Abstract
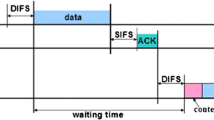
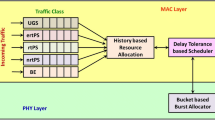
The IEEE 802.16 standard is a Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) technology which offers Quality of Service (QoS) support to different types of applications. This standard defines the physical (PHY) and medium access control (MAC) layers. Its MAC layer defines different types of QoS mechanisms to support various types of applications, being the multicast polling one of these mechanisms. Under this mechanism, based on a contention process, every connection competes to gain access to the channel in order to place its bandwidth requests.
In this paper, we propose a new signalling mechanism, called Requests Per Service Flow (RPSF), to reduce the contention phase in the frame. Additionally, we undertake a comparison of this new method with respect to other mechanisms. The simulation results show that our new proposal outperforms other mechanisms recently reported in the literature, in terms of throughput and end-to-end delay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
IEEE (2001). IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks—Part 16: air interface for fixed broadband wireless access systems (IEEE Std 802.16-2001), Published: April 8 2002, IEEE Std., December 6 2001.
IEEE (2004). IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks—Part 16: air interface for fixed broadband wireless access systems (IEEE Std 802.16-2004), Published: October 1 2004, IEEE Std., June 24 2004, revision of IEEE Std 802.16-2001.
IEEE (2003). IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks—Part 16: air interface for fixed broadband wireless access systems—Amendment 2: medium access control modifications and additional physical layer specifications for 2–11 GHz (IEEE Std 802.16a-2003), Published: April 1 2003, IEEE Std., January 29 2003, amendment to IEEE Std 802.16-2001.
IEEE (2006). IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks—Part 16: air interface for fixed broadband wireless access systems—Amendment 2: Physical and Medium Access Control Layers for Combined fixed and mobile operation in licensed bands and corrigendum 1 (IEEE Std 802.16e–2005), Published: February 28 2006, IEEE Std., December 7 2005, amendment and corrigendum to IEEE Std 802.16-2004.
Oh, S.-M., & Kim, J.-H. (2005). The analysis of the optimal contention period for broadband wireless access network. In Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on pervasive computing and communications workshops (PerCom’2005 workshops) (pp. 215–219), Kauai Island, Hawaii, March 8–12 2005.
Cho, D.-H., Song, J.-H., Kim, M.-S., & Han, K.-J. (2005). Performance Analysis of the IEEE 802.16 Wireless Metropolitan Area Network. In Proceedings of the 1st international conference on distributed frameworks for multimedia applications (DFMA’2005) (pp. 130–137). Los Alamitos: IEEE Computer Society.
Yan, J., & Kuo, G.-S. (2006). Cross-layer design of optimal contention period for IEEE 802.16 BWA systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on communications: Vol. 4 (pp. 1807–1812). ICC’2006, Istanbul, Turkey, June 11–15 2006.
Vinel, A., Zhang, Y., Lott, M., & Tiurlikov, A. (2005). Performance analysis of the random access in IEEE 802.16. In Proceedings of the 16th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications: Vol. 3 (pp. 1596–1600), PIMRC’2005, Berlin, Germany, September 11–14 2005.
Vinel, A., Zhang, Y., Ni, Q., & Lyakhov, A. (2006). Efficient request mechanism usage in IEEE 802.16. In Proceedings of the 49th IEEE global telecommunications conference, GLOBECOM’2006, San Francisco, California, USA, November 27–December 1 2006.
Doha, A., Hassanein, H. S., & Takahara, G. (2006). Performance evaluation of reservation medium access control in IEEE 802.16 networks. In Proceedings of the 4th ACS/IEEE international conference on computer systems and applications AICCSA’2006 (pp. 369–374).
Hawa, M., & Petr, D. W. (2002). Quality of service scheduling in cable and broadband wireless access systems. In 10th IEEE international workshop on quality of service (pp. 247–255), May 15–17 2002.
Kobliakov, V. A., Turlikov, A. M., & Vinel, A. V. (2006). Distributed queue random multiple access algorithm for centralized data networks. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE international symposium on consumer electronics (pp. 1–6), ISCE’2006, St. Petersburg, Russia, June 28–July 1 2006.
Delicado, J., Delicado, F. M., & Orozco-Barbosa, L. (2008). Study of the IEEE 802.16 contention-based request mechanism. Telecommunication Systems, 245, 87–98.
I. OPNET Technologies (2005). OPNET Modeler 11.5.
Forum, W. (2005). Can WiMAX address your applications? WiMAX Forum, October 24.
Karam, A., & Tobagi, F. (2000). On traffic types and service classes in the Internet. In Proceedings of the 43th IEEE global telecommunications conference: Vol. 1 (pp. 548–554), GLOBECOM’2000, San Francisco, CA, USA, November 29 2000.
IEEE (1998). Information technology—telecommunications and information exchange between systems—local and metropolitan area networks—common specifications—Part 3: media access control (MAC) bridges (ANSI/IEEE Std 802.1D), ISO/IEC (ANSI/IEEE) Std. 15 802-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the Spanish MEC and MICINN, as well as European Commission FEDER funds, under Grants CSD2006-00046 and TIN2009-14475-C04. It was also partly supported by JCCM under Grants PII2I09-0045-009916 and PEII09-0037-2328.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delicado, J., Delicado, F.M. & Orozco-Barbosa, L. RPSF: a new QoS bandwidth request mechanism for the IEEE 802.16. Telecommun Syst 50, 97–111 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-010-9392-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-010-9392-1