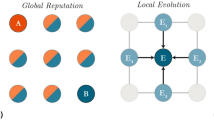
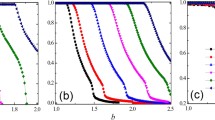
Abstract
Reputation systems are very useful in large online communities in which users may frequently have the opportunity to interact with users with whom they have no prior experience. Recently, how to enhance the cooperative behaviors in the reputation system has become to one of the key open issues. Emerging schemes focused on developing efficient reward and punishment mechanisms or capturing the social or economic properties of participants. However, whether this kind of method can work widely or not has been hard to prove until now. Research in evolutionary game theory shows that group selection (or multilevel selection) can favor the cooperative behavior in the finite population. Furthermore, some recent works give fundamental conditions for the evolution of cooperation by group selection. In the paper, we extend the original group selection theory and propose a group-based scheme to enhance cooperation for online reputation systems. Related concepts are defined to capture the social structure and ties among participants in reputation system, e.g., group, assortativity, etc. Also, we use a Fermi distribution function to reflect the bounded rationality of participants and the existence of stochastic factors in evolutionary process. Extended simulations show that our scheme can enhance cooperation and improve the average performance of participants (e.g. payoff) in reputation system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamvar S, Schlosser M, Garci-Molina H (2003) The Eigentrust algorithm for reputation management in P2P networks. In: World wide web conf (WWW2003), pp 640–651
Xiong L, Ling L (2004) Peertrust: supporting reputation-based trust for peer-to-peer electronic communities. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 16(7):843–857
Seungjoon L, Rob S, Samrat B (2003) Cooperative peer groups in NICE. In: INFOCOM, vol 2, pp 1272–1282
Damiani E, di Vimercati SDC, Paraboschi S, Samarati P (2003) Managing and sharing servents’ reputations in P2P systems. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 15(4):840–854
Wright S (1945) Tempo and mode in evolution: a critical review. Ecology 26:415–419
Wilson S, Sober E (1994) Reintroducing group selection to the human behavioral sciences. Behav Brain Sci 17(4):585–654
Traulsen A, Nowak M (2006) Evolution of cooperation by multilevel selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(29):10952–10955
Nowak M (2006) Five rules for the evolution of cooperation. Science 314(5805):1560–1563
Keller L (1999) Levels of selection in evolution. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Paulsson J (2002) Multileveled selection on plasmid replication. Genetics 161:1373–1384
Henrich J (2004) Cultural group selection, co-evolutionary processes and large-scale cooperation. J Econ Behav Organ 53:3–35
David BK, Philip KM, Charles O (2007) Using group selection to evolve leadership in populations of self-replicating digital organisms. In: GECCO, pp 293–300
Scheuring I (2009) Evolution of generous cooperative norms by cultural group selection. J Theor Biol 257:297–407
Borety B, Peter JR (2002) Group beneficial norms can spread rapidly in a structured population. J Theor Biol 215:287–296
Theodore CB (2002) Evolution of social behavior: individual and group selection. J Econ Perspect 16(2):67–88
Mui L (2002) Computational models of trust and reputation: agents, evolutionary games, and social networks. Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Sepandar K, Beverly Y, Hector GM (2003) Addressing the non-cooperation problem in competitive P2P systems. In: Workshop on economics of peer-to-peer systems, Berkeley, CA, May 2003
Yufeng W, Hori Y, Sakurai K (2008) Characterizing economic and social properties of trust and reputation systems in P2P environment. J Comput Sci Technol 23(1):129–140
Hales D, Arteconi S (2006) SLACER: a self-organizing protocol for coordination in P2P networks. IEEE Intell Syst 21(2):29–35
Hales D (2006) Emergent group level selection in a peer-to-peer network. Complexus 3:108–118
Yizhi R, Mingchu L, Kouichi S (2010) FineTrust: a fine-grained trust model for P2P networks. Secur Netw Commun. DOI:10.1002/sec.165
RunFang Z, Kai H (2007) PowerTrust: a robust and scalable reputation system for trusted peer-to-peer computing IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 18(4):460–473
Newman J (2003) The structure and function of complex network. SIAM Rev 45:167–256
Traulsen A, Nowak M (2006) Evolution of cooperation by multilevel selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:10952–10955
Clutton-Brock TH, Parker GA (1995) Punishment in animal societies. Nature 373:209–216
Fehr E, Gachter S (2002) Altruistic punishment in humans. Nature 415:137–140
Ohtsuki H, Iwasa Y, Nowak M (2009) Indirect reciprocity provides only a narrow margin of efficiency for costly punishment. Nature 457:79–82
Shaikh RJ, d’Aurol Heejo L, Sungyoung L, Yong-Jae S (2009) Group-based selection trust management scheme for clustered wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 20(11):1698–1712
Hales D, Stefano A, Andrea M, Isaac C (2007) Towards a group selection design pattern. Technical report UBLCS-2007-25, University of Bologna, Dept. of Computer Science. [DELISTR-0568]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Y., Li, M., Xiang, Y. et al. Evolution of cooperation in reputation system by group-based scheme. J Supercomput 63, 171–190 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-010-0498-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-010-0498-8