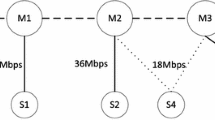
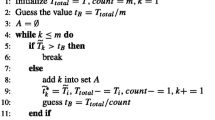Abstract
The rapid deployment of wireless mesh networks across universities and enterprises, and the pervasiveness of mobile devices equipped with Wi-Fi connectivity, has resulted in a scenario wherein end users have the option to choose from a multitude of access points at any given location. Moreover, with the increasing availability of rich online content, there has been a steady increase in mobile Internet traffic. Since the choice of access point that a user associates with will directly impact his performance, it is imperative that there exist an efficient association control mechanism, in order to enhance the end user’s experience. As part of this work, we propose Seeker, a novel framework for association control in wireless networks that utilizes “available bandwidth” as the design metric. The goal of Seeker is to assist the mesh network in making an intelligent decision regarding which access point a client should associate with. As part of our scheme, we implement and evaluate a passive tool to estimate available bandwidth in wireless networks. We then describe how we use this tool to implement our association control scheme, and evaluate it via extensive experiments on an outdoor testbed. Seeker takes into consideration the performance of the mesh backhaul, in addition to the client-to-AP link quality, thereby achieving significant advantages over traditional association control schemes for wireless-LANs.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
IEEE 802.11a standard. (1999). http://standards.ieee.org/getieee802/download/802.11a-1999.pdf, http://standards.ieee.org/getieee802/download/802.11a-1999.pd.
Optimized link state routing (olsr) protocol. (2007). http://www.olsr.or.
Orange mesh. (2008). http://orangemesh.ucdavis.ed.
Quail ridge reserve wireless mesh network. (2008). http://spirit.cs.ucdavis.edu/quailridg.
AT&T Faces 5,000 Percent Surge in Traffic. (2009). http://www.internetnews.com/mobility/article.php/384300.
Wifi Google. (2009). http://wifi.google.co.
Smart phones are making Wi-Fi hotspots hot again. http://www.physorg.com/news180286896.htm.
Abusubaih, M., & Wolisz, A. (2008). Interference-aware decentralized access point selection policy for multi-rate ieee 802.11 wireless lans. In: Proceedings of the IEEE PIMRC.
Aguayo, D., Bicket, J., Biswas, S., Judd, G., & Morris, R. (2004). Link-level measurements from an 802.11b mesh network. In: Proceedings of ACM SIGCOMM.
Argento, A., Cesana, M., Gatti, N., & Malanchini, I. (2010). A game theoretical study of access point association in wireless mesh networks. Computer Communications (In Press, Corrected Proof).
Athanasiou, G., Korakis, T., Ercetin, O., & Tassiulas, L., (2009). A cross-layer framework for association control in wireless mesh networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 8, 65–80.
Bahl, P., Adya, A., Padhye, J., & Walman, A. (2004). Reconsidering wireless systems with multiple radios. SIGCOMM Comput Commun Rev, 34, 39–46.
Bahl, P., Hajiaghayi, M., Jain, K., Mirrokni, S., Qiu, L., & Saberi, A. (2007). Cell breathing in wireless lans: Algorithms and evaluation. Mobile Computing, IEEE Transactions on 6.
Balachandran, A., Bahl, P., & Voelker, G. M. (2002). Hot-spot congestion relief and service guarantees in public-area wireless networks. SIGCOMM Comput Commun Rev, 32, 59.
Balasubramanian, N., Balasubramanian, A., Venkataramani, A. (2009). Energy consumption in mobile phones: A measurement study and implications for network applications. In: IMC ’09: Proceedings of the 9th ACM SIGCOMM conference on internet measurement conference.
Bejerano, Y., Han, S. J., & Li, L. (2007). Fairness and load balancing in wireless lans using association control. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 15.
Berg, M., & Hultell, J. (2006). On selfish distributed access selection algorithms in ieee 802.11 networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE VTC.
Bredel, M., & Fidler, M. (2008). Lecture notes in computer science, Springer, chap A Measurement study of bandwidth estimation in IEEE 802.11g wireless LANs using the DCF, pp. 314–325.
Brickley, O., Rea, S., & Pesch, D. (2005). Load balancing for qos optimisation in wireless lans utilising advanced cell breathing techniques. In: Proceedings of the IEEE VTC.
Chandra, R., & Bahl, P. (2004). Multinet: Connecting to multiple ieee 802.11 networks using a single wireless card. In: Proceedings of IEEE Infocom.
Couto, S. J. D., Aguayo, D., Bicket, J., & Morris, R. (2005). A high-throughput path metric for multi-hop wireless routing. Wireless Networks, 11, 419–434.
Croce, D., Mellia, M., & Leonardi, E. (2009). The quest for bandwidth estimation techniques for large-scale distributed systems. In: Second Workshop on Hot Topics in Measurement & Modeling of Computer Systems (HotMetrics).
Draves, R., Padhye, J., & Zill, B. (2004). Routing in multi-radio, multi-hop wireless mesh networks. In: Proceedings of ACM MobiCom, Philadelphia, PA.
Feeney, L., & Nilsson, M. (2001). Investigating the energy consumption of a wireless network interface in an ad hoc networking environment. In: Proceedings of IEEE Infocom.
Gupta, A., & Mohapatra, P. (2007). Energy consumption and conservation in wifi based phones: A measurement-based study. In: Sensor and Ad Hoc Communications and Networks (SECON).
Gupta, D., Wu, D., Mohapatra, P., & Chuah, C. N. (2009). Experimental comparison of bandwidth estimation tools for wireless mesh networks. In: The 28th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM) mini-conference.
Hu, N., & Steenkiste, P. (2003). Evaluation and characterization of available bandwidth probing techniques. Selected Areas in Communications, IEEE Journal on.
Jain, M., & Dovrolis, C. (2002). Pathload: A measurement tool for end-to-end available bandwidth. In: Passive and Active Measurements workshop (PAM).
Jones, K., & Liu, L. (2007). What where wi: An analysis of millions of wi-fi access points. In: Proceedings of IEEE PORTABLE.
Judd, G., & Steenkiste, P. (2002). Fixing 802.11 access point selection. Computer Communication Review 32.
Lakshminarayanan, K., Padmanabhan, V., & Padhye, J. (2004). Bandwidth estimation in broadband access networks. In: The 4th ACM SIGCOMM Internet Measurement Conference (IMC).
Lee, H., Kim, S., Lee, O., Choi, S., & Lee, S. J. (2008). Available bandwidth-based association in ieee 802.11 wireless lans. In: Proceedings of ACM MSWiM, Vancouver, Canada.
Lee, H. K., Hall, V., Yum, K. H., Kim, K., & Kim, E. (2006). Bandwidth estimation in wireless lans for multimedia streaming services. In: IEEE ICME.
Lu, M., & Wu, J. (2007). Localized access point selection in infrastructure wireless lan. In: Proceedings of IEEE MILCOM.
Mangold, S., & Berlemann, L. (2005). Ieee 802.11k: Improving confidence in radio resource measurements. In: Proceedings of IEEE PIMRC.
Murty, R., Padhye, J., Chandra, R., Wolman, A., & Zill, B. (2008). Designing high performance enterprise wi-fi networks. In: Proceedings of USENIX NSDI.
Neilsen, M., Ovsthus, K., & Landmark, L. (2006). Field trials of two 802.11 residual bandwidth estimation methods. In: IEEE MASS.
Nicholson, A. J., & Noble, B. D. (2008). Breadcrumbs: Forecasting mobile connectivity. In: Proceedings of the ACM MobiCom, San Francisco, CA.
Nicholson, A. J., Chawathe, Y., Chen, M. Y., Noble, B. D., & Wetherall, D. (2006). Improved access point selection. In: Proceedings of the ACM MobiSys, New York, NY, USA.
Pang, J., Greenstein, B., Kaminsky, M., McCoy, D., & Seshan, S. (2009). Wifi-reports: Improving wireless network selection with collaboration. In: Proceedings of the ACM MobiSys.
Ribeiro, V. J., Riedi, R., Baraniuk, R., Navratil, J., & Cottrell, L. (2003). Pathchirp: Efficient available bandwidth estimation for network paths. In: Passive and Active Measurements Conference (PAM).
Sarr, C., Chaudet, C., Chelius, G., & Lassous, I. G. (2008). Bandwidth estimation for ieee 802.11-based ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 7, 1228–1241.
Shriram, A., Murray, M., Hyun, Y., Brownlee, N., Broido, A., Fomenkov, M., & Claffy, K. (2005). Comparison of public end-to-end bandwidth estimation tools on high-speed links. In: Passive and Active Measurements Conference (PAM).
Strauss, J., Katabi, D., & Kaashoek, F. (2003). A measurement study of available bandwidth estimation tools. In: Proceedings of 3rd IMC.
Sundaresan, K., & Papagiannaki, K. (2006). The need for cross-layer information in access point selection algorithms. In: Proceedings of the IMC.
Vasudevan, S., Papagiannaki, K., Diot, C., Kurose, J., & Towsley, D. (2005). Facilitating access point selection in ieee 802.11 wireless networks. In: Proceedings of the IMC.
Villegas, E. G., Ferre, R. V., & Aspas, J. P. (2006). Load balancing in wlans through ieee 802.11k mechanisms. In: Proceedings of the IEEE ISCC.
Zhao, H., Garcia-Palacios, E., Wei, J., & Xi, Y. (2009). Accurate available bandwidth estimation in ieee 802.11-based ad hoc networks. Computer Communications, 32, 1050–1057.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, D., Mohapatra, P. & Chuah, CN. Seeker: A bandwidth-based association control framework for wireless mesh networks. Wireless Netw 17, 1287–1304 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-011-0349-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-011-0349-4