Abstract
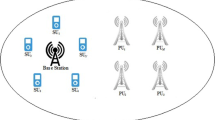
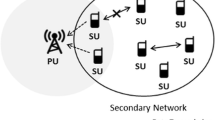
Spectrum sensing is essential for the success of the cognitive radio networks. In traditional spectrum sensing schemes, secondary users (SUs) are responsible for the spectrum sensing which could be very time and resource consuming. It leads to a great deal of inefficiency in spectrum usage and introduces many practical challenges. To tackle these challenges and leverage the spectrum opportunity more efficiently, we propose a new system that provides a spectrum sensing service for SUs using dedicated wireless spectrum sensor networks (WSSNs). In this paper we focus on the sensing channel assignment problem in WSSNs and formulate the problem as a sensing effectiveness maximization problem (SEMP). We prove that SEMP is NP-complete under the ideal case, and show that more challenges arise in real environments. To address the issue, we systematically study the design tradeoff and critical factors when maximizing the sensing effectiveness. Based on these study results we propose a sensing channel assignment algorithm (SCAS). We conduct test-bed empirical investigations as well as comprehensive simulations. Performance evaluation results show that for both the scenarios of given deployments and manual deployments, SCAS is able to sense more channels to improve the sensing effectiveness. The improvement is up to 300 % and the average improvement is 150 % compared with other simple alternatives.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In this paper we will use the spectrum and channel interchangeable if no otherwise specified.
References
Akyildiz, I. F., Lee, W., Vuran, M. C., & M. S. (2008). A survey on spectrum management in cognitive radio networks, IEEE Communications Magazine, 40–48.
IEEE802.22, working, group, and on Wireless Regional Area Networks (WRANs), http://www.ieee802.org/22/.
Stevenson, C.R., Cordeiro, C., Sofer, E., & Chouinard, G. (2005). Functional requirements for the 802.22 wran standard.
Kim, H., & Shin, K.G. (2008). In-band spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks: energy detection or feature detection?, In Proceedings of MobiCom. New York, NY: ACM, pp. 14–25.
Kondareddy, Y.R., & Agrawal, P. (2008). Synchronized mac protocol for multi-hop cognitive radio networks, In Communications, 2008. ICC’08. IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, pp. 3198–3202.
Ghasemi, A., & Sousa, E.S. (2005). Collaborative spectrum sensing for opportunistic access in fading environments, In Proceedings of IEEE DySPAN.
Online and Available, Sendora project http://www.sendora.eu/ (2008).
Xi, W., He, Y., Liu, Y., Zhao, J., Mo, L., & Yang, Z. (2009). Locating sensors in the wild: Pursuit of ranging quality, In Proceedings of ACM Sensys.
Yang, Y., Liu, Y., & Ni, L. M. (2010). Cooperative boundary detection for spectrum sensing using dedicated wireless sensor networks, In Proceedings of InfoCom.
Polastre, J., Szewczyk, R., & Culler, D. (2005). Telos: Enabling ultra-low power wireless research, In Proceeding of IPSN.
Cabric, D., Tkachenko, A., & Brodersen, R.W. (2006). Experimental study of spectrum sensing based on energy detection and network cooperation, In Proceedings of IEEE TAPAS.
Cordeiro, C., Challapali, K., & Ghosh, M. (2006). Cognitive phy and mac layers for dynamic spectrum access and sharing of tv bands, In Proceedings of TAPAS. New York, NY: ACM, p. 3.
Sutton, P., Nolan, K.E., & Doyle, L. (2007). Cyclostationary signatures for rendezvous in ofdm-based dynamic spectrum access networks, In Proceedings of IEEE DySPAN.
Datla, D., Rajbanshi, R., Wyglinski, A., & Minden, G. (2007). Parametric adaptive spectrum sensing framework for dynamic spectrum access networks, In Proceedings of IEEE DySPAN.
Ghasemi, A., & Sousa, E.S. (2005). Collaborative spectrum sensing for opportunistic access in fading environments, In Proceedings of IEEE DySPAN.
Ganesan, G., & Li, Y.G. (2005). Cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks, In Proceedings of IEEE DySPAN.
Li, Z., Yu, F.R., & Huang, M. (2009). A cooperative spectrum sensing consensus scheme in cognitive radios, In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM.
Chen, R., Park, J., & Bian, K. (2008). Robust distributed spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks, In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM.
Fodor, V., & Glaropoulos, I. Sensor networks for spectrum sensing - working assumptions and design goals, http//www.ee.kth.se/commth/projects/CROPS/docs/C2.d1.pdf.
Fekete, S.P., Kroller, A., Pfisterer, D., Fischer, S., & Buschmann, C. (2004). Neighborhood-based topology recognition in sensor networks. In Proceedings of ALGOSENSORS.
Krishnamachari, B., & Iyengar, S. (2004). Distributed bayesian algorithms for fault-tolerant event region detection in wireless sensor networks, IEEE Transactions on Computers, 53(3), 241–250.
He, Y., Shen, X., Liu, Y., Mo, L., & Da, G. (2010). Locating sensors in the wild: Pursuit of ranging quality, In Proceedings of ACM Sensys.
Shellhammer, S.J.,S. S. N, Tandra, R., & Tomcik, J. (2006). Performance of power detector sensors of dtv signals in ieee 802.22 wrans, In Proc. of TAPAS. New York, NY: ACM, p. 4.
Zhou, G., Huang, C., Yan, T., He, T., Stankovic, J.A., & Abdelzaher, T.F. (2006). Mmsn multi-frequency media access control for wireless sensor networks, In Proceedings of IEEE InfoCom.
Sklar, B. (1997). Rayleigh fading channels in mobile digital communication systems part i characterization. IEEE Communications Magazine, 35(7), 90–100.
Rappaport, T.S. (2002). Wireless communications principles and practices. Upper Saddle River: Prentice-Hall.
Chipcon, “Cc2420 data sheet,“ http//focus.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/cc2420.pdf, 2007.
Li, M., & Liu, Y. (2007). Rendered path: range-free localization in anisotropic sensor networks with holes, In MobiCom. New York, NY, USA: ACM, pp. 51–62.
Coxeter, H. (1973). Regular Polytopes. Dover.
Guibas, L., Knuth, D., & Sharir, M. (1992). Randomized incremental construction of delaunay and voronoi diagrams, Algorithmica, 7, 381–413.
Preparata, F.P., & Hong, S. (1977). Convex hulls of finite sets of points in two and three dimensions, Communications of the ACM, 20(2), 87–93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, L., Hu, C., Liu, Y. et al. SCAS: sensing channel assignment for wireless spectrum sensor networks. Wireless Netw 20, 817–831 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-013-0642-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-013-0642-5