Abstract
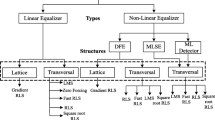
In this paper, we propose an efficient architectural design for Adaptive Decision Feedback Equalizer (ADFE) for high-speed reliable data transmission through wired as well as wireless communication channels to minimize Inter Symbol Interference (ISI). High hardware cost of the system makes an urge to redesign it in order to minimize overall circuit complexity and cost. Realization of CORDIC based pipelined ADFE architecture using reformulated LMS algorithm has not only reduced multipliers in its feed forward path, the flexibility and modularity of the components makes it possible for easy implementation also. The realization results area efficient, high speed and throughput with good convergence. The efficacy of the proposed equalizer is corroborated with MATLAB simulations for mitigation of severe channel distortion arise due to ISI in high speed communication systems.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farhang-Boroujeny, B. (2013). Adaptive filters: theory and applications. John Wiley & Sons.
R. Mishra, A. Mandal, (2012). Coordinate rotation algorithm based non-linear Adaptive Decision Feedback Equalizer, In IEEE 2012 9th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals and Devices (SSD), pp. 1–5
Volder, J. E. (1959). The CORDIC trigonometric computing technique. IRE Transactions on Electronic Computers, EC-8, 330–334.
Hu, Y. H. (1992). CORDIC-based VLSI architectures for digital signal processing. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 9(3), 16–35.
Meher, P. K., et al. (2009). 50 years of CORDIC: algorithms, architectures, and applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 56(9), 1893–1907.
Banerjee, A., Dhar, A. S., & Banerjee, S. (2001). FPGA realization of a CORDIC based FFT processor for biomedical signal processing. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 25(3), 131–142.
Hu, Y. H., & Liao, H. E. (1992). CALF: a CORDIC adaptive lattice filter. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 40(4), 990–993.
Angarita, F., Canet, M. J., Sansaloni, T., Perez-Pascual, A., & Valls, J. (2008). Efficient mapping of CORDIC algorithm for OFDM-based WLAN. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 52(2), 181–191.
S. S. Haykin, (2008). Adaptive filter theory, 4 ed., Pearson Education India.
Sung, W., Ahn, Y., & Hwang, E. (2005). VLSI implementation of an adaptive equalizer for ATSC digital TV receivers. Journal of VLSI signal processing systems for signal, image and video technology, 40(3), 301–310.
Chen, S., Hanzo, L., & Livingstone, A. (2006). MBER space-time decision feedback equalization assisted multiuser detection for multiple antenna aided SDMA systems. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 54(8), 3090–3098.
Chakraborty, M., & Pervin, S. (2003). Pipelining the adaptive decision feedback equalizer with zero latency. Signal Processing, 83(12), 2675–2681.
Shaik, R. A., & Chakraborty, M. (2013). A block floating point treatment to finite precision realization of the adaptive decision feedback equalizer. Signal Processing, 93(5), 1162–1171.
Magarini, M., Barletta, L., & Spalvieri, A. (2012). Efficient computation of the feedback filter for the hybrid decision feedback equalizer in highly dispersive channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(6), 2245–2253.
Raghunath, K. J., & Parhi, K. K. (1993). Parallel adaptive decision feedback equalizers. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 41(5), 1956–1961.
Gatherer, A., & Meng, T. H. (1993). A robust adaptive parallel DFE using extended LMS. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 41(2), 1000–1005.
Shanbhag, N. R., & Parhi, K. K. (1995). Pipelined adaptive DFE architectures using relaxed look-ahead. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 43(6), 1368–1385.
Yang, M. D., Wu, A. Y., & Lai, J. T. (2004). Fast convergent pipelined adaptive DFE architecture using post-cursor processing filter technique. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 51(2), 57–60.
Chakraborty, M., Dhar, A. S., & Lee, M. H. (2005). A trigonometric formulation of the LMS algorithm for realisation of pipelined CORDIC. IEEE Trans. Circuits and Systems, 52(9), 530–534.
Banerjee, A., & Dhar, A. S. (2013). Pipelined VLSI architecture using CORDIC for transform domain equalizer. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 70(1), 39–48.
Wu, A., Ng, C. K., & Tang, K. C. (1998). Modified booth pipelined multiplication. Electronics Letters, 34(12), 1179–1180.
Waters, R. S., & Swartzlander, E. E. (2010). A reduced complexity wallace multiplier reduction. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 59(8), 1134–1137.
Kornerup, P. (2005). Reviewing 4-to-2 adders for multi-operand addition. Journal of VLSI signal processing systems for signal, image and video technology, 40(1), 143–152.
Galbi, D., et al. (1990). U.S. Patent No. 4,901,270. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
Kuang, S.-R., Wang, J.-P., & Guo, C.-Y. (2009). Modified booth multipliers with a regular partial product array. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 56(5), 404–408.
Hu, Y. (1992). The Quantization Effects of the CORDIC Algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 40(4), 834–844.
Biswas, D., & Maharatna, K. (2015). A CORDIC-Based Low-Power Statistical Feature Computation Engine for WSN Applications. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 1–18. doi:10.1007/s00034-015-0041-5.
Noll, T. G. (1991). Carry-save architectures for high-speed digital signal processing. Journal of VLSI signal processing systems for signal, image and video technology, 3(1–2), 121–140.
Meher, P. K., & Park, S. Y. (2013). CORDIC designs for fixed angle of rotation. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 21(2), 217–228.
Lin, Y. C., Jou, S. J., & Shiue, M. T. (2012). High throughput concurrent lookahead adaptive decision feedback equalizer. IET Circuits, Devices and Systems, 6(1), 52–62.
Sailer, T., & Tröster, G. (2003). An Efficient VLSI Architecture for Computing Decision Feedback Equalizer Coefficients from the Channel State Information. Journal of VLSI signal processing systems for signal, image and video technology, 35(1), 91–103.
Chakraborty, M., Dhar, A. S., & Pervin, S. (2001). CORDIC realization of the transversal adaptive filter using a trigonometric LMS algorithm. In proceedings of 2001 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 2001 (ICASSP'01), (2), 1225–1228.
Mandal, A., Mishra, R., Kaushik, B. K., & Rizvi, N. Z. (2015). Design of LMS Adaptive Radar Detector for Non-homogeneous Interferences, IETE Technical Review. doi:10.1080/02564602.2015.1093436.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, A., Mishra, R. Design of Complex Non-Linear Adaptive Equalizer in Mitigating Severe Intersymbol Interferences. J Sign Process Syst 84, 225–236 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-015-1047-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-015-1047-8