Abstract
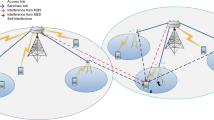
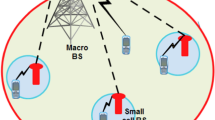
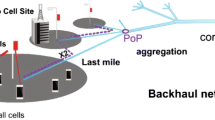
With the dense deployment of small cell networks, low-cost backhaul schemes for small cell base stations (SBSs) have attracted great attentions. Self-backhaul using cellular communication technology is considered as a promising solution. Although some excellent works have been done on self-backhaul in small cell networks, most of them do not consider the recent advances of full-duplex (FD) and massive multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) technologies. In this paper, we propose a self-backhaul scheme for small cell networks by combining FD and massive MIMO technologies. In our proposed scheme, the macro base station (MBS) is equipped with massive MIMO antennas, and the SBSs have the FD communication ability. By treating the SBSs as special macro users, we can achieve the simultaneous transmissions of the access link of users and the backhaul link of SBSs in the same frequency. Furthermore, considering the existence of inter-tier and intra-tier interference, we formulate the power allocation problem of the MBS and SBSs as an optimization problem. Because the formulated power allocation problem is a non-convex problem, we transform the original problem into a difference of convex program by successive convex approximation method and variable transformation, and then solve it using a constrained concave convex procedure based iterative algorithm. Finally, extensive simulations are conducted with different system configurations to verify the effectiveness of the proposed scheme.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
To simplify the network model, single-antenna SBS is assumed in this paper and the works of this paper can be expanded to small cell networks with multi-antenna SBS by involving multi-antenna channel model.
References
Alcatel-Lucent. (2011). The declining profitability trend of mobile data: What can be done? Assessing network costs and planning for sustainable revenue growth. Market Analysis, Tech. Rep.
Fortes, S., Aguilar-Garcia, A., Barco, R., Barba, F., Fernandez-luque, J., & Fernandez-Duran, A. (2015). Management architecture for location-aware self-organizing LTE/LTE-a small cell networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(1), 294–302.
Hoadley, J., & Maveddat, P. (2012). Enabling small cell deployment with HetNet. IEEE Wireless Communiations, 19(2), 4–5.
Xu, J., Wang, J., Zhu, Y., Yang, Y., Zheng, X., Wang, S., et al. (2014). Cooperative distributed optimization for the hyper-dense small cell deployment. IEEE Communications Magazine, 52(5), 61–67.
Ranaweera, C., Resende, M., Reichmann, K., Iannone, P., Henry, P., Kim, B.-J., et al. (2013). Design and optimization of fiber optic small-cell backhaul based on an existing fiber-to-the-node residential access network. IEEE Communications Magazine, 51(9), 62–69.
Ranaweera, C., Iannone, P., Oikonomou, K., & Reichmann, K. (2013). Design of cost-optimal passive optical networks for small cell backhaul using installed fibers. IEEE/OSA Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 5(10), A230–A239.
Hur, S., Kim, T., Love, D., Krogmeier, J., Thomas, T., & Ghosh, A. (2013). Millimeter wave beamforming for wireless backhaul and access in small cell networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61(10), 4391–4403.
Taori, R., & Sridharan, A. (2015). Point-to-multipoint in-band mmwave backhaul for 5G networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(1), 195–201.
Mahloo, M., Monti, P., Chen, J., & Wosinska, L. (2014). Cost modeling of backhaul for mobile networks. In ICC Workshops, pp. 397–402.
Sabharwal, A., Schniter, P., Guo, D., Bliss, D. W., Rangarajan, S., & Wichman, R. (2014). In-band full-duplex wireless: Challenges and opportunities. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 32(9), 1637–1652.
Bladsjo, D., Hogan, M., & Ruffini, S. (2013). Synchronization aspects in LTE small cells. IEEE Communications Magazine, 51(9), 70–77.
Hui, D., & Axnas, J. (2013). Joint routing and resource allocation for wireless self-backhaul in an indoor ultra-dense network. In Proceedings of IEEE PIMRC, pp. 3083–3088.
Erwu, L., Shan, J., Gang, S., & Luoning, G. (2006). Fair scheduling in wireless multi-hop self-backhaul networks. In Proceedings of AICT-ICIW, pp. 96–96.
Magee, A. (2010). Synchronization in next-generation mobile backhaul networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 48(10), 110–116.
Liu, G., Yu, F., Ji, H., Leung, V., & Li, X. (2015). In-band full-duplex relaying: A survey, research issues and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 17(2), 500–524.
Suraweera, H. A., Krikidis, I., Zheng, G., Yuen, C., & Smith, P. J. (2014). Low-complexity end-to-end performance optimization in MIMO full-duplex relay systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(2), 913–927.
Krikidis, I., Suraweera, H. A., Smith, P. J., & Yuen, C. (2012). Full-duplex relay selection for amplify-and-forward cooperative networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(12), 4381–4393.
Pitaval, R. A., Tirkkonen, O., Wichman, R., Pajukoski, K., Lahetkangas, E., & Tiirola, E. (2015). Full-duplex self-backhauling for small-cell 5G networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 22(5), 83–89.
Lu, L., Li, G., Swindlehurst, A., Ashikhmin, A., & Zhang, R. (2014). An overview of massive mimo: Benefits and challenges. IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications, 8(5), 742–758.
Hoydis, J., Ten Brink, S., & Debbah, M. (2013). Massive MIMO in the UL/DL of cellular networks: How many antennas do we need? IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications, 31(2), 160–171.
Hoydis, J., Hosseini, K., ten Brink, S., & Debbah, M. (2013). Making smart use of excess antennas: Massive MIMO, small cells, and TDD. Bell Labs Technical Journal, 18(2), 5–21.
Qian, L. P., Zhang, Y. J., Wu, Y., & Chen, J. (2013). Joint base station association and power control via benders’ decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(4), 1651–1665.
Lakshminarayana, S., Assaad, M., & Debbah, M. (2015). Transmit power minimization in small cell networks under time average QoS constraints. IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications, 33(10), 2087–2103.
Soh, Y. S., Quek, T., Kountouris, M., & Shin, H. (2013). Energy efficient heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications, 31(5), 840–850.
Rusek, F., Persson, D., Lau, B. K., Larsson, E., Marzetta, T., Edfors, O., et al. (2013). Scaling up MIMO: Opportunities and challenges with very large arrays. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 30(1), 40–60.
Jiang, Z., Molisch, A., Caire, G., & Niu, Z. (2015). Achievable rates of FDD massive MIMO systems with spatial channel correlation. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 14(5), 2868–2882.
Gao, Z., Dai, L., Dai, W., & Wang, Z. (2015). Block compressive channel estimation and feedback for FDD massive MIMO. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM WKSHPS 2015, pp. 49–50.
Yoo, T., & Goldsmith, A. (2006). On the optimality of multiantenna broadcast scheduling using zero-forcing beamforming. IEEE Journal of Selected Areas in Communications, 24(3), 528–541.
Riihonen, T., Werner, S., & Wichman, R. (2011). Mitigation of loopback self-interference in full-duplex MIMO relays. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 59(12), 5983–5993.
He, C., Sheng, B., Zhu, P., & You, X. (2012). Energy efficiency and spectral efficiency tradeoff in downlink distributed antenna systems. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 1(3), 153–156.
Papandriopoulos, J., & Evans, J. (2009). SCALE: A low-complexity distributed protocol for spectrum balancing in multiuser DSL networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 55(8), 3711–3724.
Julian, D., Chiang, M., O’Neill, D., & Boyd, S. (2002). QoS and fairness constrained convex optimization of resource allocation for wireless cellular and ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, Vol. 2, pp. 477–486.
Chiang, M., Tan, C. W., Palomar, D., O’Neill, D., & Julian, D. (2007). Power control by geometric programming. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 6(7), 2640–2651.
Boyd, S., & Vandenberghe, L. (2009). Convex optimization. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
An, L.T.H. (2003). DC programming for solving a class of global optimization problems via reformulation by exact penalty. In Proceedings of first international workshop on global constraint optimization and constraint satisfaction (pp. 87–101). Springer.
Horst, R., & Thoai, N. V. (1999). DC programming: Overview. Journal of Optimization Theory and Application, 103(1), 1–43.
Smola, A. J., Vishwanathan, S. V. N., & Hofmann, T. (2005). Kernel methods for missing variables. Tenth International Workshop on Artificial Intelligence & Statistics (pp. 325–332).
Lanckriet, G. R., & Sriperumbudur, B. K. (2009). On the convergence of the concave–convex procedure. In Proceedings of advances in neural information processing systems, pp. 1759–1767.
Li, H., & Adali, T. (2008). Complex-valued adaptive signal processing using nonlinear functions. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2008, 1–9.
Cheng, Y., & Pesavento, M. (2012). Joint optimization of source power allocation and distributed relay beamforming in multiuser peer-to-peer relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 60(6), 2962–2973.
Bornhorst, N., Pesavento, M., & Gershman, A. (2012). Distributed beamforming for multi-group multicasting relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 60(1), 221–232.
Winston, W. L., & Goldberg, J. B. (2004). Operations research: Applications and algorithms. Boston: Duxbury Press.
Yan, L., Bai, B., & Chen, W. (2014). On energy efficiency maximization in downlink MIMO systems exploiting multiuser diversity. IEEE Communications Letters, 18(12), 2161–2164.
Yang, Y., Quek, T., & Duan, L. (2014). Backhaul-constrained small cell networks: Refunding and QoS provisioning. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(9), 5148–5161.
Jin, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2010). Joint source and relay power optimization in multiuser cooperative wireless networks. In Proceedings of 4th International Symposium on Communications, Control and Signal Processing (ISCCSP), pp. 1–4.
Acknowledgments
This paper is jointly supported by the Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (National 863 Program) under Grant 2014AA01A701 and National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61271182.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Yu, F.R., Ji, H. et al. Power allocation in small cell networks with full-duplex self-backhauls and massive MIMO. Wireless Netw 24, 1083–1098 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1381-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1381-1