Abstract
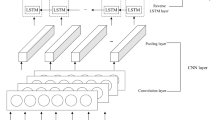
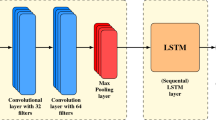
Online ride-hailing order forecasting is a very important part of the intelligent traffic dispatch system. Accurate order forecasting can reduce the flow of invalid vehicles and improve the user experience of online ride-hailing. We propose a multi-view deep long short-term memory (LSTM) network architecture (MultiView deep LSTM framework), which uses convolutional neural network and graph convolutional network to extract the temporal and spatial characteristics of online ride-hailing orders, obtains the correlation information between regional orders through the order view, regional speed view, and weather factor view, and then uses LSTM unit and attention unit to predict the order volume in real time. We use Didi Haikou, China’s online ride-hailing dataset for training, compare it with the prediction algorithms of other articles, and experiment with different choices of the contrast framework. The experimental results show that our deep learning framework can effectively capture comprehensive spatio-temporal correlation and obtain better results. The model maintained good performance at 15 min, 30 min, and 1 h. Experiments conducted on the actual demand data onto ride-hailing from Didi Haikou data prove that our method is better than the latest method.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Z, Su X, Ding Z (2020) Long-term traffic prediction based on LSTM encoder-decoder architecture. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2020.2995546
Zhou Y, Li J, Chen H, Wu Y, Wu J, Chen L (2020) A spatiotemporal attention mechanism-based model for multi-step citywide passenger demand prediction. Inf Sci 513:372–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.10.071
Yu B, Yin H, Zhu Z (2018) Spatio-temporal graph convolutional networks: a deep learning framework for traffic forecasting. In: Proceedings of the twenty-seventh international joint conference on artificial intelligence, 3634–3640. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2018/505, 1709.04875
Yang T, Tang X, Liu R (2021) Dual temporal gated multi-graph convolution network for taxi demand prediction. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06092-6
Faial D, Bernardini F, Meza EM, Miranda L, Viterbo J (2020) A methodology for taxi demand prediction using stream learning. In: 2020 international conference on systems, signals and image processing (IWSSIP). IEEE, Niterói, Brazil, pp 417–422. https://doi.org/10.1109/IWSSIP48289.2020.9145097
Bing H, Zhifeng X, Yangjie X, Jinxing H, Zhanwu M (2020) Integrating semantic zoning information with the prediction of road link speed based on taxi GPS data. Complexity 2020:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6939328
Liu D, Mou J, Liu Y, Yang Y (2020) Improved prediction of high taxi demand: a deep spatiotemporal network for hyper-imbalanced data. In: 2020 IEEE 23rd international conference on intelligent transportation systems (ITSC). IEEE, Rhodes, Greece, pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/ITSC45102.2020.9294616
Wu Z, Lian G (2020) A novel dynamically adjusted regressor chain for taxi demand prediction. In: 2020 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN). IEEE, Glasgow, UK, pp 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN48605.2020.9207160
Smith BL, Williams BM, Keith Oswald R (2002) Comparison of parametric and nonparametric models for traffic flow forecasting. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 10(4):303–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-090X(02)00009-8
Ma X, Tao Z, Wang Y, Yu H, Wang Y (2015) Long short-term memory neural network for traffic speed prediction using remote microwave sensor data. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 54:187–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2015.03.014
Zhan X, Zheng Y, Yi X, Ukkusuri SV (2017) Citywide traffic volume estimation using trajectory data. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 29(2):272–285. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2016.2621104
Ma X, Dai Z, He Z, Ma J, Wang Y, Wang Y (2017) Learning traffic as images: a deep convolutional neural network for large-scale transportation network speed prediction. Sensors 17(4):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040818
Zhang J, Zheng Y, Qi D, Li R, Yi X (2016) DNN-based prediction model for spatio-temporal data. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGSPATIAL international conference on advances in geographic information systems. ACM, Burlingame California, pp 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1145/2996913.2997016
Chai D, Wang L, Yang Q (2018) Bike flow prediction with multi-graph convolutional networks. arXiv:180710934 [cs, stat]
Ke J, Zheng H, Yang H, Xiqun Chen (2017) Short-term forecasting of passenger demand under on-demand ride services: a spatio-temporal deep learning approach. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 85:591–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2017.10.016
Chen B, Li W (2020) Multitime resolution hierarchical attention-based recurrent highway networks for taxi demand prediction. Math Probl Eng 2020:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4173094
Chen Z, Zhao B, Wang Y, Duan Z, Zhao X (2020) Multitask learning and GCN-based taxi demand prediction for a traffic road network. Sensors 20(13):3776. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20133776
Geng X, Li Y, Wang L, Zhang L, Yang Q, Ye J, Liu Y (2019) Spatiotemporal multi-graph convolution network for ride-hailing demand forecasting. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell 33:3656–3663. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33013656
Zhang C, Zhu F, Lv Y, Ye P, Wang FY (2021) MLRNN: taxi demand prediction based on multi-level deep learning and regional heterogeneity analysis. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2021.3080511
Schwemmle N (2021) Hyperparameter optimization for neural network based taxi demand prediction. BIVEC/GIBET Transp Res 2021:12
Zhang J, Zheng Y, Qi D, Li R, Yi X, Li T (2017) Predicting citywide crowd flows using deep spatio-temporal residual networks. arXiv:170102543 [cs] 1701.02543
Xiong Z, Jian Li WuH (2021) Understanding operation patterns of urban online ride-hailing services: a case study of Xiamen. Transp Policy 101:100–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2020.12.008
Shu P, Sun Y, Zhao Y, Xu G (2020) Spatial-temporal taxi demand prediction using LSTM-CNN. In: 2020 16th IEEE international conference on automation science and engineering (CASE) 2020:1226–1230
Tang J, Liang J, Liu F, Hao J, Wang Y (2021) Multi-community passenger demand prediction at region level based on spatio-temporal graph convolutional network. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 124:102951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2020.102951
Shi X, Gao Z, Lausen L, Wang H, Yeung DY, Wong WK, Woo WC (2017) Deep learning for precipitation nowcasting: a benchmark and a new model. arXiv:170603458 [cs]
Zhang S, Kang Z, Zhang Z, Lin C, Wang C, Li J (2019) A hybrid model for forecasting traffic flow: using layerwise structure and Markov transition matrix. IEEE Access 7:26002–26012. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2901118
Yan J, Xiang L, Wu C, Wu H (2020) City-scale taxi demand prediction using multisource urban geospatial data. The international archives of the photogrammetry, remote sensing and spatial information sciences XLIII-B4-2020:213–220. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-XLIII-B4-2020-213-2020
Kipf TN, Welling M (2017) Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In: 5th international conference on learning representations
Veličković P, Cucurull G, Casanova A, Romero A, Liò P, Bengio Y (2018) Graph attention networks. In: 6th international conference on learning representations
Yang F, Zhang H, Tao S (2021) Simplified multilayer graph convolutional networks with dropout. Appl Intell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02617-7
Yang T, Guo Q, Xu L, Sun H (2021) Dynamic pricing for integrated energy-traffic systems from a cyber-physical-human perspective. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 136:110419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110419
Hong G, Wang Z, Han T, Ji H (2021) Spatiotemporal multi-graph convolutional network for taxi demand prediction. In: 2021 11th international conference on information science and technology (ICIST). IEEE, Chengdu, China, pp 242–250. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIST52614.2021.9440573
Liu S, Jiang H, Chen Z (2021) Quantifying the impact of weather on ride-hailing ridership: evidence from Haikou, China. Travel Behav Soc 24:257–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tbs.2021.04.002
Wang J, Zhu W, Sun Y, Tian C (2021) An effective dynamic spatiotemporal framework with external features information for traffic prediction. Appl Intell 51(6):3159–3173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-02043-1
Zhang C, Zhu F, Wang X, Sun L, Tang H, Lv Y (2020) Taxi demand prediction using parallel multi-task learning model. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2020.3015542
Helm JM, Swiergosz AM, Haeberle HS, Karnuta JM, Schaffer JL, Krebs VE, Spitzer AI, Ramkumar PN (2020) Machine learning and artificial intelligence: definitions, applications, and future directions. Curr Rev Musculoskeletal Med 13(1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-020-09600-8
Kim T, Sharda S, Zhou X, Pendyala RM (2020) A stepwise interpretable machine learning framework using linear regression (LR) and long short-term memory (LSTM): city-wide demand-side prediction of yellow taxi and for-hire vehicle (FHV) service. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 120:102786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2020.102786
Haibo C, Ke D, Fangfang W, Ayamba EC (2020) The spatial effect of tourism economic development on regional ecological efficiency. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(30):38241–38258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09004-8
Liu Y, Lyu C, Khadka A, Zhang W, Liu Z (2020) Spatio-temporal ensemble method for car-hailing demand prediction. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 21(12):5328–5333. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2019.2948790
Haklay M, Weber P (2008) OpenStreetMap: user-generated street maps. IEEE Pervasive Comput 7(4):12–18. https://doi.org/10.1109/MPRV.2008.80
Zhao J, Gao Y, Bai Z, Wang H, Lu S (2019) Traffic speed prediction under non-recurrent congestion: based on LSTM method and BeiDou navigation satellite system data. IEEE Intell Transp Syst Mag 11(2):70–81. https://doi.org/10.1109/MITS.2019.2903431
Defferrard M, Bresson X, Vandergheynst P (2016) Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 29:3844–3852
Jin G, Cui Y, Zeng L, Tang H, Feng Y, Huang J (2020) Urban ride-hailing demand prediction with multiple spatio-temporal information fusion network. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 117:102665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2020.102665
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61772386), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province(Grant No. 2020CFB795) and Wuhan Institute of City Research Project(Grant No. 2018CYZDKY007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Zhang, H., Li, C. et al. MVDLSTM: MultiView deep LSTM framework for online ride-hailing order prediction. J Supercomput 78, 8531–8559 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-04237-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-04237-x