Abstract
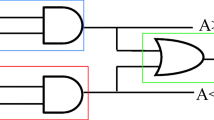
Quantum dot cellular automata (QCA) are emerging nanotechnology that offers few significant advantages like faster speed, higher circuit density, and lower power dissipation. Comparator is a fundamental and essential block in QCA logic circuit family. In this article, a single-layered and straightforward design of a QCA-based one-bit magnitude comparator has been proposed. The proposed design is 6.38%, 6.67% and ~ 10% more efficient in cell complexity, cell area and total area measurement, respectively, in comparison to prior reported designs. Furthermore, the energy dissipation of the proposed circuit has been calculated using QCADesigner-E and QCAPro tools to check the energy efficiency of the proposed circuit. The total energy dissipation of the reported magnitude comparator is 19.50 meV when measured using the QCADesigner-E tool. Similarly, according to the QCAPro tool, it has ~ 71% less energy dissipation than the existing designs.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lent CS, Tougaw PD, Porod W, Bernstein GH (1993) Quantum cellular automata. Nanotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/4/1/004
Tougaw PD, Lent CS (1996) Dynamic behavior of quantum cellular automata. J Appl Phys. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.363455
Lent CS, Tougaw PD (1997) A device architecture for computing with quantum dots. Proc IEEE 85(4):541–557. https://doi.org/10.1109/5.573740
Tougaw PD, Lent CS (1994) Logical devices implemented using quantum cellular automata. J Appl Phys. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.356375
Jeon JC (2021) Designing nanotechnology qca–multiplexer using majority function-based nand for quantum computing. J Supercomput 77:1562–1578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03341-8
Khan A, Arya R (2021) Optimal demultiplexer unit design and energy estimation using quantum dot cellular automata. J Supercomput 77:1714–1738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03320-z
Wang L, Xie G (2018) Novel designs of full adder in quantum-dot cellular automata technology. J Supercomput 74:4798–4816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2481-8
Heikalabad SR, Asfestani MN, Hosseinzadeh M (2018) A full adder structure without cross-wiring in quantum-dot cellular automata with energy dissipation analysis. J Supercomput 74:1994–2005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-017-2206-4
Sadeghi M, Navi K, Dolatshahi M (2020) Novel efficient full adder and full subtractor designs in quantum cellular automata. J Supercomput 76:2191–2205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-019-03073-4
Deng F, Xie G, Zhu R, Zhang Y (2020) A matrix representation method for decoders using majority gate characteristics in quantum-dot cellular automata. J Supercomput 76:2842–2859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-019-03084-1
Kamrani H, Heikalabad SR (2021) Design and implementation of multiplication algorithm in quantum-dot cellular automata with energy dissipation analysis. J Supercomput 77:5779–5805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03478-6
Hashemi S, Navi K (2012) New robust qca d flip flop and memory structures. Microelectron J 43(12):929–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2012.10.007
Ghosh B, Gupta S, Kumari S (2012) Quantum dot cellular automata magnitude comparators. IEEE Int Conf Electron Dev Solid State Circuit 2012:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1109/EDSSC.2012.6482766
Bahar AN, Roy K, Asaduzzaman M, Bhuiyan MMR (2017) Design and implementation of 1-bit comparator in quantum-dot cellular automata (qca). Cumhuriyet Sci J 38:146–152. https://doi.org/10.17776/csj.72358
Erniyazov S, Jeon JC (2018) Area efficient magnitude comparator based on qca. Adv Sci Technol Lett 150:75–79. https://doi.org/10.14257/astl.2018.150.19
Umira S, Qadri R, Bangi ZA, Banday MT (2018) A novel comparator-a cryptographic design in quantum dot cellular automata. In: 2018 International Conference on Sustainable Energy, Electronics, and Computing Systems (SEEMS), pp 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/SEEMS.2018.8687363
Jun-wen L, Yin-shui X (2018) A novel design of quantum-dots cellular automata comparator using five-input majority gate. In: 2018 14th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), pp. 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSICT.2018.8565804
Walus K, Dysart TJ, Jullien GA, Budiman RA (2004) QCADesigner: a rapid design and simulation tool for quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 3(1):26–31. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2003.820815
QCADesigner-E (2017). Accessed 12 Mar 2021. [Online]. https://github.com/FSillT/QCADesigner-E
Sill Torres F, Wille R, Niemann P, Drechsler R (2018) An energy-aware model for the logic synthesis of quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans Comput Aided Design Integrated Circuits Syst 37(12):3031–3041. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCAD.2018.2789782
Srivastava S, Sarkar S, Bhanja S (2009) Estimation of upper bound of power dissipation in QCA circuits. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 8(1):116–127. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCAD.2018.2789782
Srivastava S, Asthana A, Bhanja S, Sarkar S (2011) QCAPro: an error-power estimation tool for QCA circuit design. IEEE Int Symp Circuits Syst 2011:2377–2380. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCAS.2011.5938081
Timler J, Lent CS (2002) Power gain and dissipation in quantum-dot cellular automata. J Appl Phys 91(2):823–831. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1421217
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., Arya, R. High performance nanocomparator: a quantum dot cellular automata-based approach. J Supercomput 78, 2337–2353 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-03961-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-03961-8