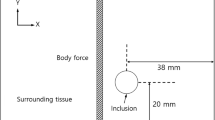
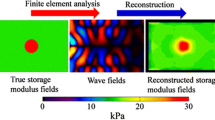
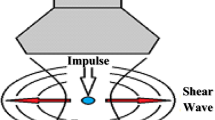
Abstract
This paper describes a simulation of signal pathway in an ultrasonic A-scan. It includes transient diffraction acoustic field, transducer response, absorption and dispersion in viscoelastic medium with arbitrary distribution function. The approach selected here aims at developing digital computer simulation of the physical process that underlies these effects. The soft tissue is considered as a viscoelastic medium, and the relaxation theory has been used to calculate the absorption and dispersion data in the tissue. A signal processing technique is developed in this paper to estimate the degradation in range of resolution due to wave absorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, M., Castaneda, B., Wu, Z., Nigwekar, P., Joseph, J. V., Rubens, D. J., & Parker, K. J. (2007). Congruence of imaging estimators and mechanical measurements of viscoelastic properties of soft tissues. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology, 33(10), 1617–1631.
Park, E., & Maniatty, A. M. (2006). Shear modulus reconstruction in dynamic elastography: time harmonic case. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 51, 3697–3721.
Yang, X. Church, C. C. (2006) A simple viscoelastic model for soft tissues in the frequency range 6–20 MHz. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 53, 1404–1411.
Nasseri, S., Bilston, L. E., & Phan-Thien, N. (2002). Viscoelastic properties of pig kidney in shear, experimental results and modelling. Rheologica Acta, 41, 180–192.
Fields, S., & Dunn, F. (1976). Correlation of echographic visualizability of tissue with biological composition and physiological state. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 60, 1409–1412.
Kallel, F., & Ophir, J. (1997). A least-squares estimator for elastography. Ultrasonic Imaging, 19, 195–208.
Alam, S. K., Ophir, J., & Konofagou, E. E. (1998). An adaptive strain estimator for elastography. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 45, 461–472.
Konofagou, E. E., Varghese, T., Ophir, J., & Alam, S. K. (1999). Power spectral strain estimators in elastography. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology, 25(7), 1115–1129.
Varghese, T., Konofagou, E. E., Ophir, J., Alam, S. K., & Bilgen, M. (2000). Direct strain estimation in elastography using spectral cross-correlation. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology, 26(9), 1525–1537.
Céspedes, I., & Ophir, J. (1993). Reduction of image noise in elastography. Ultrasonic Imaging, 15(2), 89–102.
Ophir, J., Alam, S. K., Garra, B., Kallel, F., Konofagou, E., Krouskop, T., & Varghese, T. (1999). Elastography: ultrasonic estimation and imaging of the elastic properties of tissues. Proceedings—Institution of Mechanical Engineers, 213, 203–233.
Gennisson, J.-L., Deffieux, T., Macé, E., Montaldo, G., Fink, M., & Tanter, M. (2010). Viscoelastic and anisotropic mechanical properties of in vivo muscle tissue assessed by supersonic shear imaging. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology, 36(5), 789–801.
Chen, Y. (2010). Acoustical transmission line model for ultrasonic transducers for wide-bandwidth application. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 23(2), 124–134.
Nguyen, V., Naili, S., & Sansalone, V. (2010). Simulation of ultrasonic wave propagation in anisotropic cancellous bone immense in fluid. Wave Motion, 47(2), 117–129.
Nadarajah, S., & Gupta, A. K. (2007). A generalized gamma distribution with application to drought data. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 74, 1–7.
Kak, A. C., & Dines, K. A. (1978). Signal processing of broadband pulsed ultrasound: measurement of attenuation of soft biological tissues. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, BME-25, 321–344.
Ophir, J., & Jaeger, P. (1982). Spectral shifts of ultrasonic propagation through media with nonlinear dispersive attenuation. Ultrasonic Imaging, 4, 282–289.
Obberhettinger, F. (1961). On transient solution of the baffled piston problem. Journal of Research of the National Bureau of Standards, 65-B, 1–6.
Stepanishen, P. R. (1971). Transient radiation from piston in an infinite planar baffle. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 49, 1629–1638.
Lewis, G. K. (1980). A matrix technique for analyzing the performance of multilayer front matched and backed piezoelectric ceramic transducers. Acoustical Imaging, 8, 395.
Ali, M. G. S. (1999). Discrete time model of acoustic waves transmitted through layers. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 224(2), 349.
Matheson, J. (1971). Molecular acoustics. London: Wiley-Interscience.
Pauly, H., & Schwan, H. P. (1971). Mechanism of absorption of ultrasound in liver tissue. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 50, 692–698.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farouk, R.M., Ali, M.G.S. Ultrasonic digital signal processing simulation in viscoelastic medium with generalized parametric function. Telecommun Syst 52, 1449–1456 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9622-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9622-1