Abstract
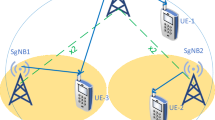
When a MS enters to the WiMAX network, a network entry procedure has to be performed. The aim of procedure is twofold. Firstly, several connections between the MS and BS are created, i.e. basic, primary and secondary management connections to control data transmissions. Secondly, the MS is admitted into the network. According to the IEEE 802.16 standard, a MS always tries to associate to BS with the highest received signal quality. This method is suitable as long as the MS is directly connected to the network via BS. However by introducing relay stations to the WiMAX architecture, the MS entry procedure needs to be modified. Mainly, the point of attachment influences the network performance. This paper proposes an optimized association procedure which takes into account the use of relays stations in the network. The obtained results show improvement of system performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
IEEE Std 802.16-2004 (Oct. 2004). IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks, Part 16: Air interface for fixed broadband wireless access systems.
IEEE Std 802.16e-2005 (Feb. 2006). IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks, Part 16: Air interface for fixed and mobile broadband wireless access systems.
IEEE: IEEE baseline document 802.16j-2006 (2007). Air interface for fixed and mobile broadband wireless access systems: multihop relay specification.
Hoymann, C., & Klagges, K. MAC frame concepts to support multihop communication in IEEE 802.16 networks.
IEEE 802.16j (2007). Baseline document for draft standard for local and metropolitan area networks Part 16: Air interface for fixed and mobile broadband wireless access systems.
Okuda, M., Zhu, C., & Vorel, D. (2008). Multihop relay extension for WiMAX network—overview and benefits of IEEE 802.16j standard. FUJITSU Science Technology Journal, 44(3), 292–302.
Jing, S., Shen, G., & Zang, K. (2007). MS/RS network entry and initialization. Paper no. C802.16j-06/286.
Ge, Y., Tham, C. K., & Kong, P. Y. (2006). A node entry process for IEEE 802.16j multihop relay networks. Paper no. C802.16j-06/211r1.
Chindapol, A., Chui, J., & Xue, Y. (2007). Relay-assisted MS network entry. Paper no. C802.16j-07/125.
Okuda, M., et al. (2007). MS network entry for non-transparent relay station with distributive scheduling. Paper no. C802.16j-07/024r2.
Okuda, M., et al. (2007). MS network entry for non-transparent relay station with centralized scheduling. Paper no. C802.16j-07/008r2.
Okuda, M., et al. (2007). MS network entry for transparent relay station. Paper no. C802.16j-07/001r4.
Ramachandran, S., & Pandey, A. (2007). Routing announcements for network entry support. Paper no. C802.16j-06_158r1.
IST-27675 STP fireworks project deliverable 3D2 (October 2007). Draft specification for the enhanced WMAN and WLAN MAC protocols.
IST-27675 STP Fireworks Project Deliverable 3D1 (April 2007) Design and specification of MAC in relaybased cooperative networks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The paper was originally presented in IWSSIP2008 conference.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mach, P., Bestak, R. & Becvar, Z. Optimization of association procedure in WiMAX networks with relay stations. Telecommun Syst 52, 1697–1704 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9661-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9661-7