Abstract
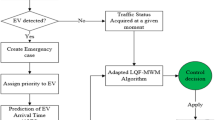
An efficient traffic signal control system (TSCS) should not only be reactive to the current traffic but also be predictive by anticipating future traffic disturbances. In this study, we investigate the potential of using convolution neural network (CNN) in detecting emergency cases and forecasting events that can interrupt the traffic flow. Case-based reasoning (CBR) is then exploited to react to detected and forecasted events. We further develop an adapted Reinforcement Leaning (RL) algorithm in building and enhancing the case bases. The proposed system inherits the advantages of CNN, CBR, and RL, which allow detection, prediction, control, evaluation, and learning in a unified framework. To assess the proposed TSCS, we compare our approach with a set of state-of-art algorithms (e.g., multi-agent preemptive case-based reasoning algorithm and multi-agent preemptive longest queue first—maximal weight matching). The proposed TSCS outperforms the benchmarking algorithms through experiments in various traffic scenarios.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araghi S, Khosravi A, Creighton D (2015) A review on computational intelligence methods for controlling traffic signal timing. Expert Syst Appl 42(3):1538–1550
Louati A, Elkosantini S, Darmoul S, Louati H (2018) Multi-agent preemptive longest queue first system to manage the crossing of emergency vehicles at interrupted intersections. Eur Transp Res Rev 10(2):52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12544-018-0317-5
Qin X, Khan AM (2012) Control strategies of traffic signal timing transition for emergency vehicle preemption. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 25:1–17
Westgate BS, Woodard DB, Matteson DS, Henderson SG (2013) Travel time estimation for ambulances using bayesian data augmentation 1. Ann Appl Stat 7(2):1139–1161
Houli D et al (2010) Multiobjective reinforcement learning for traffic signal control using vehicular ad hoc network. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process 2010(1):724035
Huang Y-S, Shiue J-Y, Luo J (2015) A traffic signal control policy for emergency vehicles preemption using timed petri nets. IFAC-PapersOnLine 48(3):2183–2188
Marcianò G, Musolino FA, Vitetta A (2014) Signal setting optimization on urban road transport networks: the case of emergency evacuation. Saf Sci 72:209–220
Eichler M, Daganzo CF (2006) Bus lanes with intermittent priority: strategy formulae and an evaluation. Transp Res Part B Methodol 40(9):731–744
Guler SI, Gayah VV, Menendez M (2016) Bus priority at signalized intersections with single-lane approaches: a novel pre-signal strategy. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 63:51–70
Dogan E, Akgungor AP, Arslan T (2016) Estimation of delay and vehicle stops at signalized intersections using artificial neural network. Eng Rev 36(2):157–165
Raj J, Bahuleyan H, Vanajakshi LD (2016) Application of data mining techniques for traffic density estimation and prediction. Transp Res Procedia 17:321–330
Kumar SV, Vanajakshi L (2015) Short-term traffic flow prediction using seasonal ARIMA model with limited input data. Eur Transp Res Rev 7(3):21
Louati Ali (2020) A hybridization of deep learning techniques to predict and control traffic disturbances. Artif Intell Rev 53(8):5675–5704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09831-8
Louati A, Louati H, Nusir M et al (2020) Multi-agent deep neural networks coupled with LQF-MWM algorithm for traffic control and emergency vehicles guidance. J Ambient Intell Human Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-01921-3
Silver D et al (2016) Mastering the game of go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 529(7587):484–489
Hammami M, Bechikh S, Louati A et al (2020) Feature construction as a bi-level optimization problem. Neural Comput & Applic 32:13783–13804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04784-z
Said R, Bechikh S, Louati A, Aldaej A, Said LB (2020) Solving Combinatorial Multi-Objective Bi-Level Optimization Problems Using Multiple Populations and Migration Schemes. In IEEE Access, vol 8, pp 141674–141695. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3013568.
Liu H, Simonyan K, Vinyals O, Fernando C, Kavukcuoglu K (2017) Hierarchical representations for efficient architecture search. In: 6th International Conference on Learning Representation, ICLR 2018
Darwish A, Hassanien AE, Das S (2020) A survey of swarm and evolutionary computing approaches for deep learning. Artif Intell Rev 53(3):1767–1812
Zhao T, Nevatia R (2001) Car detection in low resolution aerial image. In: Proceedings eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2001, vol 1, pp 710–717
Moranduzzo T, Melgani F (2014) Automatic car counting method for unmanned aerial vehicle images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52(3):1635–1647
Moranduzzo T, Melgani F (2014) Detecting cars in uav images with a catalog-based approach. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52(10):6356–6367
Shao W, Yang W, Liu G, Liu J (2012) Car detection from high-resolution aerial imagery using multiple features. In: IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium, pp 4379–4382
Swietojanski P, Ghoshal A, Renals S (2014) Convolutional neural networks for distant speech recognition. IEEE Signal Process Lett 21(9):1120–1124
Lawrence S, Giles CL, Tsoi AC, Back AD (1997) Face recognition: a convolutional neural-network approach. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 8(1):98–113
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst
Wang P, Cao Y, Shen C, Liu L, Shen HT (2015) Temporal pyramid pooling based convolutional neural networks for action recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 27(12):2613–2622
Simard PY, Steinkraus D, Platt JC (2003) Best practices for convolutional neural networks applied to visual document analysis
Pinheiro PHO, Collobert R (2014) Recurrent convolutional neural networks for scene labeling
Jain A, Tompson J, Andriluka M, Taylor GW, Bregler C (2013) Learning human pose estimation features with convolutional networks
Chen X, Xiang S, Liu C-L, Pan C-H (2014) Vehicle detection in satellite images by hybrid deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 11(10):1797–1801
Vedaldi A, Gulshan V, Varma M, Zisserman A (2009) Multiple kernels for object detection. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, 2009, pp 606–613
Lampert CH, Blaschko MB, Hofmann T (2008) Beyond sliding windows: object localization by efficient subwindow search. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1–8
Wang X, Yang M, Zhu S, Lin Y (2015) Regionlets for generic object detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(10):2071–2084
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2017) Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(6):1137–1149
Nagy AM, Simon V (2018) Survey on traffic prediction in smart cities. Pervas Mob Comput 50:148–163
de Gier J, Garoni TM, Rojas O (2010) Traffic flow on realistic road networks with adaptive traffic lights
Huisken G, van Berkum EC (2003) A comparative analysis of short-range travel time prediction methods
Yu H, Wu Z, Wang S, Wang Y, Ma X (2017) Spatiotemporal recurrent convolutional networks for traffic prediction in transportation networks
Sun S, Zhang C, Zhang Y (2017) Traffic flow forecasting using a spatio-temporal Bayesian network predictor
Li Y, Yu R, Shahabi C, Liu Y (2017) Graph convolutional recurrent neural network: data-driven traffic forecasting
Zhang J, Zheng Y, Qi D, Li R, Yi X, Li T (2018) Predicting citywide crowd flows using deep spatio-temporal residual networks. Artif Intell 259:147–166
Pan R, Yang Q, Pan SJ (2007) Mining competent case bases for case-based reasoning. Artif Intell 171(16–17):1039–1068
Ros R, Arcos JL, Lopez de Mantaras R, Veloso M (2009) A case-based approach for coordinated action selection in robot soccer. Artif Intell 173(9–10):1014–1039
Lu N, Lu J, Zhang G, Lopez de Mantaras R (2016) A concept drift-tolerant case-base editing technique. Artif Intell 230:108–133
Louati A, Elkosantini S, Darmoul S, Said LB (2019) An immune memory inspired case-based reasoning system to control interrupted flow at a signalized intersection. Artif Intell Rev 52(3):2099–2129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9604-0
Sadek AW, Smith BL, Demetsky MJ (2001) A prototype case-based reasoning system for real-time freeway traffic routing. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 9(5):353–380
De Schutter B, Hoogendoorn SP, Schuurman H, Stramigioli S (2003) A multi-agent case-based traffic control scenario evaluation system. In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, pp 678–683
Karim A, Adeli H (2003) CBR model for freeway work zone traffic management. J Transp Eng 129(2):134–145
Louati A, Elkosantini S, Darmoul S, Said LB (2016) A case-based reasoning system to control traffic at signalized intersections. IFAC-PapersOnLine 49(5):149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2016.07.105
Louati A, Elkosantini S, Darmoul S, Said LB (2017) An immune memory inspired case-based reasoning system to control interrupted flow at a signalized intersection. Artif Intell Rev, 1–31
Salimans T, Ho J, Chen X, Sidor S, Sutskever I (2017) Evolution strategies as a scalable alternative to reinforcement learning
Glick J (2015) Reinforcement learning for adaptive traffic signal control, Stanford, USA
Mannion P, Duggan J, Howley E (2016) An experimental review of reinforcement learning algorithms for adaptive traffic signal control. In: Autonomic road transport support systems, Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 47–66
Marsetič R, Šemrov D, Žura M (2014) Road artery traffic light optimization with use of the reinforcement learning. PROME Traffic Transp 26(2):101–108
Leottau DL, Ruiz-del-Solar J, Babuška R (2018) Decentralized reinforcement learning of robot behaviors. Artif Intell 256:130–159
El-Tantawy S, Abdulhai B, Abdelgawad H (2014) Design of reinforcement learning parameters for seamless application of adaptive traffic signal control. J Intell Transp Syst 18(3):227–245
Louati A, Darmoul S, Elkosantini S, Said LB (2018) An artificial immune network to control interrupted flow at a signalized intersection. Inf Sci 433–434:70–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.12.033
Darmoul Saber, Elkosantini Sabeur, Louati Ali, Said Lamjed Ben (2017) Multi-agent immune networks to control interrupted flow at signalized intersections. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 82:290–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2017.07.003
Genders W, Razavi S (2016) Using a deep reinforcement learning agent for traffic signal control
Ordóñez F, Roggen D, Ordóñez FJ, Roggen D (2016) Deep convolutional and lstm recurrent neural networks for multimodal wearable activity recognition. Sensors 16(1):115
Kim T-Y, Cho S-B (2018) Web traffic anomaly detection using C-LSTM neural networks. Expert Syst Appl 106:66–76
Wunderlich R, Elhanany I, Urbanik T (2007) A stable longest queue first signal scheduling algorithm for an isolated intersection. In: IEEE International Conference on Vehicular Electronics and Safety, pp 1–6
Wunderlich R, Elhanany I, Urbanik T (2008) A novel signal-scheduling algorithm with quality-of-service provisioning for an isolated intersection. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 9(3):536–547
De Castro LN, Timmis J (2002) Artificial immune systems: a new computational intelligence approach. Springer, London
Diala D, Sid-Ali A, Abderrahman EM, Habib C (2012) A dynamic multi-criteria aid for process driving using case-based reasoning. J Decis Syst 18(4):459–484
Marichal J-L (2004) Tolerant or intolerant character of interacting criteria in aggregation by the Choquet integral. Eur J Oper Res 155(3):771–791
Labreuche C (2003) The Choquet integral for the aggregation of interval scales in multicriteria decision making. Fuzzy Sets Syst 137(1):11–26
Bouhana A, Fekih A, Abed M, Chabchoub H (2013) An integrated case-based reasoning approach for personalized itinerary search in multimodal transportation systems. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 31:30–50
Python Software Foundation, SPADE 2.3: Python Package Index (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research in Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University for supporting and funding the corresponding author research related to traffic control and emergency management since 2018 until 2020. Moreover, the authors want to thank the nine reviewers for; 1) the time spent on evaluating the manuscript, 2) appreciating the novelty of our suggestions, and 3) finding the contributions interesting and innovative.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no financial support from any institution that could have influenced its outcome.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Louati, A., Louati, H. & Li, Z. Deep learning and case-based reasoning for predictive and adaptive traffic emergency management. J Supercomput 77, 4389–4418 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03435-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03435-3