Abstract
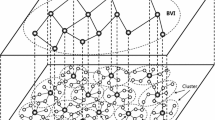
This paper presents a Broadcast and Reliable Coverage based Efficient Recursive Routing (BRCER) in Large-Scale Wireless Sensor Networks for Event-Driven Applications with Mobile Sinks (MSs). For data routing in the network, the proposed protocol updates the connectivity list by using local broadcast and multicast announcement. Instead of broadcasting in the whole network, the local broadcasting is used to save sensor node energy which maximizes the battery lifetime of sensors. However, the multicast announcement provides the appropriate path whenever the event activities are performed by MSs. In addition, reliable communication connectivity among sensor nodes, which depends on the surrounding and the deployment of sensor nodes, is also our prime concern for better quality of service (QoS). The main focus of BRCER protocol is to timely route the data with proper load distribution in the network with reliable connectivity. Theoretical concept and simulation results further validate that BRCER protocol can withstand in worse environmental conditions with effective network performance.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aziz, A. A., Sekercioglu, Y. A., Fitzpatrick, P., & Ivanovich, M. (2013). A survey on distributed topology control techniques for extending the lifetime of battery powered wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 15(1), 121–144.
Pantazis, N. A., Nikolidakis, S. A., & Vergados, D. D. (2013). Energy-efficient routing protocols in wireless sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 15(2), 551–591.
Abbas, M. M., Muhammad, Z., Saleem, K., Saqib, N. A., & Mahmood, H. (2015). Energy harvesting and management in wireless networks for perpetual operations. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, 24(03), 1550041.
Rashid, B., & Rehmani, M. H. (2016). Applications of wireless sensor networks for urban areas: A survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 60, 192–219.
Khattar, N., Sidhu, J., & Singh, J. (2019). Toward energy-efficient cloud computing: A survey of dynamic power management and heuristics-based optimization techniques. The Journal of Supercomputing, 75(8), 4750–4810.
Guo, W., & Zhang, W. (2014). A survey on intelligent routing protocols in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 38, 185–201.
Venkateswarlu, K. M., Kandasamy, A., & Chandrasekaran, K. (2015). An energy-efficient hybrid clustering mechanism for wireless sensor network. Unmanned Systems, 3(02), 109–125.
Masdari, M., & Tanabi, M. (2013). Multipath routing protocols in wireless sensor networks: A survey and analysis. International Journal of Future Generation Communication and Networking, 6(6), 181–192.
Mohamed, R. E., Ghanem, W. R., Khalil, A. T., Elhoseny, M., Sajjad, M., & Mohamed, M. A. (2018). Energy efficient collaborative proactive routing protocol for wireless sensor network. Computer Networks, 142, 154–167.
Xu, L., Collier, R., & O’Hare, G. M. (2017). A survey of clustering techniques in wsns and consideration of the challenges of applying such to 5g iot scenarios. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 4(5), 1229–1249.
Nathalie, M., & David, S.-R. (2013). Wireless sensor and robot networks: From topology control to communication aspects. Singapore: World Scientific.
Sharma, D., Ojha, A., & Bhondekar, A. P. (2018). Heterogeneity consideration in wireless sensor networks routing algorithms: A review. The Journal of Supercomputing, 75(5), 2341–2394.
Liu, N., Pan, J.-S., et al. (2019). A bi-population quasi-affine transformation evolution algorithm for global optimization and its application to dynamic deployment in wireless sensor networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2019(1), 175.
Tashtarian, F., Moghaddam, M. H. Y., Sohraby, K., & Effati, S. (2015). On maximizing the lifetime of wireless sensor networks in event-driven applications with mobile sinks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 64(7), 3177–3189.
Mahmood, M. A., Seah, W. K., & Welch, I. (2015). Reliability in wireless sensor networks: A survey and challenges ahead. Computer Networks, 79, 166–187.
Bellalta, B., Bononi, L., Bruno, R., & Kassler, A. (2016). Next generation ieee 802.11 wireless local area networks: Current status, future directions and open challenges. Computer Communications, 75, 1–25.
Tanwar, S., Kumar, N., & Rodrigues, J. J. (2015). A systematic review on heterogeneous routing protocols for wireless sensor network. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 53, 39–56.
Arora, V. K., Sharma, V., & Sachdeva, M. (2016). A survey on leach and other’s routing protocols in wireless sensor network. Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 127(16), 6590–6600.
Yu, Y., Krishnamachari, B., & Kumar, V. P. (2006). Information processing and routing in wireless sensor networks. Singapore: World Scientific.
Liu, X. (2015). Atypical hierarchical routing protocols for wireless sensor networks: A review. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(10), 5372–5383.
Afsar, M. M., & Tayarani-N, M.-H. (2014). Clustering in sensor networks: A literature survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 46, 198–226.
Krishna, P., Vaidya, N. H., Chatterjee, M., & Pradhan, D. K. (1997). A cluster-based approach for routing in dynamic networks. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 27(2), 49–64.
McDonald, A. B., & Znati, T. F. (2001). Design and performance of a distributed dynamic clustering algorithm for ad-hoc networks. In Proceedings 34th Annual Simulation Symposium, 2001, pp. 27–35. IEEE.
Gu, Y., Ren, F., Ji, Y., & Li, J. (2016). The evolution of sink mobility management in wireless sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 18(1), 507–524.
Fadel, E., Gungor, V. C., Nassef, L., Akkari, N., Malik, M. A., Almasri, S., et al. (2015). A survey on wireless sensor networks for smart grid. Computer Communications, 71, 22–33.
Ovsthus, K., Kristensen, L. M., et al. (2014). An industrial perspective on wireless sensor networks—a survey of requirements, protocols, and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 16(3), 1391–1412.
Royer, E. M., & Perkins, C. E. (1999). Multicast operation of the ad-hoc on-demand distance vector routing protocol. In: Proceedings of the 5th annual ACM/IEEE international conference on Mobile computing and networking. ACM, pp. 207–218.
Perkins, C., Belding-Royer, E., & Das, S. (2003). Ad hoc on-demand distance vector (aodv) routing. Technical Report.
Vaishampayan, R., & Garcia-Luna-Aceves, J. J. (2004). Efficient and robust multicast routing in mobile ad hoc networks. In 2004 IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Systems. IEEE, pp. 304–313.
Abdulwahid, H., Dai, B., Huang, B., & Chen, Z. (2016). Scheduled-links multicast routing protocol in manets. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 63, 56–67.
Biradar, R. C., & Manvi, S. S. (2012). Review of multicast routing mechanisms in mobile ad hoc networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 35(1), 221–239.
Garcia-Luna-Aceves, J., & Menchaca-Mendez, R. (2011). Prime: An interest-driven approach to integrated unicast and multicast routing in manets. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 19(6), 1573–1586.
Valera, A. C., Soh, W.-S., & Tan, H.-P. (2014). Survey on wakeup scheduling for environmentally-powered wireless sensor networks. Computer Communications, 52, 21–36.
Moss, D., & Levis, P. (2008). Box-macs: Exploiting physical and link layer boundaries in low-power networking. Computer Systems Laboratory Stanford University, 64(66), 120.
Polastre, J., Hill, J., & Culler, D. (2004). Versatile low power media access for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on Embedded networked sensor systems. ACM, pp. 95–107.
Buettner, M., Yee, G. V., Anderson, E., & Han, R. (2006) X-mac: a short preamble mac protocol for duty-cycled wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 4th international conference on Embedded networked sensor systems. ACM, pp. 307–320.
Sun, Y., Gurewitz, O., & Johnson, D. B. (2008). Ri-mac: a receiver-initiated asynchronous duty cycle mac protocol for dynamic traffic loads in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM conference on Embedded network sensor systems. ACM, pp. 1–14.
Huang, P., Wang, C., Xiao, L., & Chen, H. (2010). Rc-mac: A receiver-centric medium access control protocol for wireless sensor networks. In 2010 18th International Workshop on Quality of Service (IWQoS). IEEE, pp. 1–9.
Nguyen, K., Nguyen, V.-H., Le, D.-D., Ji, Y., Duong, D. A., & Yamada, S. (2014). A receiver-initiated mac protocol for energy harvesting sensor networks. In Ubiquitous information technologies and applications. Springer, pp. 603–610.
Djenouri, D., & Bagaa, M. (2016). Synchronization protocols and implementation issues in wireless sensor networks: A review. IEEE Systems Journal, 10(2), 617–627.
Luo, H., Ye, F., Cheng, J., Lu, S., & Zhang, L. (2005). Ttdd: Two-tier data dissemination in large-scale wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 11(1–2), 161–175.
Hamida, E. B., & Chelius, G. (2008). A line-based data dissemination protocol for wireless sensor networks with mobile sink. In Communications,. . ICC’08. IEEE International Conference on Communications, 2008. ICC’08. IEEE, pp. 2201–2205.
Liu, X., Zhao, H., Yang, X., & Li, X. (2013). Sinktrail: A proactive data reporting protocol for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 62(1), 151–162.
Saputro, N., Akkaya, K., & Uludag, S. (2012). A survey of routing protocols for smart grid communications. Computer Networks, 56(11), 2742–2771.
Reina, D., Toral, S., Johnson, P., & Barrero, F. (2015). A survey on probabilistic broadcast schemes for wireless ad hoc networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 25, 263–292.
Malathi, A., & Sreenath, N. (2017). Multicast routing selection for vanet using hybrid scatter search abc algorithm. In 2017 IEEE International Conference on Power, Control, Signals and Instrumentation Engineering (ICPCSI). IEEE, pp. 441–446.
Sajwan, M., Gosain, D., & Sharma, A. K. (2018). Hybrid energy-efficient multi-path routing for wireless sensor networks. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 67, 96–113.
Lafetá, T., Bueno, M. L., Brasil, C., & Oliveira, G. M. (2018). Meands: A many-objective evolutionary algorithm based on non-dominated decomposed sets applied to multicast routing. Applied Soft Computing, 62, 851–866.
Clausen, T., Cordero, J.-A., Yi, J., & Igarashi, Y. (2018). Use’em or lose’em: On unidirectional links in reactive routing protocols. Ad Hoc Networks, 73, 51–64.
Younis, M., Senturk, I. F., Akkaya, K., Lee, S., & Senel, F. (2014). Topology management techniques for tolerating node failures in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Computer Networks, 58, 254–283.
Abbasi, A. A., Younis, M. F., & Baroudi, U. A. (2012). A least-movement topology repair algorithm for partitioned wireless sensor–actor networks. International Journal of Sensor Networks, 11(4), 250–262.
Tamboli, N., & Younis, M. (2010). Coverage-aware connectivity restoration in mobile sensor networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 33(4), 363–374.
Zin, S. M., Anuar, N. B., Kiah, M. L. M., & Ahmedy, I. (2015). Survey of secure multipath routing protocols for wsns. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 55, 123–153.
Rault, T., Bouabdallah, A., & Challal, Y. (2014). Energy efficiency in wireless sensor networks: A top-down survey. Computer Networks, 67, 104–122.
Sun, W., Yang, Z., Zhang, X., & Liu, Y. (2014). Energy-efficient neighbor discovery in mobile ad hoc and wireless sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 16(3), 1448–1459.
Heinzelman, W. B., Chandrakasan, A. P., & Balakrishnan, H. (2002). An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 1(4), 660–670.
De Rango, F., Palmieri, N., & Ranieri, S. (2015). Spatial correlation based low energy aware clustering (leach) in a wireless sensor networks. Advances in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 13(4), 350–358.
Qing, L., Zhu, Q., & Wang, M. (2006). Design of a distributed energy-efficient clustering algorithm for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Computer Communications, 29(12), 2230–2237.
Wang, M.-Y., Ding, J., Chen, W.-P., & Guan, W.-Q. (2015). Search: A stochastic election approach for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 19(3), 443–446.
Li, C., Bai, J., Gu, J., Yan, X., & Luo, Y. (2018). Clustering routing based on mixed integer programming for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 72, 81–90.
Kong, L., Pan, J.-S., Tsai, P.-W., Vaclav, S., & Ho, J.-H. (2015). A balanced power consumption algorithm based on enhanced parallel cat swarm optimization for wireless sensor network. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 11(3), 729680.
Zhen, H., Li, Y., & Zhang, G.-J. (2013). Efficient and dynamic clustering scheme for heterogeneous multi-level wireless sensor networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 39(4), 454–460.
Baranidharan, B., & Santhi, B. (2016). Ducf: Distributed load balancing unequal clustering in wireless sensor networks using fuzzy approach. Applied Soft Computing, 40, 495–506.
Gupta, P., & Sharma, A. K. (2019). Clustering-based heterogeneous optimized-heed protocols for wsns. Soft Computing, 24(3), 1737–1761.
Chand, S., Singh, S., & Kumar, B. (2014). Heterogeneous heed protocol for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 77(3), 2117–2139.
Gupta, P., & Sharma, A. K. (2019). Clustering-based optimized heed protocols for wsns using bacterial foraging optimization and fuzzy logic system. Soft Computing, 23(2), 507–526.
de Oliveira Brante, G. G., Kakitani, M. T., & Souza, R. D. (2011). Energy efficiency analysis of some cooperative and non-cooperative transmission schemes in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 59(10), 2671–2677.
Memsic, M. (2012). Andover and USA, “iris sensor nodes,” Oct. 11, 2012 [online]. http://www.memsic.com/products/wireless-sensor-netwroks/wireless-modules.html.
Perlman, R. (1985). An algorithm for distributed computation of a spanningtree in an extended lan. In ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, vol. 15, no. 4. ACM, pp. 44–53.
M. M. Afsar and M.-H. Tayarani-N, “A. goldsmith, wireless communications, 1st edition. cambridge uni- versity press, 2005,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 46, pp. 198–226, 2014.
Kumar, S., Saini, M. L., & Kumar, S. (2020). Improved dymo-based aco for manet using distance and density of nodes. In Microservices in Big Data Analytics. Springer, pp. 29–38.
Kolandaisamy, R., Noor, R. M., Z’aba, M. R., Ahmedy, I., & Kolandaisamy, I. (2019). Adapted stream region for packet marking based on ddos attack detection in vehicular ad hoc networks. The Journal of Supercomputing, pp. 1–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in the proposed manuscript as the publication is concerned.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, A., Kumar, S., Gautam, P.R. et al. Broadcast and Reliable Coverage based Efficient Recursive Routing in Large-Scale WSNs. Telecommun Syst 75, 63–78 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-020-00679-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-020-00679-5