Abstract
The MAC protocol is important, especially for wireless LAN because of limited bandwidth. A great deal of research has been carried out and some of proposed schemes are effective. Specifically, considerable effort has been devoted to improving the IEEE 802.11 standard which is utilized widely. Previous theoretical analysis gave the upper bound of IEEE 802.11 DCF throughput which is far below the channel capacity and corresponding algorithm was proposed, which can achieve the throughput close to the upper bound. It seems that we cannot expect to enhance the throughput much more in a usual way. In the meantime, besides throughput, there are some other issues for DCF such as fairness and QoS support. However, except for several hybrid protocols, most proposals were either based on contention mode or schedule mode and neither of the two modes has possessed the good characters of the other.
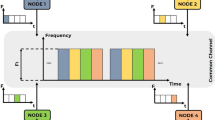
In this paper, we propose a new MAC scheme used for DCF (with no control node) that dynamically adapts to traffic changes without degradation of delay in the case of low traffic load and achieves high throughput which is close to transmission capacity in saturated case. The key idea is to divide the virtual frame into two parts, i.e., schedule part and contention part, and to enable each node to reserve a slot in schedule part. Unlike conventional hybrid protocols, every node does not have to intentionally reset any parameter according to the changing traffic load except its queue length. A distinguishing feature of this scheme is the novel way of allowing WLANs to work with low delay as in the contention-based mode and achieve high throughput as in the schedule-based mode without complicated on-line estimation required in previous schemes. This makes our scheme simpler and more reliable. Through an analysis of simulation results, we show that our scheme can greatly improve the throughput with low delay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
IEEE Std. 802.11 (1999). Wireless LAN medium access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications. Reference number ISO/IEC 8802-11, 1999(E), IEEE Std. 802.11, 1999 edition.
Crow, B. P., et al. (1977). IEEE 802.11 wireless local area networks. IEEE Communication Magazine, 35, 116–126.
Fullmer, C., & Garcia-Luna-Aceves, J. (1995). Floor acquisition multiple access (FAMA) for packet-ratio networks. In Proc. SIGCOMM’95 (pp. 262–273). Cambridge, MA.
Bharghvan, V. (1998). Performance evaluation of algorithms for wireless medium access. In IEEE international computer performance and dependability symposium IPDS’98 (pp. 142–149).
Tay, Y. C., & Chua, K. C. (2001). A capacity analysis for the IEEE 802.11 MAC protocol. ACM/Baltzer Wireless Networks, 7(2), 159–171.
Kim, J. H., & Lee, J. K. (1999). Performance of carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance protocols in wireless LANs. Wireless Personal Communications, 11(2), 161–183.
Cali, F., Conti, M., & Gregori, E. (2000). Dynamic tuning of the IEEE 802.11 protocol to achieve a theoretical throughput limit. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 8(6), 785–799.
Tian, X., et al. (2005). Improving throughputs and fairness in WLANs through dynamically optimizing backoff. IEICE Transactions on Communications, E88-B, 10, 4328–4338.
Kwon, Y., Fang, Y., & Latchman, H. (2003). A novel MAC protocol with fast collision resolution for wireless Lans. In IEEE INFOCOM’03.
Weinmiller, J., et al. (1996). Analyzing and tuning the distributed coordination function in the IEEE 802.11 DFWMAC draft standard. In Proc. MASCOT, San Jose, CA.
Wu, H., et al. (2002). Performance of reliable transport protocol over IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN: analysis and enhancement. In IEEE INFOCOM’02 (Vol. 2, pp. 599–607).
Chhaya, H. S., & Gupta, S. (1997). Performance modeling of asynchronous data transfer methods of IEEE 802.11 MAC protocol. ACM/Baltzer Wireless Networks, 3, 217–234.
Al-Karaki, J.N., & Chang, J.M. (2004). A simple distribution access control scheme for supporting QoS in IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs. In Proc. WCNC04. IEEE wireless and communications and networking conference, Atlanta.
Mangold, S., et al. (2002). IEEE 802.11e wireless LAN for QoS. In European wireless conference.
Kim, H., & Hou, J. (2003). Improving protocol capacity with model-based frame scheduling in IEEE 802.11-operated WLANs. In Proc. ACM MobiCom 2003, September 2003.
Bianchi, G. (2000). Performance analysis of the IEEE 802.11 distributed coordination function. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communication, 18(3), 535–547.
Bianchi, G., & Tinnirello, I. (2003). Kalman filter estimation of the number of competing terminals in an IEEE 802.11 network. EEE INFOCOM’03, 2, 844–852.
Pong, D., & Moors, T. (2003). Call admission control for IEEE 802.11 contention access mechanism. In Proc. Globecom, San Francisco.
Chen, X., et al. (2006). Supporting QoS in IEEE 802.11e wireless LANs. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 5(8), 2217–2227.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, X., Chen, X., Ideguchi, T. et al. Improving protocol capacity by scheduling random access on WLANs. Telecommun Syst 37, 19–28 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-008-9076-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-008-9076-2