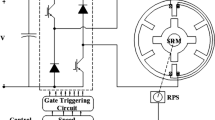
Abstract
Aiming at the sensorless control system of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) for the pure Electric Vehicle (EV), the issues of slow convergence, phase delay, and chattering caused by Sliding Mode Observer (SMO), a single current flux weakening fuzzy adaptive Super-Twisting (ST) SMO algorithm is proposed in this paper. The fuzzy adaptive algorithm is used to estimate the uncertain boundary and adaptively adjust sliding mode gain, which is used in the ST algorithm to accelerate the convergence speed of sliding mode gain, and eliminate the system delay caused by phase-locked loop and phase compensation, and improve the estimation accuracy of speed and rotor position. The single current flux weakening is used to improve the issues of d-q axis current coupling and enhance the load capacity of the field weakening area of the PMSM. The algorithm is verified by MATLAB/Simulink. The simulation results show that the single current flux-weakening fuzzy ST-SMO algorithm has faster convergence speed in the variable speed and the variable load of PMSM sensorless control system, which has significantly reduced chattering, obtained more accurate speed and rotor position, and has better dynamic response and robustness, and has widened the speed region of PMSM.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hua YZ, Zhu HQ (2020) Rotor radial displacement sensorless control of bearingless permanent magnet synchronous motor based on MRAS and suspension force compensation. ISA Trans 103(12):306–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2020.05.005
Teng Q, Bo J, Zhu J (2015) Sensorless model predictive torque control using sliding-mode model reference adaptive system observer for permanent magnet synchronous motor drive systems. Control Theory Appl 32(2):151–162. https://doi.org/10.7641/CTA.2015.13143
Yin S, Xu W, Yu CL (2020) Direct torque control of permanent magnet synchronous motor in ship propulsion system based on memory attenuation Kalman filter. J Coastal Res 110(7):80–86. https://doi.org/10.2112/JCR-SI110-020.1
Liang D, Li J, Qu R (2018) Adaptive second-order sliding-mode observer for PMSM sensorless control considering VSI nonliearity. IEEE Trans Power Electron 33(10):8994–9004. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2017.2783920
Kuttler S, Benkara KEK, Friedrich G et al (2017) Fast iron losses model of stator taking into account the flux weakening mode for the optimal sizing of high speed permanent internal magnet synchronous machine. Math Comput Simul 131(15):328–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2016.06.009
Hu YS, Li YG, Ma XD et al (2021) Flux-weakening control of dual three-phase PMSM based on vector space decomposition control. IEEE Trans Power Electron 36(7):8428–8438. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2020.3044574
Peng SQ, Song YY (2018) Sensorless vector control of PMSM based on adaptive fuzzy sliding mode observer. Control Decis 33(4):644–648. https://doi.org/10.13195/j.kzyjc.2017.0058
Wei HQ, Yu JZ, Zhang YT et al (2020) High-speed control strategy for permanent magnet synchronous machines in electric vehicles drives analysis of dynamic torque response and instantaneous current compensation. Energy Rep 6(12):2324–2335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2020.08.016
Zerdali E, Barut M (2017) The comparisons of optimized extended Kalman filters for speed-sensorless control of induction motors. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 64(6):4340–4351. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2017.2674579
Quang NK, Hieu NT, Ha QP (2014) FPGA-based sensorless PMSM speed control using reduced-order extended Kalman filters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61(12):6574–6582. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2014.2320215
Sun K, Shi YC, Huang LB et al (2015) A 2-D fuzzy logic-based MRAS scheme for sensorless control of interior permanent magnet synchronous motor drives with cyclic fluctuating loads. In: Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, pp 2475–2481. https://doi.org/10.1109/APEC.2014.6803651
Zhao Y, Qiao W, Wu L (2014) Improved rotor position and speed estimators for sensorless control of interior permanent-magnet synchronous machines. IEEE J Emerg Sel Topics Power Electron 2(3):627–639. https://doi.org/10.1109/JESTPE.2014.2298433
Kim H, Son J, Lee J (2011) A high-speed sliding-mode observer for the sensorless speed control of a PMSM. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58(9):4069–4077. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2010.2098357
Yang J, Dou M, Zhao D (2016) Adaptive sliding mode observer for sensorless control of five-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor. J Northwestern Polytechnical Univ 34(6):1057–1064. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2016.06.021
Liang DL, Li J, Qu RH (2017) Sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous machine based on second-order sliding-mode observer with online resistance estimation. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 53(4):3672–3682. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2017.2690218
Song XD, Fang JC, Han BC et al (2015) Adaptive compensation method for high-speed surface PMSM sensorless drives of EMF-based position estimation error. IEEE Trans Power Electron 31(2):1438–1449. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2015.2423319
Bhaumik A, Das S (2021) Predictive torque control strategy for speed adaptive flux observer based sensorless induction motor drive in flux-weakening region. IEEE Trans Power Electron 36(12):14110–14118. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2021.3089611
Yoo J, Lee J, Sul SK (2021) Analysis of instability in torque control of sensorless PMSM drives in flux weakening region. IEEE Trans Power Electron 36(9):10815–10826. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2021.3063720
Wang YW, Wu JB, Guo ZJ et al (2021) Fuzzy adaptive super-twisting algorithm based sliding-mode observer for sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous motor. J Eng 12:788–799. https://doi.org/10.1049/tje2.12076
Wang B, Zhao YZ, Yu Y et al (2016) Speed-sensorless induction machine control in the field-weakening region using discrete speed-adaptive full-order observer. IEEE Trans Power Electron 31(8):5759–5773. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2015.2496350.s
Dybkowski M, Orlowska-Kowalska T, Tarchala G (2013) Sensorless traction drive system with sliding mode and MRAS(CC) estimators using direct torque. Automatika 54(3):329–336. https://doi.org/10.7305/automatika.54-3.169
Miguel C, Heredero DP, Gross G et al (2020) Maximum torque per voltage flux-weakening strategy with speed limiter for PMSM drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 68(10):9254–9264. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2020.3020029
Ekanayake S, Dutta R, Rahman MF et al (2019) Performances of a fractional-slot concentrated-winding permanent magnet synchronous machine under position sensorless control in deep flux-weakening region. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 55(6):5938–5946. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2019.2931269
Liu X, Wang C, Han Y (2017) Second-order sliding mode control of DFIG based variable speed wind turbine for maximum power point tracking. Acta Autom Sin 43(8):1434–1442. https://doi.org/10.16383/j.aas.2017.e150252
Chi TR, Nguyen BH, Trovo JP et al (2020) Effect of battery voltage variation on electric vehicle performance driven by induction machine with optimal flux-weakening strategy. IET Electr Syst Transp 10(4):351–359. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-est.2020.0013
Blondin MJ, Trovao J (2019) Soft computing techniques for cruise controller tuning for an off-road electric vehicle. IET Electr Syst Transp 9(4):196–205. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-est.2019.0008
Essam E, Mohamed E (2020) Voltage regulation feedback and deadbeat predictive current control of interior PM machines. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1002/2050-7038.12413
Guo JQ, Liu X, Li SH (2021) Flux-weakening control for variable flux reluctance flux reluctance machine excited by zero-sequence current considering zero-sequence resistive voltage drop. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 36(1):272–280. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2020.3005137
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the sub-project of the National Key Research and Development Program (2016YFD0700103-02) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51675163).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wu, J., Guo, Z. et al. Flux-weakening fuzzy adaptive ST-SMO sensorless control algorithm for PMSM in EV. J Supercomput 78, 10930–10949 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-04264-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-04264-8