Abstract
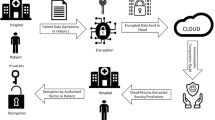
Secure transmission of medical information occupies a crucial role in the world of telemedicine applications. Reconfigurable hardware implementation offers several advantages over software implementation especially for real time security applications. This work aims to propose the novel implementation of a penta-layer medical image encryption using a reconfigurable Cyclone II Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) EP2C35F672C6. The first layer of encryption performs the row-wise and column-wise pixel permutations based on Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR). The second and third layers of encryption are based on maximal length sequence Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG) 16-bit Cellular automata (CA) circuit and Galois Field (GF) product. In the fourth layer, a synthetic image is subsequently created by chaotic clock with Phase Lock Loop (PLLs) and gates to diffuse the image pixels. This creation of synthetic image for diffusion makes the developed cryptosystem totally hardware dependent. Last layer performs the diffusion using one dimensional logistic map. The synthesized result reveals that the reconfigurable implementation of proposed encryption process consumes comparatively lesser logic elements (2480) and low power consumption (278.65 mW) with an encryption time of 215.92 ms for encrypting a 256 × 256 DICOM medical image. Finally, various analyses such as Number of Pixel Change Rate (NPCR), Unified Average Change in Intensity (UACI), Entropy, Correlation, Uniform distribution and NIST statistical test suite have been performed to prove the robustness of the algorithm against various attacks.





























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Montagnat, J., Bellet, F., Benoit-Cattin, H., Breton, V., Brunie, L., Duque, H., et al. (2004). Medical images simulation, storage, and processing on the European DataGrid testbed. Journal of Grid Computing, 2(4), 387–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-004-5744-y
Wong, S., Huang, H. K., Zaremba, L., & Gooden, D. (1995). Radiologic image compression???A review. Proceedings of the IEEE, 83(2), 194–219. https://doi.org/10.1109/5.364466
Cosman, P. C., Gray, R. M., & Olshen, R. A. (1994). Evaluating quality of compressed medical images: SNR, subjective rating, and diagnostic accuracy. Proceedings of the IEEE, 82(6), 919–932. https://doi.org/10.1109/5.286196
Bruckmann, A., & Uhl, A. (2000). Selective medical image compression techniques for telemedical and archiving applications. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 30(3), 153–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-4825(00)00004-4
Armbrust, L. J. (2009). PACS and image storage. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Small Animal Practice, 39(4), 711–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvsm.2009.04.004
Huang, H. K., Wong, A. W. K., Lou, A. S. L., Bazzill, T. M., Andriole, K., Zhang, J., et al. (1996). Clinical experience with a second-generation hospital-integrated picture archiving and communication system. Journal of Digital Imaging, 9(4), 151–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03168612
Bidgood, W. D., & Horii, S. C. (1992). Introduction to the ACR-NEMA DICOM standard. Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc, 12(2), 345–355. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiographics.12.2.1561424
Hu, J., & Han, F. (2009). A pixel-based scrambling scheme for digital medical images protection. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 32(4), 788–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2009.02.009
Menezes, A. J., Vanstone, S. A., & Van Oorschot, P. C. (1996). Handbook of applied cryptography (1st ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press, Inc..
Norcen, R., Podesser, M., Pommer, A., Schmidt, H.-P., & Uhl, A. (2003). Confidential storage and transmission of medical image data. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 33(3), 277–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-4825(02)00094-X
Lv, Y., & Tong, X. (2009). A novel method of chaotic image encryption based on LFSR. In Proceedings - International Conference on Management and Service Science, MASS 2009. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMSS.2009.5302775.
Tong, X. J. (2012). Novel bilateral-diffusion image encryption algorithm with compound chaos and LFSR. The Imaging Science Journal, 60(5), 294–304. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743131X11Y.0000000042
Abdelhaleem, S. H., Radwan, A. G., & Abd-El-Hafiz, S. K. (2013). Utilizing LFSR and Feistel networks in image encryption. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits, and Systems (pp. 601–604). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECS.2013.6815486.
Abd El-Latif, A. A., & Niu, X. (2013). A hybrid chaotic system and cyclic elliptic curve for image encryption. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 67(2), 136–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2012.07.004
Deepthi, P. P., John, D. S., & Sathidevi, P. S. (2009). Design and analysis of a highly secure stream cipher based on linear feedback shift register. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 35(2), 235–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2008.06.005
Jin, J., & Wu, Z. H. (2012). A secret image sharing based on neighborhood configurations of 2-D cellular automata. Optics and Laser Technology, 44(3), 538–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2011.08.023
Eslami, Z., Razzaghi, S. H., & Ahmadabadi, J. Z. (2010). Secret image sharing based on cellular automata and steganography. Pattern Recognition, 43(1), 397–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2009.06.007
Wolfram, S. (1986). Cryptography with Cellular Automata. In Advances in Cryptology (pp. 429–432). London: Springer-Verlag. Retrieved from http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=646751.704557.
Jin, J. (2012). An image encryption based on elementary cellular automata. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 50(12), 1836–1843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2012.06.002
Abdo, A. A., Lian, S., Ismail, I. A., Amin, M., & Diab, H. (2013). A cryptosystem based on elementary cellular automata. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 18(1), 136–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2012.05.023
Ping, P., Xu, F., & Wang, Z. J. (2014). Image encryption based on non-affine and balanced cellular automata. Signal Processing, 105, 419–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.06.020
Lima, J. B., & Novaes, L. F. G. (2014). Image encryption based on the fractional Fourier transform over finite fields. Signal Processing, 94(1), 521–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.07.020
Tao, R. T. R., Meng, X.-Y. M. X.-Y., & Wang, Y. W. Y. (2010). Image encryption with multiorders of fractional Fourier transforms. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 5(4), 734–738. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2010.2068289
Zhan, Y., Feng, X., Fu, C., Bai, G., & Ma, H. (2012). An efficient medical image cryptosystem based on chaotic maps. International Journal of Digital Content Technology and its Applications, 6(13), 265–274. https://doi.org/10.4156/jdcta.vol6.issue13.29
Behnia, S., Akhshani, A., Mahmodi, H., & Akhavan, A. (2008). A novel algorithm for image encryption based on mixture of chaotic maps. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 35(2), 408–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2006.05.011
Ravichandran, D., Praveenkumar, P., Balaguru Rayappan, J. B., & Amirtharajan, R. (2016). Chaos based crossover and mutation for securing DICOM image. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 72, 170–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.03.020
Dong, C. (2014). Color image encryption using one-time keys and coupled chaotic systems. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 29(5), 628–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.image.2013.09.006
Azzaz, M. S., Tanougast, C., Sadoudi, S., Bouridane, A., & Dandache, A. (2009). FPGA implementation of new real-time image encryption based switching chaotic systems. In Signals and Systems Conference (ISSC 2009), IET Irish (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1049/cp.2009.1733.
Ledesma-Carrillo, L. M., Lopez-Ramirez, M., Cabal-Yepez, E., Ojeda-Castaneda, J., Rodriguez-Donate, C., & Lizarraga-Morales, R. A. (2016). FPGA-based reconfigurable unit for image encryption using orthogonal functions. In 2016 International Conference on Electronics, Communications and Computers (CONIELECOMP) (pp. 168–173). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. https://doi.org/10.1109/CONIELECOMP.2016.7438570.
Kumar, S. K. N., Kumar, H. S. S., & Panduranga, H. T. (2013). Hardware software co-simulation of dual image encryption using Latin square image. In 2013 4th International Conference on Computing, Communications and Networking Technologies, ICCCNT 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCNT.2013.6726681.
Hai, C., Yu, S., Chunguang, H., Yu, S., & Qun, D. (2015). Design and Realization of Image Encryption System Based on Compound Logistic Chaotic System. In 2015 Third International Conference on Robot, Vision and Signal Processing (RVSP) (pp. 75–77). https://doi.org/10.1109/RVSP.2015.27.
Tang, Z., & Yu, S. (2012). Design and realization of digital image encryption and decryption based on multi-wing butterfly chaotic attractors. In Image and Signal Processing (CISP), 2012 5th International Congress on (pp. 1143–1147). https://doi.org/10.1109/CISP.2012.6469744.
Yen, J.-C., & Guo, J.-I. (2000). Efficient hierarchical chaotic image encryption algorithm and its VLSI realisation. IEE Proceedings - Vision, Image, and Signal Processing, 147(2), 167. https://doi.org/10.1049/ip-vis:20000208
Torres-Huitzil, C. (2013). Hardware realization of a lightweight 2D cellular automata-based cipher for image encryption. In 2013 I.E. 4th Latin American Symposium on Circuits and Systems, LASCAS 2013 - Conference Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1109/LASCAS.2013.6519023.
Jahiruzzaman, M., Hossain, A. B. M. A., & Saha, S. (2015). Implementation of 2D torus automorphisms for image encryption on FPGA. In 2nd International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information and Communication Technology, iCEEiCT 2015. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEEICT.2015.7307452.
Shah, S. S. H., & Raja, G. (2016). FPGA implementation of chaotic based AES image encryption algorithm. In IEEE 2015 International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications, ICSIPA 2015 - Proceedings (pp. 574–577). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSIPA.2015.7412256.
Stroud, C. E. (2002). A designer’s guide to built-in self-test (p. 319). New York: Springer Science & Business Media. https://doi.org/10.1007/b117480.
Mansingka, A. S., Affan Zidan, M., Barakat, M. L., Radwan, A. G., & Salama, K. N. (2013). Fully digital jerk-based chaotic oscillators for high throughput pseudo-random number generators up to 8.77 Gbits/s. Microelectronics Journal, 44(9), 744–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2013.06.007
Zidan, M. A., Radwan, A. G., & Salama, K. N. (2011). The effect of numerical techniques on differential equation based chaotic generators. In ICM 2011 Proceeding (pp. 1–4). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICM.2011.6177395.
Mansingka, A. S., Radwan, A. G., Zidan, M. A., & Salama, K. N. (2011). Analysis of bus width and delay on a fully digital signum nonlinearity chaotic oscillator. In Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems. https://doi.org/10.1109/MWSCAS.2011.6026596.
Zhang, Q., Guo, L., & Wei, X. (2013). A novel image fusion encryption algorithm based on DNA sequence operation and hyper-chaotic system. Optik - International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 124(18), 3596–3600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2012.11.018
Rajagopalan, S., Upadhyay, H. N., Rayappan, J. B. B., & Amirtharajan, R. (2014). Dual cellular automata on FPGA: An image encryptors chip. Research Journal of Information Technology, 6(3), 223–236. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjit.2014.223.236
Rajagopalan, S., Upadhyay, H. N., Rayappan, J. B. B., & Amirtharajan, R. (2014). Galois field proficient product for secure image encryption on FPGA. Research Journal of Information Technology, 6(4), 308–324. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjit.2014.308.324
Ramalingam, B., Rengarajan, A., & Rayappan, J. B. B. (2017). Hybrid image crypto system for secure image communication– A VLSI approach. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 50, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2017.02.003
Ramalingam, B., Ravichandran, D., Annadurai, A. A., Rengarajan, A., & Rayappan, J. B. B. (2017). Chaos triggered image encryption - a reconfigurable security solution. Multimedia Tools and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4811-x
Pareek, N. K., & Patidar, V. (2014). Medical image protection using genetic algorithm operations. Soft Computing, 20(2), 763–772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-014-1539-7
Kanso, A., & Ghebleh, M. (2015). An efficient and robust image encryption scheme for medical applications. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 24(1–3), 98–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2014.12.005
Xu, L., Li, Z., Li, J., & Hua, W. (2016). A novel bit-level image encryption algorithm based on chaotic maps. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 78, 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2015.09.007
Zhou, Y., Cao, W., & Philip Chen, C. L. (2014). Image encryption using binary bitplane. Signal Processing, 100, 197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.01.020
Al-Mamun, A., Rahman, S. S. M., Ahmed Shaon, T., & Hossain, M. (2017). Security analysis of AES and enhancing its security by modifying S-box with an additional byte. International journal of Computer Networks & Communications, 9(2), 69–88. https://doi.org/10.5121/ijcnc.2017.9206
Zhang, Q., & Qunding, A. (2015). Digital image encryption based on Advanced Encryption Standard(AES) algorithm. 5th International Conference on Instrumentation and Measurement, Computer, Communication, and Control, IMCCC 2015 (pp. 1218–1221). https://doi.org/10.1109/IMCCC.2015.261.
Zhang, Y., Li, X., Hou, W. (2017). A Fast Image Encryption Scheme Based on AES. In 2nd International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (pp. 624–628).
Praveenkumar, P., Amirtharajan, R., Thenmozhi, K., & Balaguru Rayappan, J. B. (2015). Medical data sheet in safe havens - a tri-layer cryptic solution. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 62, 264–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2015.04.031
Abd El-Samie, F. E., Ahmed, H. E. H., Elashry, I. F., Shahieen, M. H., Faragallah, O. S., El-Rabaie, E.-S. M., & Alshebeili, S. A. (2013). Image encryption: A communication perspective. Boca Raton: CRC Press, Inc..
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank SASTRA University for providing infrastructure through the Research & Modernization Fund (Ref.No: R&M / 0026 / SEEE – 010 / 2012 – 13) to carry out the research work. They also wish to express their sincere thanks to the INSPIRE Fellowship (No. DST/INSPIRE Fellowship/2015/IF15062), Department of Science and Technology (DST), India for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravichandran, D., Rajagopalan, S., Upadhyay, H.N. et al. Encrypted Biography of Biomedical Image - a Pentalayer Cryptosystem on FPGA. J Sign Process Syst 91, 475–501 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-018-1337-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-018-1337-z