Abstract
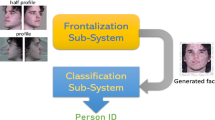
Extreme pose variation is one of the key obstacles to accurate face recognition in practice. Compared with current techniques for pose-invariant face recognition, which either expect pose invariance from hand-crafted features or data-driven deep learning solutions, or first normalize profile face images to frontal pose before feature extraction, we argue that it is more desirable to perform both tasks jointly to allow them to benefit from each other. To this end, we propose a Pose-Invariant Model (PIM) for face recognition in the wild, with three distinct novelties. First, PIM is a novel and unified deep architecture, containing a Face Frontalization sub-Net (FFN) and a Discriminative Learning sub-Net (DLN), which are jointly learned from end to end. Second, FFN is a well-designed dual-path Generative Adversarial Network which simultaneously perceives global structures and local details, incorporating an unsupervised cross-domain adversarial training and a meta-learning (“learning to learn”) strategy using siamese discriminator with dynamic convolution for high-fidelity and identity-preserving frontal view synthesis. Third, DLN is a generic Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for face recognition with our enforced cross-entropy optimization strategy for learning discriminative yet generalized feature representations with large intra-class affinity and inter-class separability. Qualitative and quantitative experiments on both controlled and in-the-wild benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model over the state-of-the-arts.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
“Near frontal” faces are almost equally visible for both sides and their yaw angles are within \(10^\circ \) from the frontal view.
We define a “near profile” pose as one that obscures many features, specifically the second eye. This roughly corresponds to the yaw angle greater than 60 degrees.
The DLN is not restricted to a certain network architecture. Advanced networks can be deployed for high performance.
Cross-domain adversarial training is optional; if there is no need to do domain adaptation, simply set \(\lambda _1\)=0.
For profile face images with large yaw angles, OpenPose may fail to locate both eyes. In such cases, we use the detected eye after center cropping as the input left/right eye patch.
The results on the profile (original) images serve as our baseline.
Each pixel in the feature map has a very large receptive field, without one-to-one correspondence with the input RGB face image nor the recovered frontal-view face image. The backbone of DLN is initialized with Light CNN-29 (Wu et al. 2015) and pre-trained on MS-Celeb-1M (Guo et al. 2016) (large-scale dataset for face recognition) and finetuned on the target dataset. Thus, the network has achieved sufficient robustness against background variance, which will focus on the facial region during recognition.
References
AbdAlmageed, W., Wu, Y., Rawls, S., Harel, S., Hassner, T., Masi, I., et al. (2016). Face recognition using deep multi-pose representations. In WACV (pp. 1–9).
Ahonen, T., Hadid, A., & Pietikainen, M. (2006). Face description with local binary patterns: Application to face recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 28(12), 2037–2041.
Berthelot, D., Schumm, T., & Metz, L. (2017) Began: Boundary equilibrium generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.10717.
Bertinetto, L., Henriques, J. F., Valmadre, J., Torr, P., & Vedaldi, A. (2016). Learning feed-forward one-shot learners. In NeurIPS (pp. 523–531).
Bowyer, K. W., Chang, K., & Flynn, P. (2006). A survey of approaches and challenges in 3d and multi-modal 3d+ 2d face recognition. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 101(1), 1–15.
Cao, J., Hu, Y., Zhang, H., He, R., & Sun, Z. (2018). Learning a high fidelity pose invariant model for high-resolution face frontalization. In NeurIPS (pp. 2867–2877).
Chen, D., Cao, X., Wen, F., & Sun, J. (2013). Blessing of dimensionality: High-dimensional feature and its efficient compression for face verification. In CVPR (pp. 3025–3032).
Chen, J.-C., Zheng, J., Patel, V. M., & Chellappa, R. (2016). Fisher vector encoded deep convolutional features for unconstrained face verification. In ICIP (pp. 2981–2985).
Chen, W., Liu, T.-Y., Lan, Y., Ma, Z.-M., & Li, H. (2009). Ranking measures and loss functions in learning to rank. In NeurIPS (pp. 315–323).
Dalal, N., & Triggs, B. (2005). Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In CVPR (pp. 886–893).
Daugman, J. G. (1985). Uncertainty relation for resolution in space, spatial frequency, and orientation optimized by two-dimensional visual cortical filters. JOSA A, 2(7), 1160–1169.
Dave, R., Vyas, A., Mojidra, S., Desai, P., & Nikita, P. (2018). Face recognition techniques: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.07288.
Ding, C., & Tao, D. (2017). Pose-invariant face recognition with homography-based normalization. Pattern Recognition, 66, 144–152.
Freiwald, W. A., & Tsao, D. Y. (2010). Functional compartmentalization and viewpoint generalization within the macaque face-processing system. Science, 330(6005), 845–851.
Ganin, Y., Ustinova, E., Ajakan, H., Germain, P., Larochelle, H., Laviolette, F., et al. (2016). Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 17(59), 1–35.
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., et al. (2014). Generative adversarial nets. in NeurIPS, 2672–2680.
Gross, R., Matthews, I., Cohn, J., Kanade, T., & Baker, S. (2010). Multi-pie. Image and Vision Computing, 28(5), 807–813.
Guo, Y., Zhang, L., Hu, Y., He, X., & Gao, J. (2016). Ms-celeb-1m: A dataset and benchmark for large-scale face recognition. In ECCV (pp. 87–102).
Hao, S., Wang, W., Ye, Y., Nie, T., & Bruzzone, L. (2017). Two-stream deep architecture for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 56(4), 2349–2361.
Hassner, T., Harel, S., Paz, E., & Enbar, R. (2015). Effective face frontalization in unconstrained images. In CVPR (pp. 4295–4304).
Hassner, T., Masi, I., Kim, J., Choi, J., Harel, S., Natarajan, P., et al. (2016). Pooling faces: template based face recognition with pooled face images. in CVPRW (pp. 59–67).
Hu, Y., Wu, X., Yu, B., He, R., & Sun, Z. (2018). Pose-guided photorealistic face rotation. In CVPR (pp. 8398–8406).
Huang, G. B., Ramesh, M., Berg, T., & Learned-Miller, E. (2007). Labeled faces in the wild: A database for studying face recognition in unconstrained environments (pp. 07–49). University of Massachusetts, Amherst, Tech. Rep.
Huang, R., Zhang, S., Li, T., & He, R. (2017). “Beyond face rotation: Global and local perception gan for photorealistic and identity preserving frontal view synthesis,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04086.
Kan, M., Shan, S., Chang, H., & Chen, X. (2014). Stacked progressive auto-encoders (spae) for face recognition across poses. in CVPR, 1883–1890.
Kang, B.-N., & Kim, D. (2013). Face identification using affine simulated dense local descriptors. In URAI (pp. 346–351).
Kingma, D. P., & Welling, M. (2013). Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6114.
Klare, B. F., Klein, B., Taborsky, E., Blanton, A., Cheney, J., Allen, K., et al. (2015). Pushing the frontiers of unconstrained face detection and recognition: Iarpa janus benchmark a. In CVPR (pp. 1931–1939).
LeCun, Y. (1997). The mnist database of handwritten digits. http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/.
Liu, W., Wen, Y., Yu, Z., Li, M., Raj, B., & Song, L. (2017). Sphereface: Deep hypersphere embedding for face recognition. In CVPR (pp. 6738–6746).
Maaten, L. v d, & Hinton, G. (2008). Visualizing data using t-SNE. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 9(Nov), 2579–2605.
Masi, I., Rawls, S., Medioni, G., & Natarajan, P. (2016). Pose-aware face recognition in the wild. In CVPR (pp. 4838–4846).
Masi, I., Tran, A. T., Leksut, J. T., Hassner, T., & Medioni, G. (2016). Do we really need to collect millions of faces for effective face recognition?. arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.07057.
Mirza, M., & Osindero, S. (2014). Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.1784.
Ohayon, S., Freiwald, W. A., & Tsao, D. Y. (2012). What makes a cell face selective? The importance of contrast. Neuron, 74(3), 567–581.
Parkhi, O. M., Vedaldi, A., & Zisserman, A. (2015). Deep face recognition. In BMVC.
Ranjan, R., Sankaranarayanan, S., Castillo, C. D., & Chellappa, R. (2016). An all-in-one convolutional neural network for face analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.00851.
Rezende, D. J., Mohamed, S., & Wierstra, D. (2014). Stochastic backpropagation and approximate inference in deep generative models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1401.4082.
Sagonas, C., Panagakis, Y., Zafeiriou, S., & Pantic, M. (2015). Robust statistical face frontalization. In ICCV (pp. 3871–3879).
Sankaranarayanan, S., Alavi, A., Castillo, C. D., & Chellappa, R. (2016). Triplet probabilistic embedding for face verification and clustering. In BTAS (pp. 1–8).
Schroff, F., Kalenichenko, D., & Philbin, J. (2015). Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In CVPR (pp. 815–823).
Sengupta, S., Chen, J.-C., Castillo, C., Patel, V. M., Chellappa, R., & Jacobs, D. W. (2016). Frontal to profile face verification in the wild. In WACV (pp. 1–9).
Simon, T., Joo, H., Matthews, I., & Sheikh, Y. (2017). Hand keypoint detection in single images using multiview bootstrapping. In CVPR.
Simonyan, K., Parkhi, O. M., Vedaldi, A., & Zisserman, A. (2013). Fisher vector faces in the wild. In BMVC.
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2014). “Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556.
Sun, Y., Liang, D., Wang, X., & Tang, X. (2015). Deepid3: Face recognition with very deep neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1502.00873.
Sun, Y., Wang, X., & Tang, X. (2015). Deeply learned face representations are sparse, selective, and robust. In CVPR (pp. 2892–2900).
Taigman, Y., Yang, M., Ranzato, M., & Wolf, L. (2014). Deepface: Closing the gap to human-level performance in face verification. In CVPR (pp. 1701–1708).
Taigman, Y., Yang, M., Ranzato, M., & Wolf, L. (2015). Web-scale training for face identification. In CVPR (pp. 2746–2754).
Tran, L., Yin, X., & Liu, X. (2017). Disentangled representation learning gan for pose-invariant face recognition. In CVPR.
Wang, D., Otto, C., & Jain, A. K. (2015). Face search at scale: 80 million gallery. arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.07242.
Wang, W., Tulyakov, S., & Sebe, N. (2018). Recurrent convolutional shape regression. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 40(11), 2569–2582.
Wang, W., Yan, Y., Cui, Z., Feng, J., Yan, S., & Sebe, N. (2018). Recurrent face aging with hierarchical autoregressive memory. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 41(3), 654–668.
Weinberger, K. Q., & Saul, L. K. (2009). Distance metric learning for large margin nearest neighbor classification. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 10(Feb), 207–244.
Wen, Y., Zhang, K., Li, Z., & Qiao, Y. (2016). A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In ECCV (pp. 499–515).
Wu, X., He, R., Sun, Z., & Tan, T. (2015). A light cnn for deep face representation with noisy labels. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.02683.
Xiao, S., Feng, J., Xing, J., Lai, H., Yan, S., & Kassim, A. (2016). Robust facial landmark detection via recurrent attentive-refinement networks. In ECCV (pp. 57–72).
Xiao, S., Liu, L., Nie, X., Feng, J., Kassim, A. A., & Yan, S. (2016). A live face swapper. In ACM MM (pp. 691–692).
Xiong, C., Zhao, X., Tang, D., Jayashree, K., Yan, S., & Kim, T.-K. (2015). Conditional convolutional neural network for modality-aware face recognition. in ICCV, 3667–3675.
Yim, J., Jung, H., Yoo, B., Choi, C., Park, D., & Kim, J. (2015). Rotating your face using multi-task deep neural network. In CVPR (pp. 676–684).
Yin, X., & Liu, X. (2017). Multi-task convolutional neural network for pose-invariant face recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 27, 964–975.
Zhao, J., Cheng, Y., Cheng, Y., Yang, Y., Zhao, F., Li, J., et al. (2019). Look across elapse: Disentangled representation learning and photorealistic cross-age face synthesis for age-invariant face recognition. AAAI, 33, 9251–9258.
Zhao, J., Cheng, Y., Xu, Y., Xiong, L., Li, J., Zhao, F., et al. (2018). Towards pose invariant face recognition in the wild. In CVPR (pp. 2207–2216).
Zhao, J., Li, J., Tu, X., Zhao, F., Xin, Y., Xing, J., Liu, H., Yan, S., Feng, J. (2019). Multi-prototype networks for unconstrained set-based face recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.04755.
Zhao, J., Xiong, L., Cheng, Y., Cheng, Y., Li, J., Zhou, L., et al. (2018). 3D-aided deep pose-invariant face recognition. In IJCAI (pp. 1184–1190).
Zhao, J., Xiong, L., Jayashree, P. K., Li, J., Zhao, F., Wang, Z., et al. (2017). Dual-agent gans for photorealistic and identity preserving profile face synthesis. In NeurIPS (pp. 65–75).
Zhao, J., Xiong, L., Li, J., Xing, J., Yan, S., & Feng, J. (2018). “3d-aided dual-agent gans for unconstrained face recognition,” T-PAMI.
Zhao, W., Chellappa, R., Phillips, P. J., & Rosenfeld, A. (2003). Face recognition: A literature survey. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 35(4), 399–458.
Zhu, X., Lei, Z., Yan, J., Yi, D., & Li, S. Z. (2015). High-fidelity pose and expression normalization for face recognition in the wild. In CVPR (pp. 787–796).
Zhu, Z., Luo, P., Wang, X., & Tang, X. (2013). Deep learning identity-preserving face space. In ICCV (pp. 113–120).
Zhu, Z., Luo, P., Wang, X., & Tang, X. (2014). Multi-view perceptron: a deep model for learning face identity and view representations. in NeurIPS, 217–225.
Acknowledgements
The work of Junliang Xing was partially supported by the National Science Foundation of China 61672519.
The work of Jiashi Feng was partially supported by NUS startup R-263-000-C08-133, MOE Tier-I R-263-000-C21-112, NUS IDS R-263-000-C67-646 and ECRA R-263-000-C87-133.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Tinne Tuytelaars.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Xing, J., Xiong, L. et al. Recognizing Profile Faces by Imagining Frontal View. Int J Comput Vis 128, 460–478 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-019-01252-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-019-01252-7