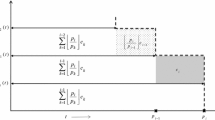
Abstract
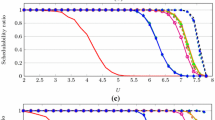
A schedulability test is derived for the global Earliest Deadline Zero Laxity (EDZL) scheduling algorithm on a platform with multiple identical processors. The test is sufficient, but not necessary, to guarantee that a system of independent sporadic tasks with arbitrary deadlines will be successfully scheduled, with no missed deadlines, by the multiprocessor EDZL algorithm. Global EDZL is known to be at least as effective as global Earliest-Deadline-First (EDF) in scheduling task sets to meet deadlines. It is shown, by testing on large numbers of pseudo-randomly generated task sets, that the combination of EDZL and the new schedulability test is able to guarantee that far more task sets meet deadlines than the combination of EDF and known EDF schedulability tests.
In the second part of the paper, an improved version of the EDZL-schedulability test is presented. This new algorithm is able to efficiently exploit information on the slack values of interfering tasks, to iteratively refine the estimation of the interference a task can be subjected to. This iterative algorithm is shown to have better performance than the initial test, in terms of schedulable task sets detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker TP (2003) Multiprocessor EDF and deadline monotonic schedulability analysis. In: Proc of the 24th IEEE real-time systems symposium, Cancun, Mexico, pp 120–129
Baker TP (2006) A comparison of global and partitioned EDF schedulability tests for multiprocessors. In: International conf on real-time and network systems, Poitiers, France, pp 119–127
Baker TP, Cirinei M (2006) A necessary and sometimes sufficient condition for the feasibility of sets of sporadic hard-deadline tasks. In: Proc of the 27th IEEE real-time systems symposium, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Baker TP, Cirinei M (2007) Brute-force determination of multiprocessor schedulability for sets of sporadic hard-deadline tasks. In: Principles of distributed systems, 11th int conf, OPODIS 2007, Guadeloupe, French West Indies. Springer, Berlin, pp 62–75
Bertogna M, Cirinei M, Lipari G (2005) Improved schedulability analysis of EDF on multiprocessor platforms. In: Proc of the 17th Euromicro conference on real-time systems, Palma de Mallorca, Spain, pp 209–218
Cho S, Lee S-K, Han A, Lin K-J (2002) Efficient real-time scheduling algorithms for multiprocessor systems. IEICE Trans Commun E 85-B(12):2859–2867
Cirinei M (2007) Exploiting the power of multiprocessors for real-time systems. PhD thesis, Scuola Superiore S Anna, Pisa, Italy
Cirinei M, Baker TP (2007) EDZL scheduling analysis. In: Proc EuroMicro conference on real-time systems, to appear
Goossens J, Funk S, Baruah S (2003) Priority-driven scheduling of periodic task systems on multiprocessors. Real Time Syst 25(2–3):187–205
Ha R (1995) Validating timing constraints in multiprocessor and distributed systems. PhD thesis, Dept of Computer Science, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, IL
Ha R, Liu JWS (1994) Validating timing constraints in multiprocessor and distributed real-time systems. In: Proc of the 14th IEEE international conf on distributed computing systems, Poznan, Poland. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, pp 162–171
Park M, Han S, Kim H, Cho S, Cho Y (2005) Comparison of deadline-based scheduling algorithms for periodic real-time tasks on multiprocessor. IEICE Trans Inf Syst E 88-D(3):658–661
Piao X, Han S, Kim H, Park M, Cho Y, Cho S (2006) Predictability of earliest deadline zero laxity algorithm for multiprocessor real time systems. In: Proc of the 9th IEEE international symposium on object and component-oriented real-time distributed computing, Gjeongju, Korea
Sprunt B, Sha L, Lehoczky L (1989) Aperiodic task scheduling for hard real-time systems. Real-Time Syst 1(1):27–60
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This is an extended version of the ECRTS’07 paper of Cirinei and Baker (2007), with corrections of some flaws in that original paper and a new iterative schedulability test based on Cirinei (2007).
This material is based upon work supported in part by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 0509131, and a DURIP grant from the Army Research Office.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baker, T.P., Cirinei, M. & Bertogna, M. EDZL scheduling analysis. Real-Time Syst 40, 264–289 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11241-008-9061-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11241-008-9061-6