Abstract
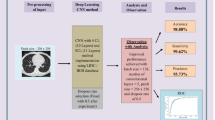
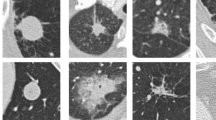
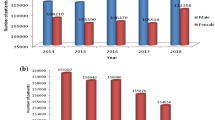
To solve the problems of low sensitivity and high false positive rate of current lung nodule detection technology, and to explore the correlation between neuropeptide correlative substances and lung nodules, in the study, the deep learning-based computerized tomography (CT) images were used to detect lung nodules. Specifically, a multi-scale three-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN) was established for lung nodule detection. First, high-quality candidate nodules were obtained by a two-dimensional CNN. Then, three-dimensional CNNs of different scales were constructed for candidate nodules of different sizes, and the fused model was used to classify candidate nodules. Finally, the detection results of the single network, the two-dimensional CNN, and the fused network were compared. Meanwhile, the serum levels of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and substance P (SP) were detected in patients with lung injury caused by lung nodules, so as to analyze the correlation between neuropeptide correlative substances and lung nodules. The results showed that the detection sensitivity of the fused network was 85.8% and 92.9% when the number of false positives was 1 and 4, respectively, which were higher than that of the single network and two-dimensional CNN. However, the content of VIP in the serum of patients with pulmonary nodules was significantly reduced, while the content of SP was significantly increased. Therefore, the algorithm proposed in this study can effectively improve the sensitivity of the pulmonary nodule detection system and reduce false positive rate; at the same time, neuropeptide correlative substances may be correlated with the lung injury caused by pulmonary nodules.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tobias P, Fenghai D, Srinivasan R et al (2018) Novel high-resolution computed tomography-based radiomic classifier for screen-identified pulmonary nodules in the National Lung Screening Trial. PLoS ONE 13(5):e0196910
Zheng H, Wu X, Yin J et al (2019) Clinical applications of liquid biopsies for early lung cancer detection. Am J Cancer Res 9(12):2567–2579
Hsiao YT, Fan MJ, Huang AC et al (2018) Deguelin impairs cell adhesion, migration and invasion of human lung cancer cells through the NF-κB signaling pathways. Am J Chin Med 46(1):209–229
Dhara AK, Mukhopadhyay S, Dutta A et al (2017) Content-based image retrieval system for pulmonary nodules: assisting radiologists in self-learning and diagnosis of lung cancer. J Digit Imaging 30(1):63–77
Suvas S (2017) Role of substance P neuropeptide in inflammation, wound healing, and tissue homeostasis. J Immunol 199(5):1543–1552
Lyons CL, Tshibalanganda M, Plessis AD (2019) Using CT-scanning technology to quantify damage of the stem-boring beetle, Aphanasium australe, a biocontrol agent of Hakea sericea in South Africa. Biocontrol Sci Tech 30(1):1–9
Jiang L, Wu B, Song Y et al (2017) Mass transfer coefficient measurement during brine flush in a CO2-filled packed bed by X-ray CT scanning. Int J Heat Mass Transf 115:615–624
Takahashi R, Kajikawa Y (2017) Computer-aided diagnosis: a survey with bibliometric analysis. Int J Med Inform 101(5):58–67
Choi YJ, Baek JH, Park HS et al (2017) A computer-aided diagnosis system using artificial intelligence for the diagnosis and characterization of thyroid nodules on ultrasound: initial clinical assessment. Thyroid 27(4):546–552
Lv XQ, Wu L, Gu Y et al (2018) Detection of low dose CT pulmonary nodules based on 3D convolution neural network. Opt Precis Eng 26(5):1211–1218
Zheng S, Guo J, Cui X et al (2020) Automatic pulmonary nodule detection in CT scans using convolutional neural networks based on maximum intensity projection. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(3):797–805
Mzoughi H, Njeh I, Wali A et al (2020) Deep multi-scale 3D convolutional neural network (CNN) for MRI gliomas brain tumor classification. J Digit Imaging 33(4):903–915
Zuo W, Zhou F, He Y et al (2019) Automatic classification of lung nodule candidates based on a novel 3D convolution network and knowledge transferred from a 2D network. Med Phys 46(12):5499–5513
Pezeshk A et al (2018) 3D convolutional neural networks for automatic detection of pulmonary nodules in chest CT. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 23(5):2080–2090
Lee CC, Tsai ST, Yang CH (2018) Lung nodule detection using ensemble classifier in computed tomography images. Sens Mater 30(2):1859–1868
Steuer CW, Yu SC, Liewald JF et al (2017) Fast cAMP modulation of neurotransmission via neuropeptide signals and vesicle loading. Curr Biol 27(4):495–507
Gospocic J, Shields EJ, Glastad KM et al (2017) The neuropeptide corazonin controls social behavior and caste identity in ants. Cell 170(4):748–759
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, L., Gao, J. Adoption of computerized tomography images in detection of lung nodules and analysis of neuropeptide correlative substances under deep learning algorithm. J Supercomput 77, 7584–7597 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03538-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03538-x