Abstract
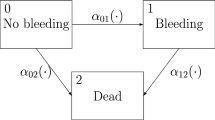
This study considers a functional concurrent hidden Markov model. The proposed model consists of two components. One is a transition model for elucidating how potential covariates influence the transition probability from one state to another. The other is a conditional functional linear concurrent regression model for characterizing the state-specific effects of functional covariates. A distribution-free random effect is introduced to the conditional model to describe the dependency of individual functional observations. The soft-thresholding operator and the adaptive group lasso are introduced to simultaneously accommodate the local and global sparsity of the functional coefficients. A Bayesian approach is developed to jointly conduct estimation, variable selection, and the detection of zero-effect regions. This proposed approach incorporates the dependent Dirichlet process with stick-breaking prior for accommodating the unspecified distribution of the random effect and a blocked Gibbs sampler for efficient posterior sampling. Finally, the empirical performance of the proposed method is evaluated through simulation studies, and the utility of the methodology is demonstrated by an application to the analysis of air pollution and meteorological data.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agresti, A.: Categorical Data Analysis, vol. 792. Wiley (2012)
Altman, R.M.: Mixed hidden Markov models: an extension of the hidden Markov model to the longitudinal data setting. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 102(477), 201–210 (2007)
Alvarez, H.A.O., Myers, O.B., Weigel, M., Armijos, R.X.: The value of using seasonality and meteorological variables to model intra-urban PM2.5 variation. Atmos. Environ. 182, 1–8 (2018)
Bartolucci, F., Farcomeni, A.: A multivariate extension of the dynamic logit model for longitudinal data based on a latent Markov heterogeneity structure. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 104(486), 816–831 (2009)
Berkner, K., Wells, R.O., Jr.: Smoothness estimates for soft-threshold denoising via translation-invariant wavelet transforms. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 12(1), 1–24 (2002)
Celeux, G., Forbes, F., Robert, C. P., & Titterington, D. M. (2006). Deviance information criteria for missing data models
Cappé, O., Moulines, E., Rydén, T.: Inference in Hidden Markov Models. Springer (2006)
Chen, Y., Goldsmith, J., Ogden, R.T.: Variable selection in function-on-scalar regression. Stat 5(1), 88–101 (2016)
Ciarleglio, A., Ogden, R.T.: Wavelet-based scalar-on-function finite mixture regression models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 93, 86–96 (2016)
Donaldson, K., Li, X., MacNee, W.: Ultrafine (nanometre) particle mediated lung injury. J. Aerosol Sci. 29(5–6), 553–560 (1998)
Donoho, D.L., Johnstone, I.M.: Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage. Biometrika 81(3), 425–455 (1994)
Eilers, P.H., Marx, B.D.: Flexible smoothing with B-splines and penalties. Stat. Sci. 11(2), 89–102 (1996)
Eubank, R., Huang, C., Maldonado, Y.M., Wang, N., Wang, S., Buchanan, R.: Smoothing spline estimation in varying-coefficient models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 66(3), 653–667 (2004)
Feng, X., Wang, G., Wang, Y., Song, X.: Structure detection of semiparametric structural equation models with Bayesian adaptive group lasso. Stat. Med. 34(9), 1527–1547 (2015)
Frühwirth-Schnatter, S.: Markov chain Monte Carlo estimation of classical and dynamic switching and mixture models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 96(453), 194–209 (2001)
Gao, W., Zhang, X., Yang, L., Liu, H.: An improved Sobel edge detection. In: 2010 3rd International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology, vol. 5, pp. 67–71 (2010). IEEE
Gelfand, A.E., Kottas, A., MacEachern, S.N.: Bayesian nonparametric spatial modeling with Dirichlet process mixing. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 100(471), 1021–1035 (2005)
Gertheiss, J., Maity, A., Staicu, A.-M.: Variable selection in generalized functional linear models. Stat 2(1), 86–101 (2013)
Ghosal, R., Maity, A., Clark, T., Longo, S.B.: Variable selection in functional linear concurrent regression. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 69(3), 565–587 (2020)
Goldsmith, J., Schwartz, J.E.: Variable selection in the functional linear concurrent model. Stat. Med. 36(14), 2237–2250 (2017)
Guo, R., Zhu, H., Chow, S.-M., Ibrahim, J.G.: Bayesian lasso for semiparametric structural equation models. Biometrics 68(2), 567–577 (2012)
Hazlett, H.C., Gu, H., Munsell, B.C., Kim, S.H., Styner, M., Wolff, J.J., Elison, J.T., Swanson, M.R., Zhu, H., Botteron, K.N., et al.: Early brain development in infants at high risk for autism spectrum disorder. Nature 542(7641), 348–351 (2017)
Ip, E., Zhang, Q., Rejeski, J., Harris, T., Kritchevsky, S.: Partially ordered mixed hidden Markov model for the disablement process of older adults. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 108(502), 370–384 (2013)
Ishwaran, H., James, L.: Gibbs sampling methods for stick-breaking priors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 96, 161–173 (2001)
Ishwaran, H., Zarepour, M.: Markov chain Monte Carlo in approximate Dirichlet and beta two-parameter process hierarchical models. Biometrika 87(2), 371–390 (2000)
James, G.M., Wang, J., Zhu, J., et al.: Functional linear regression that’s interpretable. Ann. Stat. 37(5A), 2083–2108 (2009)
Kang, J., Reich, B.J., Staicu, A.-M.: Scalar-on-image regression via the soft-thresholded Gaussian process. Biometrika 105(1), 165–184 (2018)
Kang, K., Cai, J., Song, X., Zhu, H.: Bayesian hidden Markov models for delineating the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 28(7), 2112–2124 (2019)
Kent, J.T.: Continuity properties for random fields. Ann. Probab. 17(4), 1432–1440 (1989)
Kim, J.S., Maity, A., Staicu, A.-M.: Additive nonlinear functional concurrent model. Stat. Interface 11(4), 669 (2018)
Kowal, D.R., Matteson, D.S., Ruppert, D.: A Bayesian multivariate functional dynamic linear model. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 112(518), 733–744 (2017)
Lang, S., Brezger, A.: Bayesian P-splines. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 13(1), 183–212 (2004)
Leroux, B.G.: Maximum-likelihood estimation for hidden Markov models. Stoch. Process. Appl. 40(1), 127–143 (1992)
Lin, Z., Cao, J., Wang, L., Wang, H.: Locally sparse estimator for functional linear regression models. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 26(2), 306–318 (2017)
Lu, L., Jin, W., Wang, X.: Non-local means image denoising with a soft threshold. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22(7), 833–837 (2014)
Lu, Z., Khondker, Z., Ibrahim, J.G., Wang, Y., Zhu, H., Initiative, A.D.N., et al.: Bayesian longitudinal low-rank regression models for imaging genetic data from longitudinal studies. Neuroimage 149, 305–322 (2017)
MacEachern, S.N.: Dependent nonparametric processes. In: ASA Proceedings of the Section on Bayesian Statistical Science, vol. 1, pp. 50–55 (1999). Alexandria: American Statistical Association
MacEachern, S.N.: Dependent Dirichlet processes, pp. 1–40. Unpublished manuscript, Department of Statistics, The Ohio State University (2000)
Manrique, T., Crambes, C., Hilgert, N., et al.: Ridge regression for the functional concurrent model. Electron. J. Stat. 12(1), 985–1018 (2018)
Martino, A., Guatteri, G., Paganoni, A.M.: Hidden Markov models for multivariate functional data. Stat. Probab. Lett. 167, 108917 (2020)
Maruotti, A.: Mixed hidden Markov models for longitudinal data: an overview. Int. Stat. Rev. 79(3), 427–454 (2011)
Ni, X., Huang, H., Du, W.: Relevance analysis and short-term prediction of PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing based on multi-source data. Atmos. Environ. 150, 146–161 (2017)
Park, T., Casella, G.: The Bayesian Lasso. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 103(482), 681–686 (2008)
Pope Iii, C.A., Burnett, R.T., Thun, M.J., Calle, E.E., Krewski, D., Ito, K., Thurston, G.D.: Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 287(9), 1132–1141 (2002)
Qu, A., Li, R.: Quadratic inference functions for varying-coefficient models with longitudinal data. Biometrics 62(2), 379–391 (2006)
Qu, L., Song, X., Sun, L.: Identification of local sparsity and variable selection for varying coefficient additive hazards models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 125, 119–135 (2018)
Schwartz, J.: The distributed lag between air pollution and daily deaths. Epidemiology 11(3), 320–326 (2000)
Scott, S.L., James, G.M., Sugar, C.A.: Hidden Markov models for longitudinal comparisons. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 100(470), 359–369 (2005)
Sethuraman, J.: A constructive definition of Dirichlet priors. Stat. Sin. 4(2), 639–650 (1994)
Silverman, J.O.R.W.: Functional Data Analysis. Wiley Online Library (2004)
Song, X., Lu, Z.: Semiparametric transformation models with Bayesian P-splines. Stat. Comput. 22, 1085–1098 (2012)
Song, X., Xia, Y., Zhu, H.: Hidden Markov latent variable models with multivariate longitudinal data. Biometrics 73(1), 313–323 (2017)
Wang, S., Huang, M., Wu, X., Yao, W.: Mixture of functional linear models and its application to CO2-GDP functional data. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 97, 1–15 (2016)
Wang, P., Guo, H., Hu, J., Kota, S.H., Ying, Q., Zhang, H.: Responses of PM2.5 and O3 concentrations to changes of meteorology and emissions in China. Sci. Total Environ. 662, 297–306 (2019)
Wu, C.O., Chiang, C.-T., Hoover, D.R.: Asymptotic confidence regions for kernel smoothing of a varying-coefficient model with longitudinal data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 93(444), 1388–1402 (1998)
Xie, Y., Zhao, B., Zhang, L., Luo, R.: Spatiotemporal variations of PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations between 31 Chinese cities and their relationships with SO\(_2\), NO\(_2\), CO and O\(_3\). Particuology 20, 141–149 (2015)
Xu, Z., Chen, S.X., Wu, X.: Meteorological change and impacts on air pollution: results from North China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 125(16), e2020JD032423 (2020)
Yang, Y.: Novel methods for estimation and inference in varying coefficient models. PhD thesis (2020)
Yao, F., Fu, Y., Lee, T.C.: Functional mixture regression. Biostatistics 12(2), 341–353 (2011)
Ye, M., Lu, Z., Li, Y., Song, X.: Finite mixture of varying coefficient model: estimation and component selection. J. Multivar. Anal. 171, 452–474 (2019)
Zhang, H., Li, Y.: Unified principal component analysis for sparse and dense functional data under spatial dependency. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 40, 1523–1537 (2021)
Zhang, W., Wang, H., Zhang, X., Peng, Y., Zhong, J., Wang, Y., Zhao, Y.: Evaluating the contributions of changed meteorological conditions and emission to substantial reductions of PM2.5 concentration from winter 2016 to 2017 in Central and Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 716, 136892 (2020)
Zhou, J., Wang, N.-Y., Wang, N.: Functional linear model with zero-value coefficient function at sub-regions. Stat. Sin. 23(1), 25–50 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This research was fully supported by Research Grant Council of the Hong Kong Special Administration Region (GRF 14301918, 14302220).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Song, X. Functional concurrent hidden Markov model. Stat Comput 33, 57 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-023-10226-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-023-10226-2