Abstract
This paper presents a gradient-based multi-hop clustering protocol combined with a mobile sink (MS) solution for efficient data gathering in wireless sensor networks. The main insight for the clustering algorithm is drawn from image processing field and namely from the watershed transform, widely used for image segmentation. The proposed algorithm creates multi-hop clusters whose cluster heads (CHs) as well as cluster members near the CHs have high energy reserves. Specifically, the energy of the sensors in a cluster increases progressively as getting closer to the CH. As the nodes closer to the CH are most burdened with relaying of data from other cluster members, the higher levels of available energy at these nodes prolong the network lifetime eventually. After cluster formation, a MS periodically visits each CH and collects the data from cluster members already gathered at the CH. Simulation results show the higher performance of the proposed scheme in comparison to other competent approaches in the literature.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
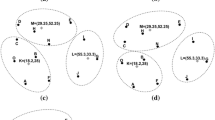
Similar behavior (and corresponding differences in favor of our clustering-based data gathering protocol) is observed for the other numbers of sensor nodes too, for all the three protocols.
Note also here that the energy consumed during the local and global re-clustering procedures required in our data gathering scheme has been included in all the corresponding measurements.
References
Olariu, S., & Stojmenovic, I. (2006). Design guidelines for maximizing lifetime and avoiding energy holes in sensor networks with uniform distribution and uniform reporting. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’06 conference (pp. 1–12).
Basagni, S., Carosi, A., Melachrinoudis, E., Petrioli, C., & Wang, Z. M. (2008). Controlled sink mobility for prolonging WSNs lifetime. Wireless Networks, 14(6), 831–858.
Ammari, H., & Das, S. K. (2008). Promoting heterogeneity mobility and energy-aware Voronoi diagram in Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE TPDS, 19(7), 995–1008.
Bao, X., Liu, L., Zhang, S., & Bao, F. (2010). An energy balanced multihop adaptive clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE ICSPS conference (pp. 47–51).
Galilée, B., Mamalet, F., Renaudin, M., & Coulon, P. (2007). Parallel asynchronous watershed algorithm. IEEE TPDS, 18(1), 44–56.
Soille, P. (2004). Morphological image analysis, principles and applications. New York: Springer.
Castalia: WSNs Simulator. (2007). National ICT Australia. http://castalia.npc.nicta.com.au/.
Konstantopoulos, C., Mamalis, B., Pantziou, G., & Thanasias, V. (2012). Watershed-based clustering for energy efficient data gathering in wireless sensor networks with mobile collector. In Proceedings of EUROPAR conference, lncs 7484 (pp. 754–766).
Li, X., Nayak, A., & Stojmenovic, I. (2010). Sink mobility in wireless sensor networks. In Wireless sensor and actuator networks, chap. 6 (pp. 153–184). New York: Wiley.
Sugihara, R., & Gupta, R. (2010). Optimal speed control of mobile node for data collection in sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 9(1), 127–139.
Shah, R., Roy, S., Jain, S., & Brunette, W. (2003). Data MULEs: modeling and analysis of a three-tier architecture for sparse sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 1(2–3), 215–233.
Kumar, A. K., & Sivalingam, K. M. (2010). Energy-efficient mobile data collection in wireless sensor networks with delay reduction using wireless communication. In Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on communication systems and networks (pp. 1–10).
Luo J., & Hubaux, J. P. (2005). Joint mobility and routing for lifetime elongation in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’05 conference (pp. 1735–1746).
Demirbas, M., Soysal, O., & Tosun, A. (2007). Data salmon: A greedy mobile basestation protocol for efficient data collection in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of DCOSS’07 conference, LNCS 4549 (pp. 267–280).
Vincze, Z., Vass, D., Vida, R., Vidacs, A., & Telcs, A. (2007). Adaptive sink mobility in event-driven densely deployed wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc & Sensor Wireless Networks, 3(2–3), 255–284.
Friedmann, L., & Boukhatem, L. (2007). Efficient multi-sink relocation in wireless sensor network. In Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on networking and services (p. 90).
Konstantopoulos, C., Pantziou, G., Gavalas, D., Mpitziopoulos, A., & Mamalis, B. (2012). A rendezvous-based approach for energy-efficient sensory data collection from mobile sinks. IEEE TPDS, 23(5), 809–817.
Tirta, Y., Li, Z., Lu, Y. H., & Bagchi, S. (2004). Efficient collection of sensor data in remote fields using mobile collectors. In Proceedings of IEEE ICCCN conference (pp. 515–520).
Ma, M., & Yang, Y. (2007). SenCar: An energy-efficient data gathering mechanism for large-scale multihop sensor networks. IEEE TPDS, 18(10), 1476–1488.
Rao, J., & Biswas, S. (2010). Network-assisted sink navigation for distributed data gathering: Stability and delay-energy trade-offs. Computer Communications, 33, 160–175.
Xing, G., Wang, T., Jia, W., & Li, M. (2008). Rendezvous design algorithms for wireless sensor networks with a mobile base station. In Proceedings of ACM MobiHoc conference (pp. 231–239).
Hamida, E., & Chelius, G. (2008). Strategies for data dissemination to mobile sinks in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Communications, 15(6), 31–37.
Chatzigiannakis, I., Kinalis, A., & Nikoletseas, S. (2008). Efficient data propagation strategies in wireless sensor networks using a single mobile sink. Computer Communications, 31, 896–914.
Xing, G., Wang, T., Xie, Z., & Jia, W. (2008). Rendezvous planning in wireless sensor networks with mobile elements. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 7(12), 1430–1443.
Somasundara, A. A., Kansal, A., Jea, D. D., Estrin, D., & Srivastava, M. B. (2006). Controllably mobile infrastructure for low energy embedded networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 5(8), 958–973.
Gao, S., Zhang, H., & Das, S. K. (2011). Efficient data collection in wireless sensor networks with path-constrained mobile sinks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 10(4), 592–608.
Xuan, H. L., & Lee, S. (2004). A coordination-based data dissemination protocol for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the first intelligent sensors, sensor networks & information processing conference (pp. 13–18).
Kim, H. S., Abdelzaher T. F., & Kwon, W. H. (2003). Minimum energy asynchronous dissemination to mobile sinks in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the first international conference on embedded networked sensor systems (pp. 193–204).
Gandham, S., Dawande, M., Prakash R., & Venkatesan, S. (2003). Energy efficient schemes for wireless sensor networks with multiple mobile base stations. In Proceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM conference (pp. 377–381).
Papadimitriou I., & Georgiadis, L. (2005). Maximum lifetime routing to mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the international conference on software, telecommunications and computer networks (pp. 42–46).
Wang, Z. M., Basagni, S., Melachrinoudis E., & Petrioli, C. (2005). Exploiting sink mobility for maximizing sensor networks lifetime. In Proceedings of the 38th Hawaii international conference on system sciences (p. 287a).
Chatzigiannakis, I., Kinalis, A., Nikoletseas, S., & Rolim, J. (2007). Fast and energy efficient sensor data collection by multiple mobile sinks. In Proceedings of MOBIWAC’07 conference (pp. 25–32).
Basagni, S., Carosi, A., Petrioli, C., & Phillips, C. (2011). Coordinated and controlled mobility of multiple sinks for maximizing the lifetime of wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 17(3), 759–778.
Liu, W., Lu, K., Wang, J., Huang, L., & Wu, D. (2012). On the throughput capacity of wireless sensor networks with mobile relays. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 61(4), 1801–1809.
Li, K., & Hua, K. A. (2012). Mobile data collection networks for wireless sensors. In Proceedings of the 5th multimedia communications services and security conference (pp. 200–211).
Di Francesco, M., Das, S. K., & Anastasi, G. (2011). Data collection in wireless sensor networks with mobile elements: A survey. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 8(1), 7.
Miller, C. E., Tucker, A. W., & Zemlin, R. A. (1960). Integer programming formulation and traveling salesman problem. Journal of ACM, 7, 326–329.
Liang, W., & Liu, Y. (2007). Online data gathering for maximizing network lifetime in sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 6(1), 2–11.
Nikoletseas, S., & Rolim, J. (2011). Optimal data gathering paths and energy-balance mechanisms in wireless networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 9(6), 1036–1048.
Dagher, J. C., Marcellin, M. W., & Neifeld, M. A. (2007). A theory for maximizing the lifetime of sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 55(2), 323–332.
Mamalis, B., Gavalas, D., Konstantopoulos, C., & Pantziou, G. (2009). Clustering in wireless sensor networks. In Y. Zhang, L. T. Yang, J. Chen (Eds.), RFID and sensor networks: Architectures, protocols, security and integrations, Chap. 12 (pp. 324–353). New York: CRC Press.
Meyer, F. (1994). Topographic distance and watershed lines. Signal Processing, 38, 113–125.
Moga, A., Cramariuc, B., & Gabbouj, M. (1998). Parallel watershed transformation algorithms for image segmentation. Parallel Computing, 24, 1981–2001.
Trieu, D., & Maruyama, T. (2007). Real-time image segmentation based on a parallel and pipelined watershed algorithm. Real-Time Image Processing, 2, 319–329.
Helsgaun, K. (2000). An effective implementation of the Lin-Kernighan traveling salesman heuristic. European Journal of Operational Research, 126(1), 106–130.
Lin, S., & Kernighan, B. W. (1973). An effective heuristic algorithm for the traveling-salesman problem. Operations Research, 21(2), 498–516.
Sugihara, R., & Gupta, R. K. (2008). Improving the data delivery latency in sensor networks with controlled mobility. In Proceedings of international conference on distributed computing in sensor systems, LNCS 5067 (pp. 386–399). New York: Springer.
Acknowledgments
This research has been co-financed by the European Union (European Social Fund—ESF) and Greek national funds through the Operational Program “Education and Lifelong Learning” of the National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF)—Research Funding Program: Archimedes III. Investing in knowledge society through the European Social Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konstantopoulos, C., Mamalis, B., Pantziou, G. et al. An image processing inspired mobile sink solution for energy efficient data gathering in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Netw 21, 227–249 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-014-0779-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-014-0779-x