATHENS, GA 2007.
Crowder, R., Hughes, G., & Hall, W. (2002). An agent based approach to finding expertise. In International Conference on Practical Aspects of Knowledge Management (pp. 179–188). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Dienes, K. R. (2015). Completing h. Journal of Informatics, 9(2), 385–397.
Egghe, L. (2006). Theory and practise of the g-index. Scientometrics, 69(1), 131–152.
El-Adaway, I. H., Ali, G., Assaad, R., Elsayegh, A., & Abotaleb, I. S. (2019). Analytic overview of citation metrics in the civil engineering domain with focus on construction engineering and management specialty area and its subdisciplines. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 145(10), 04019060.
Falagas, M. E., Pitsouni, E. I., Malietzis, G. A., & Pappas, G. (2008). Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, web of science, and Google Scholar: Strengths and weaknesses. The FASEB Journal, 22(2), 338–342.
Hariri-Ardebili, M. A., & Saouma, V. (2015). Quantitative failure metric for gravity dams. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 44(3), 461–480.
Harzing, A. W. (2014). A longitudinal study of Google Scholar coverage between 2012 and 2013. Scientometrics, 98(1), 565–575.
Hirsch, J. E. (2005). An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences, 102(46), 16569–16572.
Jin, B. (2006). H-index: An evaluation indicator proposed by the scientist. Science Focus, 1(1), 8–9.
Jin, B., Liang, L., Rousseau, R., & Egghe, L. (2007). The R-and AR-indices: Complementing the h-index. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(6), 855–863.
Katsaros, D., Akritidis, L., & Bozanis, P. (2009). The f index: Quantifying the impact of coterminal citations on scientists’ ranking. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 60(5), 1051–1056.
Liang, R., & Jiang, X. (2016). Scientifc ranking over heterogeneous academic hypernetwork. In AAAI (pp. 20–26).
Mingers, J. (2009). Measuring the research contribution of management academics using the Hirsch-index. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 60(9), 1143–1153.
Moed, H. F., Bar-Ilan, J., & Halevi, G. (2016). A new methodology for comparing Google Scholar and scopus. Journal of Informetrics, 10(2), 533–551.
Raheel, M., Ayaz, S., & Afzal, M. T. (2018). Evaluation of h-index, its variants and extensions based on publication age and citation intensity in civil engineering. Scientometrics, 114(3), 1107–1127.
Sidiropoulos, A., Katsaros, D., & Manolopoulos, Y. (2007). Generalized Hirsch h-index for disclosing latent facts in citation networks. Scientometrics, 72(2), 253–280.
Springer, D. B., Tarassenko, L., & Clifford, G. D. (2015). Logistic regression-HSMM-based heart sound segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 63(4), 822–832.
Teixeira, A. A., & Mota, L. (2012). A bibliometric portrait of the evolution, scientific roots and influence of the literature on university-industry links. Scientometrics, 93(3), 719–743.
Tol, R. (2009). The h-index and its alternatives: An application to the 100 most prolific economists. Scientometrics, 80(2), 317–324.
Van Raan, A. F. (2006). Comparison of the Hirsch-index with standard bibliometric indicators and with peer judgment for 147 chemistry research groups. Scientometrics, 67(3), 491–502.
West, R., & Stenius, K. (2004). Publishing addiction science: A guide for the perplexed. In UK7 International Society of Addiction Journal Editors, London
Wilsdon, J., Allen, L., Belfore, E., Campbell, P., Curry, S. H., Jones, R., et al. (2015). The metric tide: Report of the independent review of the role of metrics in research assessment and management. Technical report.
Wu, Q. (2010). The w-index: A measure to assess scientific impact by focusing on widely cited papers. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 61(3), 609–614.
Zhang, C. T. (2009). The e-index, complementing the h-index for excess citations. PLoS ONE, 4(5), e54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Usman, M., Mustafa, G. & Afzal, M.T. Ranking of author assessment parameters using Logistic Regression. Scientometrics 126, 335–353 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03769-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03769-y