Abstract
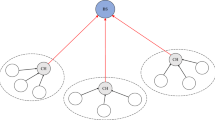
The Distributed Mobility-Adaptive Clustering (DMAC) due to Basagni partitions the nodes of a mobile ad hoc network into clusters, thus giving the network a hierarchical organization. This algorithm supports the mobility of the nodes, even during the cluster formation. The main feature of DMAC is that in a weighted network (in which two or more nodes cannot have the same weight), nodes have to choose the clusterheads taking into account only the node weight, i.e. the mobility when a node weight is the inverse of its speed. In our approach many nodes may have the same speed and hence the same weight. We assume that nodes have no identities and the number of nodes, say n, is the only known parameter of the network. After the randomized clustering, we show that the initialization problem can be solved in a multi-hop ad hoc wireless network of n stations in O(k 1/2log 1/2 k)+D b −1+O(log (max (P i )+log 2max (P i )) broadcast rounds with high probability, where k is the number of clusters, D b is the blocking diameter and max (P i ), 1≤i≤k, is the maximum number of nodes in a cluster. Thus the initialization protocol presented here uses less broadcast rounds than the one in Ravelemanana (IEEE Trans. Parallel Distributed Syst. 18(1):17–28 2007).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awerbuch B (1985) Complexity of networks synchronization. J ACM 32(4):804–823
Baker D, Ephremides A (1981) The architectural organization of a mobile radio network via a distributed algorithm. In: IEEE transactions on communications COM-29, vol 11, pp 1694–1701
Banerjee S, Khuller S (2001) A clustering scheme for hierarchical control in multi-hop wireless networks. In: Proceedings of the 20th IEEE infocom 2001, vol 2, pp 1028–1037
Basagni S (1999) Distributed clustering for ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of the 1999 international symposium on parallel architectures, algorithms, and networks (I-SPAN’ 99). IEEE Computer Society, pp 310–315
Basagni S, Ghosh R (2005) Limiting the impact of mobility on ad hoc clustering. In: Proceedings of the second ACM inter. workshop on performance evaluation of wireless ad hoc, sensor, and ubiquitous networks (PE-WASUN’ 05). IEEE Computer Society, pp 197–204
Chaterjee M, Das SK, Turgut D (2002) WCA: A weighted clustering algorithm for mobile ad hoc networks. Clust Comput 5:193–204
Czumai A, Rytter W (2006) Broadcasting algorithms in radio networks with unknown topology. J Algorithms 60(2):115–143
Ephremides A (1983) Design concepts for a mobile-user radio network. Comput Electr Eng 10(3):127–135
Feller W (1968) An introduction to probability theory and its applications. Wiley, New York
Gerla M, Lin C (1997) Adaptive clustering for mobile wireless networks. J Selected Areas Commun 15(7):1265–1275
Gerla M, Tsa J (1995) Multicluster, mobile, multimedia radio network. Wirel Netw 1(3):255–265
Lavault C, Zaks S (1989) Constructing spanning trees in anonymous networks. Proc ACM PODC’89. ACM Press, New York, pp. 319–328
McDonald AB, Znati TA (1999) A mobility-based framework for adaptive clustering in wireless ad hoc networks. IEEE J Selected Areas Commun Special Issue on Wireless Ad Hoc Networks 17(8): 1466–1487
Mellier R, Myoupo JF (2006) A weighted clustering algorithm for mobile ad hoc networks with non-unique weights, the second international conference on wireless and mobile communications (ICWMC 2006). Bucharest, Romania, July 29–31
Myoupo JF, Ravelomanana V, Thimonier L (2003) Average casde analysis-based protocols to initialize packet radio networks. Wirel Commun Mobile Comput 3:539–548
Nakano K, Olariu S (2000) Randomized initialization protocols for ad hoc networks. IEEE Trans Parallel Distr Syst 11:749–759
Nocetti FG, Solango JS, Stojmenovic I (2003) Connectivity-based k-hop clustering in wireless networks. Telecommun Syst 22(1–4):205–220
Raab M, Steger A (1998) Balls into bins: a simple and tight analysis. In: Randomized and approximation techniques in computer science (RANDOM’98). Lecture notes in computer science, vol 1518. Springer, Berlin, pp 159–170
Ravelomanana V (2007) Optimal initialization and gossiping algorithms for random radio networks. IEEE Trans Parallel Distributed Syst 18(1):17–28
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Myoupo, J.F., Cheikhna, A.O. & Sow, I. A randomized clustering of anonymous wireless ad hoc networks with an application to the initialization problem. J Supercomput 52, 135–148 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-009-0274-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-009-0274-9