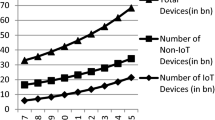
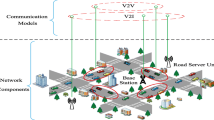
Abstract
Internet of Energy (IoE) provides two-way communication for reform of energy utilization between service providers and consumers. To provide secure, efficient, and reliable operations in IoE should be protected from cyber-attacks. Many frameworks have been proposed so far to address security and privacy concerns of these systems. In the vehicle-grid system, we propose a useful mutual authenticated key agreement framework using elliptic curve cryptography and hash function. The aim of the proposed protocol is to maintain secure communication between vehicles and the grid system with reliable computation and communication costs. In the proposed protocol, a vehicular user securely access services that are provided by the grid server. We prove the security of the proposed framework in formal and informal ways. We also show the correctness of the mutual authentication and key agreement of this framework by using Burrows–Abadi–Needham logic. We provide formal security verification of the proposed protocol by using AVISPA tool. Further, we show that this work is better in terms of computation and communication costs compare to other related protocols in the same environment. As a result, the proposed framework is a real life-application in this system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, W.-Z., Elgendy, I. A., Hammad, M., Iliyasu, A. M., Du, X., Guizani, M., & Abd El-Latif, A. A. (2020). Secure and optimized load balancing for multitier IoT and edge-cloud computing systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(10), 8119–8132.
Abou-Nassar, E. M., Iliyasu, A. M., El-Kafrawy, P. M., Song, O.-Y., Bashir, A. K., & Abd El-Latif, A. A. (2020). Ditrust chain: Towards blockchain-based trust models for sustainable healthcare IoT systems. IEEE Access, 8, 111223–111238.
Mirsadeghi, F., Rafsanjani, M. K., & Gupta, B. B. (2020). A trust infrastructure based authentication method for clustered vehicular ad hoc networks. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications., 14, 2537–2553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-020-01010-4
Stergiou, C. L., Psannis, K. E., & Gupta, B. B. (2020). Iot-based big data secure management in the fog over a 6g wireless network. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(7), 5164–5171.
Abd El-Latif, A. A., Abd-El-Atty, B., Venegas-Andraca, S. E., Elwahsh, H., Piran, M. J., Bashir, A. K., et al. (2020). Providing end-to-end security using quantum walks in IoT networks. IEEE Access, 8, 92687–92696.
Gad, R., Talha, M., Abd El-Latif, A. A., Zorkany, M., Ayman, E.-S., Nawal, E.-F., & Muhammad, G. (2018). Iris recognition using multi-algorithmic approaches for cognitive internet of things (CIoT) framework. Future Generation Computer Systems, 89, 178–191.
Mishra, A., Gupta, N., & Gupta, B. (2021). Defense mechanisms against DDoS attack based on entropy in SDN-cloud using pox controller. Telecommunication Systems, 77(1), 47–62.
Zhou, K., Yang, S., & Shao, Z. (2016). Energy internet: The business perspective. Applied Energy, 178, 212–222.
Gupta, B., & Quamara, M. (2020). An overview of internet of things (IoT): Architectural aspects, challenges, and protocols. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 32, e4946.
Gungor, V. C., Sahin, D., Kocak, T., Ergut, S., Buccella, C., Cecati, C., & Hancke, G. P. (2012). A survey on smart grid potential applications and communication requirements. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 9, 28–42.
Gharavi, H., & Ghafurian, R. (2011). Smart grid: The electric energy system of the future (Vol. 99). IEEE.
Abd El-Latif, A. A., Abd-El-Atty, B., Mehmood, I., Muhammad, K., Venegas-Andraca, S. E., & Peng, J. (2021). Quantum-inspired blockchain-based cybersecurity: Securing smart edge utilities in IoT-based smart cities. Information Processing & Management, 58, 102549.
Li, D., Deng, L., Gupta, B. B., Wang, H., & Choi, C. (2019). A novel CNN based security guaranteed image watermarking generation scenario for smart city applications. Information Sciences, 479, 432–447.
Sani, A. S., Yuan, D., Jin, J., Gao, L., Yu, S., & Dong, Z. Y. (2019). Cyber security framework for internet of things-based energy internet. Future Generation Computer Systems, 93, 849–859.
Aggarwal, S., Kumar, N., & Gope, P. (2021). An efficient blockchain-based authentication scheme for energy-trading in v2g networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 17(10), 6971–6980. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.3030949
Dong, Z. (2016). Towards an intelligent future energy grid. New South Wales: The University of Sydney.
Canetti, R., & Krawczyk, H. (2001). Analysis of key-exchange protocols and their use for building secure channels. In International conference on the theory and applications of cryptographic techniques (pp. 453–474). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44987-6_28
Wu, D., & Zhou, C. (2011). Fault-tolerant and scalable key management for smart grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2, 375–381.
Xia, J., & Wang, Y. (2012). Secure key distribution for the smart grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 3, 1437–1443.
Nicanfar, H., & Leung, V. C. (2013). Multilayer consensus ECC-based password authenticated key-exchange (MCEPAK) protocol for smart grid system. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 4, 253–264.
Park, J. H., Kim, M., & Kwon, D. (2013). Security weakness in the smart grid key distribution scheme proposed by Xia and Wang. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 4, 1613–1614.
Odelu, V., Das, A. K., Wazid, M., & Conti, M. (2016). Provably secure authenticated key agreement scheme for smart grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 9, 1900–1910.
Tsai, J.-L., & Lo, N.-W. (2016). Secure anonymous key distribution scheme for smart grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 7, 906–914.
Chen, Y., Martínez, J.-F., Castillejo, P., & López, L. (2017). An anonymous authentication and key establish scheme for smart grid: Fauth. Energies, 10, 1354.
Gope, P., & Sikdar, B. (2018). Privacy-aware authenticated key agreement scheme for secure smart grid communication. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 10, 3953–3962.
Mohammadali, A., Haghighi, M. S., Tadayon, M. H., & Mohammadi-Nodooshan, A. (2016). A novel identity-based key establishment method for advanced metering infrastructure in smart grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 9, 2834–2842.
Gope, P., & Sikdar, B. (2019). An efficient privacy-preserving authentication scheme for energy internet-based vehicle-to-grid communication. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 10, 6607–6618.
Li, X., Wu, F., Kumari, S., Xu, L., Sangaiah, A. K., & Choo, K.-K.R. (2019). A provably secure and anonymous message authentication scheme for smart grids. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 132, 242–249.
Mahmood, K., Chaudhry, S. A., Naqvi, H., Kumari, S., Li, X., & Sangaiah, A. K. (2018). An elliptic curve cryptography based lightweight authentication scheme for smart grid communication. Future Generation Computer Systems, 81, 557–565.
He, D., Wang, H., Khan, M. K., & Wang, L. (2016). Lightweight anonymous key distribution scheme for smart grid using elliptic curve cryptography. IET Communications, 10, 1795–1802.
Khan, A. A., Kumar, V., Ahmad, M., & Rana, S. (2021). Lakaf: Lightweight authentication and key agreement framework for smart grid network. Journal of Systems Architecture, 116, 102053.
Yang, Z., Yu, S., Lou, W., & Liu, C. (2011). Privacy-preserving communication and precise reward architecture for v2g networks in smart grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2, 697–706.
Guo, H., Wu, Y., Bao, F., Chen, H., & Ma, M. (2011). Ubapv2g: A unique batch authentication protocol for vehicle-to-grid communications. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2, 707–714.
Abdallah, A., & Shen, X. S. (2016). Lightweight authentication and privacy-preserving scheme for v2g connections. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66, 2615–2629.
Tanveer, M., Zahid, A. H., Ahmad, M., Baz, A., & Alhakami, H. (2020). Lake-IoD: Lightweight authenticated key exchange protocol for the internet of drone environment. IEEE Access, 8, 155645–155659.
Luo, M., Chang, X., Nie, L., Yang, Y., Hauptmann, A. G., & Zheng, Q. (2017a). An adaptive semisupervised feature analysis for video semantic recognition. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 48, 648–660.
Luo, M., Nie, F., Chang, X., Yang, Y., Hauptmann, A. G., & Zheng, Q. (2017b). Adaptive unsupervised feature selection with structure regularization. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 29, 944–956.
Stallings, W. (2006). Cryptography and Network Security, 4/E, Pearson Education India.
Kumari, A., Yahya Abbasi, M., Kumar, V., & Khan, A. A. (2019). A secure user authentication protocol using elliptic curve cryptography. Journal of Discrete Mathematical Sciences and Cryptography, 22, 521–530.
Khan, A. A., Kumar, V., & Ahmad, M. (2019). An elliptic curve cryptography based mutual authentication scheme for smart grid communications using biometric approach. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2019.04.013
Stinson, D. R. (2006). Some observations on the theory of cryptographic hash functions. Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 38, 259–277.
Kumar, V., Jangirala, S., & Ahmad, M. (2018). An efficient mutual authentication framework for healthcare system in cloud computing. Journal of Medical Systems, 42, 1–25.
Wang, W., Huang, H., Zhang, L., & Su, C. (2021). Secure and efficient mutual authentication protocol for smart grid under blockchain. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 14(5), 2681–2693.
Abbasinezhad-Mood, D., & Nikooghadam, M. (2018). An anonymous ECC-based self-certified key distribution scheme for the smart grid. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 65, 7996–8004.
Islam, S. H. (2014). Provably secure dynamic identity-based three-factor password authentication scheme using extended chaotic maps. Nonlinear Dynamics, 78, 2261–2276.
Khan, A. A., Kumar, V., Ahmad, M., Rana, S., & Mishra, D. (2020). Palk: Password-based anonymous lightweight key agreement framework for smart grid. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 121, 106121.
Chaudhry, S. A., Naqvi, H., Sher, M., Farash, M. S., & Hassan, M. U. (2017). An improved and provably secure privacy preserving authentication protocol for sip. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 10, 1–15.
Burrows, M., Abadi, M., & Needham, R. M. (1989). A logic of authentication. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 426, 233–271.
Chaturvedi, A., Mishra, D., & Mukhopadhyay, S. (2017). An enhanced dynamic id-based authentication scheme for telecare medical information systems. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 29, 54–62.
Kumar, V., Ahmad, M., Mishra, D., Kumari, S., & Khan, M. K. (2020). Rseap: Rfid based secure and efficient authentication protocol for vehicular cloud computing. Vehicular Communications, 22, 100213.
Armando, A., Basin, D., Cuellar, J., Rusinowitch, M., & Viganó, L. (2006). Avispa: automated validation of internet security protocols and applications. ERCIM News,64, 76
Armando, A., Basin, D., Boichut, Y., Chevalier, Y., Compagna, L., Cuéllar, J., Drielsma, P. H., Héam, P.-C. , Kouchnarenko, O., Mantovani, J., et al. (2005). The avispa tool for the automated validation of internet security protocols and applications. In International conference on computer aided verification (pp. 281–285). Springer, Berlin.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thanks Editor-in-Chief: Prof. Muhammad Khurram Khan and anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and valuable suggestions that have resulted in the improvement of this manuscript. The author acknowledges Dr. Iftikhar and Dr. Aisha Jabeen, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi for valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A.A., Kumar, V., Ahmad, M. et al. A secure and efficient key agreement framework for critical energy infrastructure using mobile device. Telecommun Syst 78, 539–557 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-021-00826-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-021-00826-6