Abstract
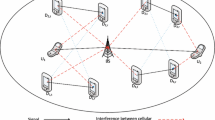
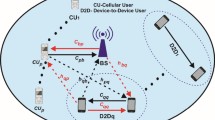
Underlaying device-to-device (D2D) communication is suggested as a promising technology for the next generation cellular networks (5G), where users in close proximity can transmit directly to one another bypassing the base station. However, when D2D communications underlay cellular networks, the potential gain from resource sharing is highly determined by how the interference is managed. In order to mitigate the resource reuse interference between D2D user equipment and cellular user equipment in a multi-cell environment, we propose a resource allocation scheme and dynamic power control for D2D communication underlaying uplink cellular network. Specifically, by introducing the fractional frequency reuse (FFR) principle into the multi-cell architecture, we divide the cellular network into inner region and outer region. Combined with resource partition method, we then formulate the optimization problem so as to maximize the total throughput. However, due to the coupled relationship between resource allocation and power control scheme, the optimization problem is NP-hard and combinational. In order to minimize the interference caused by D2D spectrum reuse, we solve the overall throughput optimization problem by dividing the original problem into two sub-problems. We first propose a heuristic resource pairing algorithm based on overall interference minimization. Then with reference to uplink fractional power control (FPC), a dynamic power control method is proposed. By introducing the interference constraint, we use a lower bound of throughput as a cost function and solve the optimal power allocation problem based on dual Lagrangian decomposition method. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves efficient performance compared with existing methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
3GPP TS 36.300, v9.9.0, Rel.9, in Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) and Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN), overall description 2013.
IMT-2020 (5G) Promotion Group. White Paper on 5G Wireless Technology Architecture, 2015.05. http://www.imt-2020.cn/.
Gupta, A., & Jha, R. K. A. (2015). Survey of 5G network: architecture and emerging technologies. IEEE Access, 3, 1206–1232.
Wei, L. L., Hu, R. Q., Qian, Y., et al. (2014). Enable device-to-device communications underlaying cellular networks: challenges and research aspects. IEEE Communication Magazine, 52(6), 90–96.
Doppler, K., Rinne, M. P., Janis, P., et.al. (2009). Device-to-device communications; functional prospects for LTE-advanced networks. In IEEE international conference on communications workshops (ICC Workshops 2009), pp. 1–6.
3GPP TR 23.703 v0.5, Rel 12, in Technical Specification Group Services and System Aspects, Study on architecture enhancements to support Proximity Services (ProSe), June 2013.
Wireless World Initiative New Radio—WINNER+ D2.1, Preliminary WINNER+ System Concept, May 2009.
Feng, D. Q., Lu, L., Wu, Y. Y., et al. (2013). Device-to-device communications underlaying cellular Networks. IEEE Transaction on Communications, 61(8), 3541–3551.
Qiao, J., Shen, X. S., Mark, J. W., et al. (2015). Enabling device-to-device communications in millimeter-wave 5G cellular networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(1), 209–215.
Lee, N., Lin, X., Andrews, J. G., et al. (2015). Power control for D2D underlaid cellular networks: Modeling, algorithms, and analysis. IEEE Journal on in Selected Areas in Communications, 33(1), 1–13.
Zhang, G. P., Yang, K., Liu, P., et al. (2015). Power allocation for full-duplex relaying-based D2D communication underlaying cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 64(10), 4911–4916.
Azam, M., Ahmad, M., Naeem, M., et al. (2015). Joint admission control, mode selection and power allocation in D2D communication systems. IEEE Transaction on Vehicular Technology, 9, 1–13.
Gu, J., Jae Bae, S., Choi, B.-G., et al. (2011). Dynamic power control mechanism for interference coordication of device-to-device communication in cullular networks. In 2011 third international conference on ubiquitous and future networks (ICUFN 2011), pp. 71–75.
Essassi, S., Siala, M., & Cherif, S. (2011). Dynamic fractional power control for LTE uplink. In 2011 IEEE 22nd international symposium on personal indoor and mobile radio communications (PIMRC 2011), pp. 1606–1610.
Zhang, Z. K., Hu, Q., Qian, Y., et al. (2015). D2D communication underlay in uplink cellular networks with fractional power control and fractional frquency reuse. In 2015 IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM), San Diego, USA, pp. 1–7.
Novlan, T. D., Ganti, R. K., Ghosh, A., et al. (2011). Analytical evaluation of fractional frequency reuse for OFDMA cellular networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(12), 4294–4305.
Chae, H., Gu, J., Choi, B., et al. (2011). Radio resource allocation scheme for device-to-device communication in cellular networks using fractional frequency reuse. In 2011 17th Asia-Pacific conference on communications (APCC 2011), Sabah, Malaysian, pp. 58–62.
Zhu, H., & Wang, J. (2014). Device-to-device communication in cellular networks with fractional frequency reuse. In 2014 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC 2014), Sydney, Australia, pp. 5503–5507.
Janis, P., Koivunen, V., Ribeiro, C., et al. (2009). Interference-aware resource allocation for device-to-device radio underlaying cellular networks. In 2009 IEEE 69th vehicular technology conference (VTC Spring), Barcelona, spain, pp. 1–5.
Xing, C. W., Ma, S. D., Fei, Z. S., et al. (2013). A general robust linear transceiver design for Amplify-and-Forward multi-hop MIMO relaying systems. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 61(5), 1196–1209.
Mumtaz, S., & Rodriguez, J. (Eds.). (2014). Smart device to smart device communication (pp. 1–7). Switzerland: Springer.
Nokia Corporation. (2010). Method and apparatus for providing interference measurement for D2D communication. US, A1, Pub. No: 2010/0093364.
Xing, C. W., Ma, S. D., & Zhou, Y. Q. (2015). Matrix-monotonic optimization for MIMO Systems. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 63(2), 334–348.
Wang, L., & Wu, H. Q. (2014). Fast pairing of device-to-device link underlay for spectrum sharing with cellular users. IEEE Communications Letters, 18(10), 1803–1806.
Zhang, Y., Xu, Y., Gao, M., et al. (2015). Resource management in device-to-device underlaying cellular network. In 2015 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), New Orleans, USA, pp. 1631–1636.
Dahlman, E., Prakvall, S., Skold, J., & Beming, P. (2008). 3G evolution HSPA and LTE for mobile broadband. Burlington: Elsevier.
3GPP TS 36.101 V8.4.0. Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRAN): User Equipment(UE) radio transmission and reception (Release 8). December 2008.
Sesia, S., Toufik, I., Baker, M. (2011). LTE-The UMTS Long Term Evolution From Theory to Practice (2nd ed.). Wiley.
Zhao, N., Yu, F. R., Sun, H., et al. (2016). Adaptive power allocation schemes for spectrum sharing in interference-alignment-based cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 65(5), 3700–3714.
Wang, J., Zhu, D., Zhao, C., et al. (2013). Resource sharing of underlaying device-to-device and uplink cellular communications. IEEE Communications Letters, 17(6), 1148–1151.
Zhao, W., & Wang, S. (2014). Low complexity power allocation for device-to-device communication underlaying cellular networks. In 2014 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC), Sydney, Australia, pp. 5532–5537.
Moghaddam, M. H., Mohamed-pour, K., & Andargoli, S. M. H. (2016). Weighted sum throughput maximisation for cooperative relay-aided multi-cell orthogonal frequency division multiple access cellular networks considering partial fairness. IET Communications, 10(7), 778–789.
Stephen, B., & Lieven, V. (2003). Convex optimization. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Seong, K. (2008). Cross layer resource allocation for multi-user communication systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University.
3GPP TR36.814V0.4.1, Physical layer aspects for evolved UTRA. http://www.3gpp.org.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61501371), National 863 High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Project Number: 2014AA01A703), National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China(Project Number: 2014ZX03001025-006), The International Exchange and Cooperation Projects of Shaanxi Province (Project Number: 2016KW-046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, F., Wang, Bc., Sun, Cy. et al. Resource allocation and dynamic power control for D2D communication underlaying uplink multi-cell networks. Wireless Netw 24, 549–563 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1351-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1351-7