Abstract
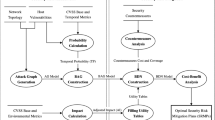
When establishing a network attack strategy, target network information is not certain, and the attacker lacks comprehensive, reliable and real-time attack information, making it difficult to perform an attack. To address this issue, a complex scientific network attack method is proposed. The attacker’s income, losses, costs and encountered risks related to a cyberattack are analysed, an index system is established, and a dynamic Bayesian network is used to comprehensively assess the attack effects on network nodes to overcome drawbacks of the traditional node importance assessment method, which relies on a single network topological index or makes static assessments of the target node. A simulation experiment shows that the proposed method synthesizes more node information and observed data for the attack, thereby avoiding the discrepancy between actual attack effects and theoretical expectations of attacks from static assessment and delivering higher levels of attack accuracy and efficiency than previous methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
14 February 2024
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-05971-8
References
Akoglu L, Tong H, Koutra D (2015) Graph based anomaly detection and description: a survey. Data Min Knowl Disc 29(3):626–688
Andrieu C, De FN, Doucet A (2014) Robust full Bayesian learning for radial basis networks. Neural Comput 13(10):2359–2407
Hellmann T, Staudigl M (2014) Evolution of social networks. Eur J Oper Res 234(3):583–596
Moignard V, Woodhouse S, Haghverdi L et al (2015) Decoding the regulatory network for blood development from single-cell gene expression measurements. Nat Biotechnol 33(3):269
Patel J, Shah S, Thakkar P et al (2015) Predicting stock and stock price index movement using trend deterministic data preparation and machine learning techniques. Expert Syst Appl 42(1):259–268
Bagnall A, Lines J, Hills J et al (2015) Time-series classification with COTE: the collective of transformation-based ensembles. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 27(9):2522–2535
Tatar A, Amorim MDD, Fdida S et al (2014) A survey on predicting the popularity of web content. J Internet Serv Appl 5(1):8
Gagnepain P, Henson RN, Anderson MC (2014) Suppressing unwanted memories reduces their unconscious influence via targeted cortical inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(13):E1310
Yerima SY, Sezer S, Mcwilliams G (2016) Analysis of Bayesian classification-based approaches for Android malware detection. Inf Secur IET 8(1):25–36
Ji Z, Ji H (2016) TSCAN: pseudo-time reconstruction and evaluation in single-cell RNA-seq analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 44(13):e117–e117
Kooij JFP, Schneider N, Flohr F et al (2014) Context-based pedestrian path prediction. Lect Notes Comput Sci 8694:618–633
Cecile B, David CJ, Matteo M et al (2015) Clustering attributed graphs: models, measures and methods. Netw Sci 3(3):408–444
Amer MR, Peng L, Todorovic S (2014) HiRF: hierarchical random field for collective activity recognition in videos. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, Cham, pp 572–585
Naderpour M, Lu J, Zhang G (2014) An intelligent situation awareness support system for safety-critical environments. Decis Support Syst 59(1):325–340
Tahan G, Rokach L, Shahar Y (2014) Mal-ID: automatic malware detection using common segment analysis and meta-features. J Mach Learn Res 13(13):949–979
Mohammed MA, Ghani MKA, Arunkumar N, Hamed RI, Abdullah MK, Burhanuddin MA (2018) A real time computer aided object detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma using genetic algorithm and artificial neural network based on Haar feature fear. Future Gener Comput Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.07.022
Ashokkumar P, Arunkumar N, Don S (2018) Intelligent optimal route recommendation among heterogeneous objects with keywords. Comput Electr Eng 68:526–535
Hussein AF, Kumar A, Burbano-Fernandez M, Gustavo Ramirez-Gonzalez G, Abdulhay E, de Albuquerque VHC (2018) An automated remote cloud-based heart rate variability monitoring system. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2831209
Sarvaghad-Moghaddam M, Orouji AA, Ramezani Z, Elhoseny M, Farouk A, Arun Kumar N (2018) Modelling the spice parameters of SOI MOSFET using a combinational algorithm. Clust Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2289-6
Khanna A, Jain S, Aggarwal T, Kumar A, Gupta D, Julka A, Albuquerque V (2018) Optimized cuttlefish algorithm for diagnosis of parkinson’s disease. Cognit Syst Res 52:36–48
Hussein AF, ArunKumar N, Ramirez-Gonzalez G, Abdulhay E, Tavares JMR, de Albuquerque VHC (2018) A medical records managing and securing blockchain based system supported by a genetic algorithm and discrete wavelet transform. Cognit Syst Res 52:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.05.004
Wei J, Meng F, Arunkumar N (2018) A personalized authoritative user-based recommendation for social tagging. Future Gener Comput Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.03.048
Acknowledgements
Financial support was received through the Excellent Talent Foundation of China West Normal University (No: 17YC497).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-024-05971-8
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zaiyi, P. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Network security situation analysis based on a dynamic Bayesian network and phase space reconstruction. J Supercomput 76, 1342–1357 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2575-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2575-3