Abstract
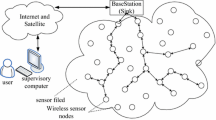
In wireless sensor networking applications, collecting sensed data and relaying it to the base station in an energy efficient manner is of paramount importance. It follows that power management and energy-efficient communication techniques become necessary to maximize network lifetime for wireless sensor networks (WSNs). In this paper, our objective is to distribute energy consumption evenly and maximize the network lifetime by utilizing data aggregation and in-network compression technique. We mainly focus on the combined problem of data routing with data aggregation during routing such that minimizing the number of packets to transmit and achieve our objective. We propose a multi chain routing algorithm executed with compressive sensing for data aggregating in WSNs. We show that by using our compressive sensing based routing algorithm significant reduction in data traffic can be achieved, resulting in power saving and thus prolong the network lifetime.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heinzelman, W., Chandrakasan, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2002) Energy efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd annual Hawaii international conference, 2000, Vol. 2, pp. 3005–3014.
Chou, J., Petrovic, D., & Ramchandran, K. (2003). A distributed and adaptive signal processing approach toreducing energy consumption in sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE Infocom, pp. 1054–1062
Anastasi, Giuseppe, Conti, Marco, Di Francesco, Mario, & Passarella, Andrea. (2009). Energy conservation in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Ad Hoc Network, 7(3), 537–568.
Fasolo, E., Rossi, M., Widmer, J., & Zorzi, M. (2007). In-network aggregation techniques for wireless sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Wireless Communications, 14(2), 7087.
Ahn, G., Hong, S. G., Miluzzo, E., Campbell, A. T., & Cuomo, F. (2006). Funneling-MAC: A localized, sink-oriented MAC for boosting fidelity in sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 4th international conference on embedded networked sensor systems, Vol. 293, p. 306. doi:10.1145/1182807.1182837.
Boulis, A., Ganeriwal, S., & Srivastava, M. B. (2003). Aggregation in sensor networks: An energy-accuracy trade-off. In Proceedings of the 1st IEEE international workshop on sensor network protocols and applications, pp. 128-138. doi:10.1109/SNPA.2003.1203363.
Intanagonwiwat, C., Estrin, D., Govindan, R., & Heidemann, J. (2002). Impact of network density on data aggregation in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of 22nd international conference on distributed computing systems, pp. 457–458. doi:10.1109/ICDCS.2002.1022289.
Galluccio, L., Campbell, A. T., & Palazzo, S. (2005). Concert: Aggregation- based congestion control for sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on embedded networked sensor systems, pp. 274–275. doi:10.1145/1098918.1098951.
Galluccio, L., Palazzo, S., & Campbell, A. T. (2009). Modeling and designing efficient data aggregation in wireless sensor networks under entropy and energy bounds. International Journal of Wireless Information Networks, 16(175), 183.
Al-Karaki, J. N., & Kamal, A. E. (2004). Routing techniques in wireless sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Wireless Communications, 116(6), 6–28. doi:10.1109/MWC.2004.1368893.
Handy, M. J., Haase, M., & Timmermann, D. (2002). Low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy with deterministic cluster-head selection. In 4th international workshop on mobile and wireless communications network, 2002, pp. 368–372.
Lindsey, S., & Raghavendra, C. (2002). PEGASIS: Power efficient gathering in sensor information systems. Aerospace Conference Proceedings, 3, 1125–1130.
Meenu, M., & Techand Vandana, A. P. (2012). Modified PEGASIS in WSN to increase network life time. International Journal of Computer Applications (0975–8887), 52(19), 7–10.
Cui, J., & Valois, F. (2013). Data aggregation in wireless sensor networks: Compressing or Forecasting? Rapport de recherche, INRIA, RR-8362.
Donoho, D. (2006). Compressed sensing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52(4), 1289–1306.
Kolo, J. G., Shanmugam, S. A., Lim, D. W. G., Ang, L.-M., & Seng, K. P. (2012) An adaptive lossless data compression scheme for wireless sensor networks. Journal of Sensors, 2012, Article ID 539638, 20. doi:10.1155/2012/539638.
Chong, L., & Feng, W. (2009). Compressive data gathering for large-scale wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 15th annual international conference on mobile computing and networking, Beijing, China, 2009.
Luo, J., Xiang, L., & Rosenberg, C. (2010). Does compressed sensing improve the throughput of wireless sensor networks? In ICC, pp. 1–6. IEEE.
Xiang, L., Luo, J., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2011). Compressed data aggregation for energy efficient wireless sensor networks. In SECON, pp. 46–54. IEEE.
Haupt, J., Bajwa, W. U., Rabbat, M., & Nowak, R. (2008). Compressed sensing for networked data. IEEE on Signal Processing Magazine, 25(2), 92–101.
Duarte, M. F., Sarvotham, S., Wakin, M. B., Baron, D., & Baraniuk, R. G. (2005). Joint sparsity models for distributed compressed sensing. In Online Proceedings of the workshop on signal processing with adaptative sparse structured representations (SPARS), Rennes, France.
Wu, X., & Liu, M. (2012). In-situ soil moisture sensing: Measurement scheduling and estimation using compressive sensing. In F. Zhao, A. Terzis, K. Whitehouse, (Eds.), IPSN (pp. 1–12). New York: ACM.
Wang, J., Tang, S., Yin, B., & Li, X.-Y. (2012). Data gathering in wireless sensor networks through intelligent compressive sensing. In A. G. Greenberg, K. Sohraby, (Eds.), INFOCOM, pp. 603–611. IEEE.
Zheng, H., Xiao, S., Wang, X., & Tian, X. (2012). Energy and latency analysis for in-network computation with compressive sensing in wireless sensor networks. In A. G. Greenberg, K. Sohraby, (Eds.), INFOCOM, pp. 2811–2815. IEEE.
Baron, D., Duarte, M. F., Sarvotham, S., Wakin, M. B., & Baraniuk, R. G. (2005) An information theoretic approach to distributed compressed sensing. In Allerton conference on communication, control, and computing, Allerton, IL, September 2005.
Choi, K., Wang, J., Zhu, L., Suh, T. S., Boyd, S., & Xing, L. (2010). Compressed sensing based cone-beam computed tomography reconstruction with a first-order method. Medical Physics, 37, 5113–5125.
Cand‘es, E., & Tao, T. (2006). Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52(2), 489–509.
Donoho, D. (2006). Compressed sensing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52(4), 1289–1306.
Tropp, J. A., & Gilbert, A. C. (2007). Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 53(12), 4655–4666.
Ali, S. A. E.-F., Refaay, S. K. (2012). Chain based fault tolerant routing protocols. Network Protocols and Algorithms, 4(3) 79–103.
Intel Berkely Reseach Lab (IBRL) dataset, 2004, http://db.csail.mit.edu/labdata/labdata.html.
Werner-Allen, G., Lorincz, K., Ruiz, M., Marcillo, O., Johnson, J., Lees, J., et al. (2006). Deploying a wireless sensor network on an active volcano. In IEEE internet computing, special issue on data- driven applications in sensor networks, March/April 2006.
Li, G., He, J., & Fu, Y. (2008). Group-based intrusion detection system in wireless sensor networks. Computer Communications, 31, 4324–4332.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salim, A., Osamy, W. Distributed multi chain compressive sensing based routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Netw 21, 1379–1390 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-014-0852-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-014-0852-5