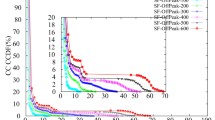
Abstract
Speed variation is one of the main challenges in deriving the connectivity related predictions in mobile ad-hoc networks, especially in vehicular ad hoc networks (VANETs). In such a dynamic network, a piece of information can be rapidly propagated through dedicated short-range communication, or can be carried by vehicles when multihop connectivity is unavailable. This paper proposes a novel analytical model that carefully computes the connectivity distance for a single direction of a free-flow highway. The proposed model adopts a time-varying vehicular speed assumption and mathematically models the mobility of vehicles inside connectivity. According to the dynamic movability scenario, a novel and accurate closed form formula is proposed for probability density function of connectivity. Moreover, using vehicular spatial distribution, joint Poisson distribution of vehicles in a multilane highway and tail probability of the expected number of vehicles inside single lane in a multilane highway are mathematically investigated. The accuracy of analytical results is verified by simulation. The concluded results provide helpful insights towards designing new applications and improving performance of existing applications on VANETs.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jakubiak, J., & Koucheryavy, Y. (2008). State of the art and research challenges for VANETs. In Proceedings of 5th IEEE consumer communications and networking conference (pp. 912–916).
Blum, J., Eskandarian, A., & Hoffman, L. (2004). Challenges of intervehicle ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 5(4), 347–351.
Li, F., & Wang, Y. (2007). Routing in vehicular ad hoc networks: A survey. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2(2), 12–22.
Toor, Y., Muhlethaler, P., & Laouiti, A. (2008). Vehicle ad hoc networks: applications and related technical issues. Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 10(3), 74–88.
Yena, Y. S., Chaob, H. C., Changd, R. S., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2011). Flooding-limited and multi-constrained QoS multicast routing based on the genetic algorithm for MANETs. Mathematical and Computer Modeling, 53(11–12), 2238–2250.
Linfoot, S., Adarbah, H. Y., Arafeh, B., & Duffy, A. (2013). Impact of physical and virtual carrier sensing on the route discovery mechanism in noisy MANETs. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 59(3), 515–520.
Zeadally, S., Hunt, R., Chen, Y. S., Irwin, A., & Hassan, A. (2012). Vehicular ad hoc networks (VANETS): Status, results, and challenges. Telecommunication System, 50(4), 217–241.
Ahmed, Z., Jamal, H., Khan, S., Mehboob, R., & Ashraf, A. (2009). Cognitive communication device for vehicular networking. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 55(2), 371–375.
Viriyasitavat, W., Boban, M., Tsai, H. M., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2015). Vehicular communications: Survey and challenges of channel and propagation models. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 10(2), 55–66.
Jiau, M. K., Huang, S. C., Hwang, J. N., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2015). Multimedia services in cloud-based vehicular networks. IEEE Intelligent Transportation System Magazine, 7(3), 62–79.
Zhang, Z., Mao, G., & Anderson, B. D. O. (2011). On the Information propagation process in mobile vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 60(5), 2314–2325.
Agarwal, A., Starobinski, D., & Little, T. D. C. (2012). Phase transition of message propagation speed in delay-tolerant vehicular networks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 13(1), 249–263.
Liu, Y., Xiong, N., Zhao, Y., Vasilakos, A. V., Gao, J., & Jia, Y. (2010). Multi-layer clustering routing algorithm for wireless vehicular sensor networks. IET Communications, 4(7), 810–816.
Woungang, I., Dhurandher, S. K., Anpalagan, A., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2013). Routing in opportunistic networks. New York: Springer.
Meng, T., Wu, F., Yang, Z., Chen, G., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2015). Spatial reusability-aware routing in multi-hop wireless networks. Computers, IEEE Transactions on Computers,. doi:10.1109/TC.2015.2417543
Zhou, J., Dong, X., Cao, Z., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2015). Secure and privacy preserving protocol for cloud-based vehicular DTNs. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 10(6), 1299–1314.
Dvir, A., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2011). Backpressure-based routing protocol for DTNs. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 41(4), 405–406.
Zeng, Y., Xiang, K., Li, D., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2013). Directional routing and scheduling for green vehicular delay tolerant networks. Wireless Networks, 19(2), 161–173.
Spyropoulos, T., Rais, R. N. B., Turletti, T., Obraczka, K., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2010). Routing for disruption tolerant networks: Taxonomy and design. Wireless Networks, 16(8), 2349–2370.
Vasilakos, A. V., Zhang, Y., & Spyropoulos, T. (2012). Delay tolerant networks: Protocols and applications. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Yousefi, S., Altman, E., El-Azouzi, R., & Fathy, M. (2008). Analytical model for connectivity in vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 57(6), 3341–3356.
Ho, I. W. H., & Leung, K. K. (2007). Node connectivity in vehicularad hoc networks with structuredmobility. In Proceedings of 32nd IEEE conference on local computer networks (pp. 635–642).
Spanos, D. P., & Murray, R. M. (2004). Robust connectivity of networked vehicles. In Proceedings of 43rd IEEE conference on decision and control (Vol. 3, pp. 2893–2898).
Artimy, M. M., Phillips, W. J. & Robertson, W. (2005). Connectivity with static transmission range in vehicular ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of 3rd annual communication networks and services research conference (pp. 237–242).
Khabazian, M., & Ali, M. K. M. (2008). A performance modeling of connectivity in vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 57(4), 2440–2450.
Artimy, M. M., Robertson, W., & Phillips, W. J. (2004). Connectivity in inter-vehicle ad hoc networks. Proceedings of the Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, 1, 293–298.
Zhang, Z., Mao, G., & Anderson, B. D. O. (2014). Stochastic characterization of information propagation process in vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 15(1), 122–135.
Baccelli, E., Jacquet, P., Mans, B., & Rodolakis, G. (2012). Highway vehicular delay tolerant networks: Information propagation speed properties. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 58(3), 1743–1756.
Chen, C., Du, X., Pei, Q., & Jin, Y. (2013). Connectivity analysis for free-flow traffic in VANETs: A statistical approach. Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks. doi:10.1155/2013/598946.
Chen, C., Liu, L., Du, X. B., Wei, X. L., & Pei, C. X. (2012). Available connectivity analysis under free flow state in VANETs. EURASIP Journal of Wireless Communications and Networking. doi:10.1186/1687-1499-2012-270.
Cheng, L., & Panichpapiboon, S. (2012). Effects of intervehicle spacing distributions on connectivity of VANET: A case study from measured highway traffic. IEEE Communications Magazine, 50(10), 90–97.
Durrani, S., Zhou, X., & Chandra, A. (2010). Effect of vehicle mobility on connectivity of vehicular ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 72nd vehicular technology conference (pp. 1–5).
Kafsi, M., Papadimitratos, P., Dousse, O., Alpcan, T., & Hubaux, J. P. (2008). Vanet connectivity analysis. IEEE Workshop on Automotive Networking and Applications.
Nagel, R. (2010). The effect of vehicular distance distributions andmobility on VANET communications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, San Diego, Calif, USA (pp. 1190–1194).
Cardote, A., Sargento, S., & Steenkiste, P. (2010). On the connection availability between relay nodes in a VANET. In Proceedings of IEEE globecom workshops, Miami (pp. 181–185).
Wu, H., Fujimoto, R. M., Riley, G. F., & Hunter, M. (2009). Spatial propagation of information in vehicular networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(1), 420–443.
Leutzbach, W. (1998). Introduction to the theory of traffic flow. NewYork: Springer.
Godehardt, E., & Jaworski, J. (1996). On the connectivity of a random interval graph. Random Structure and Algorithms, 9(1/2), 137–161.
Hall, P. (1998). Introduction to the theory of coverage processes. Hoboken: Wiley.
TalebiFard, P., Leung, V. C. M., Amadeo, M., Campolo, C., & Molinaro, A. (2015). Information-centric networking for VANETs. Chapter vehicular ad hoc networks (pp. 503–524). Switzerland: Springer.
Quan, W., Xu, C., Vasilakos, A. V., Guan, J., Zhang, H., & Grieco, L. A. (2014). TB2F: Tree-bitmap and bloom-filter for a scalable and efficient name lookup in content-centric networking. In Proceedings of IEEE IFIP networking conference, Trondheim (pp. 1–9).
Rahimi, M. R., Ren, J., Liu, C. H., Vasilakos, A. V., & Venkatasubramanian, N. (2014). Mobile cloud computing: A survey, state of art and future directions. Mobile Networks and Applications, 19(2), 133–143.
Wang, X., Vasilakos, A. V., Chen, M., Liu, Y., & Kwon, T. T. (2012). A survey of green mobile networks: Opportunities and challenges. Mobile Networks and Applications, 17(1), 4–20.
Yang, M., Li, Y., Jin, D., Zeng, L., Wu, X., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2015). Software-defined and virtualized future mobile and wireless networks: A survey. ACM/Springer Mobile Networks and Applications, 20(1), 4–18.
Vasilakos, A. V., Li, Z., Simon, G., & You, W. (2015). Information centric network: Research challenges and opportunities. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 52, 1–10.
Li, P., Guo, S., Yuy, S., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2012). CodePipe: An opportunistic feeding and routing protocol for reliable multicast with pipelined network coding. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM (pp. 100–108).
Youssef, M., Ibrahim, M., Abdelatif, M., Chen, L., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2014). Routing metrics of cognitive radio networks: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 16(1), 92–109.
Yao, Y., Cao, Q., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2013). EDAL: An energy-efficient, delay-aware, and lifetime-balancing data collection protocol for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE 10th international conference on mobile ad-hoc and sensor systems (pp. 182–190).
Zhang, X. M., Zhang, Y., Yan, F., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2015). Interference-based topology control algorithm for delay-constrained mobile ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 14(4), 742–754.
Rudack, M., Meincke, M., & Lott, M. (2002). On the dynamics of ad hoc networks for inter vehicle communications (IVC). Las Vegas: In proceedings of ICWN.
Roess, P. P., Prassas, E. S., & McShane, W. R. (2004). Traffic engineering. New Jersey: Pearson/Prentice Hall.
Ross, S. M. (2011). Introduction to probability models (10th ed.). New York: Elsevier.
Yan, Z., Jiang, H., Shen, Z., Chang, Y., & Huang, L. (2012). k-Connectivity analysis of one-dimensional linear VANETs. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 61(1), 426–433.
Liu, L., Song, Y., Zhang, H., Ma, H., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2015). Physarum optimization: A biology-inspired algorithm for the Steiner tree problem in networks. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 64(3), 819–832.
Li, P., Guo, S., Yu, S., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2014). Reliable multicast with pipelined network coding using opportunistic feeding and routing. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 25(12), 3264–3273.
Song, Y., Liu, L., Ma, H., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2014). A biology-based algorithm to minimal exposure problem of wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 11(3), 417–430.
Zhang, Z. Vehicular ad hoc networks. (2013). [Online]. http://zijie.net/manet/vanet/
Zarei, M., Rahmani, A. M., & Farazkish, R. (2011). CCTF: Congestion control protocol based on trustworthiness of nodes in wireless sensor networks using fuzzy logic. International Journal of Ad Hoc and Ubiquitous Computing, 8(1/2), 54–63.
Zarei, M., Rahmani, A. M., Farazkish, R., & Zahirnia, S. (2010). FCCTF: Fairness congestion control for a disTrustful wireless sensor network using fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of IEEE 10th international conference on hybrid intelligent systems (pp. 1–6).
Zarei, M., Rahmani, A. M., Sasan, A., & Teshnehlab, M. (2009). Fuzzy based trust estimation for congestion control in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on intelligent networking and collaborative systems (pp. 233–236).
Vasilakos, A. V., Saltouros, M. P., Atlassis, A. F., & Pedrycz, W. (2003). Optimizing QoS routing in hierarchical ATM networks using computational intelligence techniques. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics—Part C Applications and Reviews, 33(3), 297–312.
Acampora, G., Gaeta, M., Loia, V., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2010). Interoperable and adaptive fuzzy services for ambient intelligence applications. ACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive Systems (TAAS), 5(2), 8.
Manvaha, S., Srinivasan, D., Tham, C. K., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2004). Evolutionary fuzzy multi-objective routing for wireless mobile ad hoc networks. CEC2004 Congress on Evolutionary Computation, 2, 1964–1971.
Xiang, L., Luo, J. & Vasilakos, A. V. (2011). Compressed data aggregation for energy efficient wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of 8th annual IEEE communications society conference on sensor, mesh and ad hoc communications and networks (pp. 46–54).
Duarte, P. B. F., Fadlullah, Z Md, Vasilakos, A. V., & Kato, N. (2012). On the partially overlapped channel assignment on wireless mesh network backbone: A game theoretic approach. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 30(1), 119–127.
Busch, C., Kannan, R., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2012). Approximating congestion+ dilation in networks via “Quality of Routing” games. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 61(9), 1270–1283.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zarei, M., Rahmani, A.M. & Samimi, H. Connectivity analysis for dynamic movement of vehicular ad hoc networks. Wireless Netw 23, 843–858 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-1189-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-1189-4