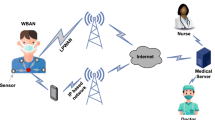
Abstract
According to the World Health Organization, most of the world population is affected by chronic diseases, obesity, cardiovascular diseases and diabetes while another dominant problem is of aging population. Thus, it is desirable to have cost effective solutions for health monitoring, especially for countries that have minimum conventionally trained healthcare staff and infrastructure. Healthcare has shifted from hospital dominant services to patient dominant services which has thrived WBANs to provide ubiquitous health monitoring by virtue of wearable or implantable sensor nodes that commonly monitor biological signals. As the society becomes more health conscious, WBANs have the potential to revolutionize the way people integrate their health and information technology. Hence, WBANs are desired to strengthen conventional healthcare systems. Notwithstanding the current achievements, technological advances, proposed solutions and commercialized products; WBANs still experience many obstacles in their foolproof adoption. This paper surveys the plethora of WBAN applications and network architecture in detail used for data collection, data transmission and data analysis that form sensor analyst system in the realm of Internet of Things. Wireless communicational technologies are also discussed in this paper. Also, we have categorized the routing protocols and have provided with their critical qualitative analysis. Towards the end we discuss several projects in the field of WBANs and some open research areas. These findings on how the sensor nodes, newest routing protocols and data analysis techniques influence ubiquitous health monitoring sets this survey apart from the already existing surveys on WBANs.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
OECD Health Statistics 2017 (see http://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=SHA for recent updates).
Healthcare Industry in India 2017 (see https://www.ibef.org/industry/healthcare-india.aspx for recent updates).
References
2017 global health care outlook: Making progress against persistent challenges. https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/life-sciences-and-health-care/articles/global-health-care-sector-outlook.html. Accessed June 14, 2017.
Parkka, J., Ermes, M., Korpipaa, P., Mantyjarvi, J., Peltola, J., & Korhonen, I. (2006). Activity classification using realistic data from wearable sensors. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 10(1), 119–128.
Winkley, J., Jiang, P., & Jiang, W. (2012). Verity: An ambient assisted living platform. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 58(2), 364–373.
Leonov, V. (2013). Thermoelectric energy harvesting of human body heat for wearable sensors. IEEE Sensors Journal, 13(6), 2284–2291.
Poh, M. Z., Swenson, N. C., & Picard, R. W. (2010). Motion-tolerant magnetic earring sensor and wireless earpiece for wearable photoplethysmography. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 14(3), 786–794.
Zhang, T., Ser, W., Daniel, G. Y. T., Zhang, J., Yu, J., Chua, C., et al. (2010). Sound based heart rate monitoring for wearable systems. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Body Sensor Networks (pp. 139–143).
Shany, T., Redmond, S. J., Narayanan, M. R., & Lovell, N. H. (2012). Sensors-based wearable systems for monitoring of human movement and falls. IEEE Sensors Journal, 12(3), 658–670.
Kan, Y. C., & Chen, C. K. (2012). A wearable inertial sensor node for body motion analysis. IEEE Sensors Journal, 12(3), 651–657.
D’Angelo, L. T., Neuhaeuser, J., Zhao, Y., & Lueth, T. C. (2014). Simple-use sensor set for wearable movement and interaction research. IEEE Sensors Journal, 14(4), 1207–1215.
Yan, L., Bae, J., Lee, S., Roh, T., Song, K., & Yoo, H.-J. (2011). A 3.9 mw 25-electrode reconfigured sensor for wearable cardiac monitoring system. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 46(1), 353–364.
Ravanshad, N., Rezaee-Dehsorkh, H., Lotfi, R., & Lian, Y. (2014). A level-crossing based QRS-detection algorithm for wearable ECG sensors. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 18(1), 183–192.
Top 10 health care innovations: Achieving more for less. https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/de/Documents/life-sciences-health-care/Top-10-health-care-innovations-DE.pdf. Accessed December 14, 2017.
Tobón, D. P., Falk, T. H., & Maier, M. (2013). Context awareness in wbans: A survey on medical and non-medical applications. IEEE Wireless Communications, 20(4), 30–37.
Van Daele, P., Moerman, I., & Demeester, P. (2014). Wireless body area networks: Status and opportunities. In Proceedings of XXXIth IEEE General Assembly and Scientific Symposium (URSI GASS) (pp. 1–4).
Latré, B., Braem, B., Moerman, I., Blondia, C., & Demeester, P. (2011). A survey on wireless body area networks. Wireless Networks, 17(1), 1–18.
Hanson, M. A., Powell, H. C, Jr., Barth, A. T., Ringgenberg, K., Calhoun, B. H., Aylor, J. H., et al. (2009). Body area sensor networks: Challenges and opportunities. Computer, 42(1), 58.
Chen, M., Gonzalez, S., Vasilakos, A., Cao, H., & Leung, V. C. (2011). Body area networks: A survey. Mobile Networks and Applications, 16(2), 171–193.
Cao, H., Leung, V., Chow, C., & Chan, H. (2009). Enabling technologies for wireless body area networks: A survey and outlook. IEEE Communications Magazine, 47(12), 84–93.
Xu, X., Shu, L., Guizani, M., Liu, M., & Lu, J. (2015). A survey on energy harvesting and integrated data sharing in wireless body area networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2015, 1–18.
Zhang, Y., Sun, L., Song, H., & Cao, X. (2014). Ubiquitous wsn for healthcare: Recent advances and future prospects. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 1(4), 311–318.
Touati, F., & Tabish, R. (2013). U-healthcare system: State-of-the-art review and challenges. Journal of Medical Systems, 37(3), 9949.
Nadeem, A., Hussain, M. A., Owais, O., Salam, A., Iqbal, S., & Ahsan, K. (2015). Application specific study, analysis and classification of body area wireless sensor network applications. Computer Networks, 83, 363–380.
Rashid, B., & Rehmani, M. H. (2016). Applications of wireless sensor networks for urban areas: A survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 60, 192–219.
Ullah, S., Higgins, H., Braem, B., Latre, B., Blondia, C., Moerman, I., et al. (2012). A comprehensive survey of wireless body area networks. Journal of Medical Systems, 36(3), 1065–1094.
Li, M., Lou, W., & Ren, K. (2010). Data security and privacy in wireless body area networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 17(1), 51–58.
Movassaghi, S., Abolhasan, M., Lipman, J., Smith, D., & Jamalipour, A. (2014). Wireless body area networks: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 16(3), 1658–1686.
Castillejo, P., Martinez, J.-F., Rodriguez-Molina, J., & Cuerva, A. (2013). Integration of wearable devices in a wireless sensor network for an e-health application. IEEE Wireless Communications, 20(4), 38–49.
Penzel, T., Kemp, B., Klosch, G., Schlögl, A., Hasan, J., Varri, A., et al. (2001). Acquisition of biomedical signals databases. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, 20(3), 25–32.
Arnon, S., Bhastekar, D., Kedar, D., & Tauber, A. (2003). A comparative study of wireless communication network configurations for medical applications. IEEE Wireless Communications, 10(1), 56–61.
Hassan, M. M., Lin, K., Yue, X., & Wan, J. (2017). A multimedia healthcare data sharing approach through cloud-based body area network. Future Generation Computer Systems, 66, 48–58.
Diallo, O., Rodrigues, J. J., Sene, M., & Niu, J. (2014). Real-time query processing optimization for cloud-based wireless body area networks. Information Sciences, 284, 84–94.
Rolim, C. O., Koch, F. L., Westphall, C. B., Werner, J., Fracalossi, A., & Salvador, G. S. (2010). A cloud computing solution for patient’s data collection in health care institutions. In Proceedings of Second IEEE International Conference on e-Health, Telemedicine, and Social Medicine (ETELEMED’10) (pp. 95–99).
Pandey, S., Voorsluys, W., Niu, S., Khandoker, A., & Buyya, R. (2012). An autonomic cloud environment for hosting ecg data analysis services. Future Generation Computer Systems, 28(1), 147–154.
Rashid, Z., Farooq, U., Jang, J. K., & Park, S. H. (2011). Cloud computing aware ubiquitous health care system. In Proceedings of e-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB) (pp. 1–4).
Wan, J., Zou, C., Ullah, S., Lai, C.-F., Zhou, M., & Wang, X. (2013). Cloud-enabled wireless body area networks for pervasive healthcare. IEEE Network, 27(5), 56–61.
Almashaqbeh, G., Hayajneh, T., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2014). A cloud-based interference-aware remote health monitoring system for non-hospitalized patients. In Proceedings of IEEE Global Communications Conference (pp. 2436–2441).
Almashaqbeh, G., Hayajneh, T., Vasilakos, A. V., & Mohd, B. J. (2014). QoS-aware health monitoring system using cloud-based wbans. Journal of Medical Systems, 38(10), 1–20.
Parane, K. A., Patil, N. C., Poojara, S. R., & Kamble, T. S. (2014). Cloud based intelligent healthcare monitoring system. In Proceedings of International Conference on Issues and Challenges in Intelligent Computing Techniques (ICICT) (pp. 697–701).
Fortino, G., Di Fatta, G., Pathan, M., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2014). Cloud-assisted body area networks: State-of-the-art and future challenges. Wireless Networks, 20(7), 1925–1938.
Joshi, J., Kurian, D., Bhasin, S., Mukherjee, S., Awasthi, P., Sharma, S., et al. (2016). Health monitoring using wearable sensor and cloud computing. In Proceedings of International Conference on Cybernetics, Robotics and Control (CRC), (pp. 104–108).
Ghanavati, S., Abawajy, J., & Izadi, D. (2016). An alternative sensor cloud architecture for vital signs monitoring. In Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), (pp. 2827–2833).
Rachkidi, E., Cherkaoui, E. H., Ait-Idir, M., Agoulmine, N., Taher, N. C., Santos, M., et al. (2015). Cooperative dynamic e-health service placement in mobile cloud computing. In Proceedings of 17th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Application & Services (HealthCom) (pp. 627–632).
Rachkidi, E., Cherkaoui, E. H., Ait-Idir, M., Agoulmine, N., Taher, N. C., Santos, M., et al. (2015). Towards efficient automatic scaling and adaptive cost-optimized ehealth services in cloud. In Proceedings of IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 1–6).
Roopali, & Kumari, R. (2015). An efficient data offloading to cloud mechanism for smart healthcare sensors. In Proceedings of 1st IEEE International Conference on Next Generation Computing Technologies (NGCT) (pp. 90–95).
Quwaider, M., & Jararweh, Y. (2015). Smart community health awareness model. In Proceedings of 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Systems (ICICS), (pp. 228–233).
Akyildiz, I. F., & Vuran, M. C. (2010). Wireless sensor networks (1st ed.). New York: Wiley.
Sohraby, K., Minoli, D., & Znati, T. (2007). Wireless sensor networks: Technology, protocols, and applications (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Mukhopadhyay, S. C. (2015). Wearable sensors for human activity monitoring: A review. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(3), 1321–1330.
Liang, T., & Yuan, Y. J. (2016). Wearable medical monitoring systems based on wireless networks: A review. IEEE Sensors Journal, 16(23), 8186–8199.
Shebli, F., Dayoub, I., M’foubat, A. O., Rivenq, A., & Rouvaen, J. (2007). Minimizing energy consumption within wireless sensors networks using optimal transmission range between nodes. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications (pp. 105–108).
Cavallari, R., Martelli, F., Rosini, R., Buratti, C., & Verdone, R. (2014). A survey on wireless body area networks: Technologies and design challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 16(3), 1635–1657.
Seyedi, M., Kibret, B., Lai, D. T., & Faulkner, M. (2013). A survey on intrabody communications for body area network applications. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 60(8), 2067–2079.
Heinzelman, W. R., Chandrakasan, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2000). Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd IEEE Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (pp. 1–10).
Datta, N. (2014). Study and design of energy efficient block cipher for wireless body area networks (WBANs).
Hu, F., Liu, X., Shao, M., Sui, D., & Wang, L. (2017). Wireless energy and information transfer in wban: An overview. IEEE Network, 31(3), 90–96.
Huang, C., Zhang, R., & Cui, S. (2014). Optimal power allocation for outage probability minimization in fading channels with energy harvesting constraints. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 13(2), 1074–1087.
Zhou, X., Zhang, R., & Ho, C. K. (2013). Wireless information and power transfer: Architecture design and rate-energy tradeoff. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61(11), 4754–4767.
Bi, S., Ho, C. K., & Zhang, R. (2015). Wireless powered communication: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(4), 117–125.
Akkaya, K., & Younis, M. (2005). A survey on routing protocols for wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 3(3), 325–349.
Abolhasan, M., Wysocki, T., & Dutkiewicz, E. (2004). A review of routing protocols for mobile ad hoc networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 2(1), 1–22.
Movassaghi, S., Abolhasan, M., & Lipman, J. (2013). A review of routing protocols in wireless body area networks. Journal of Networks, 8(3), 559–575.
Effatparvar, M., Dehghan, M., & Rahmani, A. M. (2016). A comprehensive survey of energy-aware routing protocols in wireless body area sensor networks. Journal of Medical Systems, 40(9), 201–228.
Maskooki, A., Soh, C. B., Gunawan, E., & Low, K. S. (2011). Opportunistic routing for body area network. In Proceedings of IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC) (pp. 237–241).
Tang, Q., Tummala, N., Gupta, S. K. S., & Schwiebert, L. (2005). Communication scheduling to minimize thermal effects of implanted biosensor networks in homogeneous tissue. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 52(7), 1285–1294.
Javaid, N., Abbas, Z., Fareed, M., Khan, Z., & Alrajeh, N. (2013). M-attempt: A new energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless body area sensor networks. Procedia Computer Science, 19, 224–231.
Movassaghi, S., Abolhasan, M., & Lipman, J. (2012). Energy efficient thermal and power aware (ETPA) routing in body area networks. In Proceedings of 23rd IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications-(PIMRC) (pp. 1108–1113).
Tang, Q., Tummala, N., Gupta, S. K., & Schwiebert, L. (2005). Tara: Thermal-aware routing algorithm for implanted sensor networks. In Proceedings of International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems (pp. 206–217).
Bag, A., Bassiouni, M. A. (2006). Energy efficient thermal aware routing algorithms for embedded biomedical sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems (pp. 604–609).
Bag, A., & Bassiouni, M. A. (2007). Hotspot preventing routing algorithm for delay-sensitive biomedical sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Portable Information Devices (PORTABLE07) (pp. 1–5).
Bag, A., & Bassiouni, M. A. (2008). Routing algorithm for network of homogeneous and id-less biomedical sensor nodes (rain). In Proceedings of IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS) (pp. 68–73).
Kim, B.-S., Kang, S., Lim, J., Kim, K. H., & Kim, K.-I. (2017). A mobility-based temperature-aware routing protocol for wireless body sensor networks. In Proceedings of International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN) (pp. 63–66).
Bangash, J. I., Khan, A. W., & Abdullah, A. H. (2015). Data-centric routing for intra wireless body sensor networks. Journal of Medical Systems, 39(9), 91.
Ahourai, F., Tabandeh, M., Jahed, M., & Moradi, S. (2009). A thermal-aware shortest hop routing algorithm for in vivo biomedical sensor networks. In Proceedings of 6th International Conference on Information Technology: New Generations (ITNG’09) (pp. 1612–1613).
Amrita, C. M., & Renold, A. P. (2014). Routing protocol for low power lossy networks. In Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Communication Control and Computing Technologies (ICACCCT) (pp. 1457–1461).
Krishnamurthy, A. G., Jun, J., & Agrawal, D. P. (2014). Temperature aware probabilistic sleep cycle management for body area sensor networks. In Proceedings of 11th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems (MASS) (pp. 519–520).
Kamal, R., Rahman, M. O., & Hong, C. S. (2011). A lightweight temperature scheduling routing algorithm for an implanted sensor network. In Proceedings of International Conference on ICT Convergence (ICTC) (pp. 396–400).
Watteyne, T., Augé-Blum, I., Dohler, M., & Barthel, D. (2007). Anybody: A self-organization protocol for body area networks. In Proceedings of the ICST 2nd International Conference on Body Area Networks (pp. 1–6).
Culpepper, J., Dung, L., & Moh, M. (2003). Hybrid indirect transmissions (HIT) for data gathering in wireless micro sensor networks with biomedical applications. In Proceedings of 18th IEEE Annual Workshop on Computer Communications (CCW 2003) (pp. 124–133).
Culpepper, B. J., Dung, L., & Moh, M. (2004). Design and analysis of hybrid indirect transmissions (HIT) for data gathering in wireless micro sensor networks. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 8(1), 61–83.
Moh, M., Culpepper, B. J., Dung, L., Moh, T.-S., Hamada, T., & Su, C.-F. (2005). On data gathering protocols for in-body biomedical sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference (GLOBECOM’05) (Vol. 5, pp. 2991–2996).
Ortiz, A. M., Ababneh, N., Timmons, N., & Morrison, J. (2012). Adaptive routing for multihop IEEE 802.15. 6 wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks (SoftCOM) (pp. 1–5).
Chang, J.-Y., & Ju, P.-H. (2014). An energy-saving routing architecture with a uniform clustering algorithm for wireless body sensor networks. Future Generation Computer Systems, 35, 128–140.
Liang, L., Ge, Y., Feng, G., Ni, W., & Wai, A. A. P. (2014). A low overhead tree-based energy-efficient routing scheme for multi-hop wireless body area networks. Computer Networks, 70, 45–58.
Afsana, F., Jahan, N., & Kaiser, M. (2015). An energy efficient cluster based forwarding scheme for body area network using nano-scale electromagnetic communication. In Proceedings of IEEE International WIE Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (WIECON-ECE) (pp. 491–494).
Singh, K., & Singh, R. K. (2015). An energy efficient fuzzy based adaptive routing protocol for wireless body area network. In Proceedings of IEEE UP Section Conference on Electrical Computer and Electronics (UPCON) (pp. 1–6).
ul Huque, M. T. I., Munasinghe, K. S., Abolhasan, M., & Jamalipour, A. (2013). Sea-ban: Semi-autonomous adaptive routing in wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ICSPCS) (pp. 1–7).
Rajagopalan, R. (2016). Energy efficient routing algorithm for patient monitoring in body sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE 13th International Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN) (pp. 141–146).
Sankaranarayanan, S. (2009). Intelligent agent based information routing in wireless body sensor mesh networks. In Proceedings of International Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications Networks, 2009 (pp. 1–5).
Li, C., Zhang, Z., Xiong, F., & Liu, Q. (2015). An efficient and stable route protocol in wearable body networks. In Proceedings of First International Conference on Computational Intelligence Theory, Systems and Applications (CCITSA) (pp. 104–109).
Madan, R., Cui, S., Lall, S., & Goldsmith, N. A. (2006). Cross-layer design for lifetime maximization in interference-limited wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 5(11), 3142–3152.
Melodia, T., Vuran, M. C., & Pompili, D. (2005). The state of the art in cross-layer design for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of International Workshop of the EuroNGI Network of Excellence (pp. 78–92).
Zasowski, T., A system concept for ultra wideband (UWB) body area networks. http://www.nari.ee.ethz.ch/wireless/pubs/p/Thesis_Thomas. Accessed July 4, 2016.
Braem, B., Latré, B., Blondia, C., Moerman, I., & Demeester, P. (2008). Improving reliability in multi-hop body sensor networks. In Proceedings of Second International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications (SENSORCOMM’08) (pp. 342–347).
Ruzzelli, A. G., Jurdak, R., O’Hare, G. M., & Van Der Stok, P. (2007). Energy-efficient multi-hop medical sensor networking. In Proceedings of 1st ACM SIGMOBILE International Workshop on Systems and Networking Support for Healthcare and Assisted Living Environments (pp. 37–42).
Bag, A., & Bassiouni, M. A. (2009). Biocomm-a cross-layer medium access control (MAC) and routing protocol co-design for biomedical sensor networks. International Journal of Parallel, Emergent and Distributed Systems, 24(1), 85–103.
Khan, Z. A., Sivakumar, S., Phillips, W., & Aslam, N. (2014). A new patient monitoring framework and energy-aware peering routing protocol (epr) for body area network communication. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 5(3), 409–423.
Liang, X., & Balasingham, I. (2007). A QoS-aware routing service framework for biomedical sensor networks. In Proceedings of 4th IEEE international Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (pp. 342–345).
Nadeem, Q., Javaid, N., Mohammad, S., Khan, M., Sarfraz, S., Gull, M. (2013). Simple: Stable increased-throughput multi-hop protocol for link efficiency in wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Broadband and Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications (BWCCA) (pp. 221–226).
Braem, B., Latre, B., Moerman, I., Blondia, C., & Demeester, P. (2006). The wireless autonomous spanning tree protocol for multihop wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of 3rd Annual International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Networking & Services (pp. 1–8).
Latre, B., Braem, B., Moerman, I., Blondia, C., Reusens, E., Joseph, W., et al. (2007). A low-delay protocol for multihop wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of 4th Annual International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Networking & Services (pp. 1–8).
Elhadj, H. B., Elias, J., Chaari, L., & Kamoun, L. (2016). A priority based cross layer routing protocol for healthcare applications. Ad Hoc Networks, 42, 1–18.
Zhou, Y., Sheng, Z., Mahapatra, C., Leung, V. C., & Servati, P. (2017). Topology design and cross-layer optimization for wireless body sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 59, 48–62.
Awang, A., & Abbasi, U. F. (2015). Performance evaluation of cross-layer opportunistic mac/routing with node’s mobility for wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of 12th IEEE Malaysia International Conference on Communications (MICC) (pp. 30–35).
Ababneh, N., Timmons, N., & Morrison, J. (2012) Cross-layer optimization protocol for guaranteed data streaming over wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (pp. 118–123).
Elhadj, H. B., Bradai, N., Boudjit, S., Chaari, L., & Kamoun, L. (2015). A priority based cross layer data dissemination protocol for healthcare applications. In Proceedings of 12th Annual IEEE Conference on Consumer Communications and Networking (pp. 615–616).
Ivanov, S., Botvich, D., & Balasubramaniam, S. (2012). Cooperative wireless sensor environments supporting body area networks. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 58(2), 284–292.
Sevin, A., Bayilmis, C., & Kirbas, I. (2016). Design and implementation of a new quality of service-aware cross-layer medium access protocol for wireless body area networks. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 56, 145–156.
Prabh, K. S., Royo, F., Tennina, S., & Olivares, T. (2016). A mac protocol for reliable communication in low power body area networks. Journal of Systems Architecture, 66, 1–13.
Quwaider, M., & Biswas, S. (2010). DTN routing in body sensor networks with dynamic postural partitioning. Ad Hoc Networks, 8(8), 824–841.
Quwaider, M., & Biswas, S. (2009). Probabilistic routing in on-body sensor networks with postural disconnections. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM International Symposium on Mobility Management and Wireless Access (pp. 149–158).
Liang, X., Li, X., Shen, Q., Lu, R., Lin, X., Shen, X., et al. (2012). Exploiting prediction to enable secure and reliable routing in wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM (pp. 388–396).
Quwaider, M., & Biswas, S. (2009). On-body packet routing algorithms for body sensor networks. In Proceedings of First International Conference on Networks and Communications (pp. 171–177).
Elias, J. (2014). Optimal design of energy-efficient and cost-effective wireless body area networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 13, 560–574.
Omer, S., Vesilo, R., Dutkiewicz, E., & Zhang, Q. (2015). An lqi based dual-channel routing protocol for wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of International Conference on Telecommunication Networks and Applications Conference (ITNAC) (pp. 320–325).
Ambigavathi, M., & Sridharan, D. (2015). Priority based aodv routing protocol for critical data in wireless body area network. In Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Signal Processing, Communication and Networking (ICSCN) (pp. 1–5).
Kaur, N., & Singh, S. (2017). Optimized cost effective and energy efficient routing protocol for wireless body area networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 61, 65–84.
Smail, O., Kerrar, A., Zetili, Y., & Cousin, B. (2016). Esr: Energy aware and stable routing protocol for wban networks. In Proceedings of International Conference on Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC) (pp. 452–457).
Singh, S., Negi, S., Uniyal, A., & Verma, S. K. (2016). Modified new-attempt routing protocol for wireless body area network. In Proceedings of International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication, & Automation (ICACCA) (pp. 1–5).
Moosavi, H., & Bui, F. M. (2016). Routing over multi-hop fading wireless body area networks with reliability considerations. In Proceedings of IEEE 38th Annual International Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) (pp. 4941–4945).
Juneja, P., & Jain, S. (2015). Tree based energy efficient routing scheme for body area network. In Proceedings of International Conference on Advances in Computer Engineering and Applications (ICACEA) (pp. 940–947).
Afridi, A., Javaid, N., Jamil, S., Akbar, M., Khan, Z. A., & Qasim, U. (2014) Heat: Horizontal moveable energy-efficient adaptive threshold-based routing protocol for wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops (WAINA) (pp. 474–478).
Yang, S., Lu, J.-L., Yang, F., Kong, L., Shu, W., & Wu, M.-Y. (2013). Behavior-aware probabilistic routing for wireless body area sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 444–449).
Khan, Z. A., Sivakumar, S., Phillips, W., & Robertson, B. (2013). A qos-aware routing protocol for reliability sensitive data in hospital body area networks. Procedia Computer Science, 19, 171–179.
Seo, S.-H., Gopalan, S. A., Chun, S.-M., Seok, K.-J., Nah, J.-W., & Park, J.-T. (2010). An energy-efficient configuration management for multi-hop wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of 3rd IEEE International Conference on Broadband Network and Multimedia Technology (IC-BNMT) (pp. 1235–1239).
Liang, X., Balasingham, I., & Byun, S. S. (2008). A reinforcement learning based routing protocol with QoS support for biomedical sensor networks. In Proceedings of first IEEE International Symposium on Applied Sciences on Biomedical and Communication Technologies (pp. 1–5).
Djenouri, D., & Balasingham, I. (2009). New QoS and geographical routing in wireless biomedical sensor networks. In Proceedings of Sixth International Conference on Broadband Communications, Networks, and Systems (pp. 1–8).
Razzaque, M. A., Hong, C. S., & Lee, S. (2011). Data-centric multiobjective QoS-aware routing protocol for body sensor networks. Sensors, 11(1), 917–937.
Khan, Z. A., Sivakumar, S. C., Phillips, W. J., & Robertson, B. (2014). Qprr: Qos-aware peering routing protocol for reliability sensitive data in body area network communication. The Computer Journal, 58(8), 1701–1716.
Naputta, Y., & Usaha, W. (2012). Rl-based routing in biomedical mobile wireless sensor networks using trust and reputation. In Proceedings of International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS) (pp. 521–525).
Hassanpour, S., Vejdanparast, Y., Asadi, B., & Zargar, P. (2011). Improving reliability of routing in wireless body area sensor networks using genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Science and Automation Engineering (Vol. 2, pp. 590–593).
Gomathi, C., & Santhiyakumari, N. (2016). Ofsr: An optimized fuzzy based swarm routing for wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN) (pp. 507–512).
Sandhu, M. M., Akbar, M., Behzad, M., Javaid, N., Khan, Z. A., & Qasim, U. (2014). Reec: Reliable energy efficient critical data routing in wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Broadband and Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications (BWCCA) (pp. 446–451).
Huang, X., Shan, H., & Shen, X. (2011). On energy efficiency of cooperative communications in wireless body area network. In 2011 IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC) (pp. 1097–1101).
Talha, S., Ahmad, R., & Kiani, A. K. (2015). Priority based energy aware (pea) routing protocol for wbans. In Proceedings of IEEE 82nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall) (pp. 1–5).
Liao, Y., Leeson, M. S., Higgins, M. D., & Bai, C. (2016). An incremental relay based cooperative routing protocol for wireless in-body sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE 12th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob) (pp. 1–6).
Rout, D. K., & Das, S. (2015). Hybrid relaying for sensor to external communication in multi relay body area networks. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Informatics, Communication and Energy Systems (SPICES) (pp. 1–5).
Rout, D. K., & Das, S. (2017). Reliable communication in UWB body area networks using multiple hybrid relays. Wireless Networks, 23(8), 2555–2570.
Abbasi, U. F., Awang, A., & Hamid, N. H. (2013). Performance investigation of using direct transmission and opportunistic routing in wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of IEEE Symposium on Computers & Informatics (ISCI) (pp. 60–65).
Mao, X., Tang, S., Xu, X., Li, X.-Y., & Ma, H. (2011). Energy-efficient opportunistic routing in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 22(11), 1934–1942.
Abbasi, U. F., Awang, A., & Hamid, N. H. (2014). A cross-layer opportunistic mac/routing protocol to improve reliability in wban. In Proceedings of Asia-Pacific Conference on Communications (APCC) (pp. 36–41).
Hamida, E. B., Alam, M. M., Maman, M., & Denis, B. (2014). Short-term link quality estimation for opportunistic and mobility aware routing in wearable body sensors networks. In Proceedings of IEEE 10th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob) (pp. 519–526).
Ahmed, S., Javaid, N., Yousaf, S., Ahmad, A., Sandhu, M. M., Imran, M., et al. (2015). Co-laeeba: Cooperative link aware and energy efficient protocol for wireless body area networks. Computers in Human Behavior, 51, 1205–1215.
Guo, C., Prasad, R. V., & Jacobsson, M. (2010). Packet forwarding with minimum energy consumption in body area sensor networks. In Proceedings of 7th IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC) (pp. 1–6).
Zhang, Q., Kortermand, K., Jacobsen, R. H., & Toftegaard, T. S. (2012). Reactive virtual coordinate routing protocol for body sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) (pp. 3388–3393).
Sheu, T.-L., & Siao, J.-R. (2014). A reversed-routing tree with self-reconfiguration for body sensor networks. In Proceedings of International Symposium on Wireless Personal Multimedia Communications (WPMC) (pp. 322–327).
Zhang, K., Liang, X., Baura, M., Lu, R., & Shen, X. S. (2014). Phda: A priority based health data aggregation with privacy preservation for cloud assisted wbans. Information Sciences, 284, 130–141.
Medjahed, H., Istrate, D., Boudy, J., & Dorizzi, B. (2009). Human activities of daily living recognition using fuzzy logic for elderly home monitoring. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE) (pp. 2001–2006).
Medjahed, H., Istrate, D., Boudy, J., Baldinger, J. L., & Dorizzi, B. (2011). A pervasive multi-sensor data fusion for smart home healthcare monitoring. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ) (pp. 1466–1473).
Misra, S., & Chatterjee, S. (2014). Social choice considerations in cloud-assisted wban architecture for post-disaster healthcare: Data aggregation and channelization. Information Sciences, 284, 95–117.
Gravina, R., Alinia, P., Ghasemzadeh, H., & Fortino, G. (2017). Multi-sensor fusion in body sensor networks: State-of-the-art and research challenges. Information Fusion, 35, 68–80.
Anooj, P. (2012). Clinical decision support system: Risk level prediction of heart disease using weighted fuzzy rules. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 24(1), 27–40.
Amaral, J. L., Lopes, A. J., Jansen, J. M., Faria, A. C., & Melo, P. L. (2012). Machine learning algorithms and forced oscillation measurements applied to the automatic identification of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 105(3), 183–193.
Yoo, I., Alafaireet, P., Marinov, M., Pena-Hernandez, K., Gopidi, R., Chang, J. F., et al. (2012). Data mining in healthcare and biomedicine: A survey of the literature. Journal of Medical Systems, 36(4), 2431–2448.
Black, A. S., & Sahama, T. (2014). ehealth-as-a-service (eHaaS): The industrialisation of health informatics, a practical approach. In Proceedings of 16th IEEE International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom) (pp. 555–559).
Cao, L., Philip, S. Y., & Kumar, V. (2015). Nonoccurring behavior analytics: A new area. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 30(6), 4–11.
Kumarage, H., Khalil, I., Alabdulatif, A., Tari, Z., & Yi, X. (2016). Secure data analytics for cloud-integrated internet of things applications. IEEE Cloud Computing, 3(2), 46–56.
Shi, G., Geng, C., Liu, H., Su, H., Jin, Y., & Sun, S. (2016). The human body characteristic parameters extraction and disease tendency prediction based on multi-sensing fusion algorithms. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems (CYBER) (pp. 126–130).
Baytas, I., Lin, K., Wang, F., Jain, A. K., & Zhou, J. (2016). Phenotree: Interactive visual analytics for hierarchical phenotyping from large-scale electronic health record. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 18(11), 2257–2270.
Miah, S. J., Hasan, J., & Gammack, J. G. (2017). On-cloud healthcare clinic: An e-health consultancy approach for remote communities in a developing country. Telematics and Informatics, 34(1), 311–322.
Gong, Y., Fang, Y., & Guo, Y. (2016). Private data analytics on biomedical sensing data via distributed computation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 13(3), 431–444.
Davis, K., Owusu, E., Bastani, V., Marcenaro, L., Hu, J., Regazzoni, C., et al. (2016). Activity recognition based on inertial sensors for ambient assisted living. In Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION) (pp. 371–378).
Ahmadi, A., Mitchell, E., Destelle, F., Gowing, M., O’Connor, N. E., Richter, C., et al. (2014). Automatic activity classification and movement assessment during a sports training session using wearable inertial sensors. In Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN) (pp. 98–103).
Tapp, H., McWilliams, A., Ludden, T., Kuhn, L., Taylor, Y., Alkhazraji, T., et al. (2014). Comparing traditional and participatory dissemination of a shared decision making intervention (adapt-nc): A cluster randomized trial. Implementation Science, 9(1), 158.
Mourão-Miranda, J., Hardoon, D. R., Hahn, T., Marquand, A. F., Williams, S. C., Shawe-Taylor, J., et al. (2011). Patient classification as an outlier detection problem: An application of the one-class support vector machine. Neuroimage, 58(3), 793–804.
Li, J., Liu, L.-S., Fong, S., Wong, R. K., Mohammed, S., Fiaidhi, J., et al. (2017). Adaptive swarm balancing algorithms for rare-event prediction in imbalanced healthcare data. PLoS ONE, 12(7), e0180830.
Jiang, P., Winkley, J., Zhao, C., Munnoch, R., Min, G., & Yang, L. T. (2016). An intelligent information forwarder for healthcare big data systems with distributed wearable sensors. IEEE Systems Journal, 10(3), 1147–1159.
Walker, W. P., & Bhatia, D. K. (2014). Automated ingestion detection for a health monitoring system. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 18(2), 682–692.
Nguyen, T., Khosravi, A., Creighton, D., & Nahavandi, S. (2015). Classification of healthcare data using genetic fuzzy logic system and wavelets. Expert Systems with Applications, 42(4), 2184–2197.
Alaa, A. M., Moon, K. H., Hsu, W., & van der Schaar, M. (2016). Confidentcare: A clinical decision support system for personalized breast cancer screening. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 18(10), 1942–1955.
Dargie, W., & Poellabauer, C. (2010). Fundamentals of wireless sensor networks: Theory and practice (1st ed.). New York: Wiley.
Zhang, Z., Wang, H., Wang, C., & Fang, H. (2015). Cluster-based epidemic control through smartphone-based body area networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 26(3), 681–690.
Ko, J., Lu, C., Srivastava, M. B., Stankovic, J. A., Terzis, A., & Welsh, M. (2010). Wireless sensor networks for healthcare. Proceedings of the IEEE, 98(11), 1947–1960.
Karl, H., & Willig, A. (2007). Protocols and architectures for wireless sensor networks (1st ed.). New York: Wiley.
Yu, J., Park, L., Park, J., Cho, S., & Keum, C. (2016). Cor-mac: Contention over reservation mac protocol for time-critical services in wireless body area sensor networks. Sensors, 16(5), 656.
Ullah, F., Abdullah, A. H., Kaiwartya, O., & Arshad, M. M. (2017). Traffic priority-aware adaptive slot allocation for medium access control protocol in wireless body area network. Computers, 6(1), 9.
Abidi, B., Jilbab, A., & Haziti, M. E. L. (2017). Wireless sensor networks in biomedical: Wireless body area networks. In Europe and MENA Cooperation Advances in Information and Communication Technologies (pp. 321–329). Cham: Springer.
IEEE 802.15 working group for wireless personal area network. http://www.ieee802.org/15/. Accessed November 14, 2016.
Sharma, R., Ryait, H. S., & Gupta, A. K. (2016). Wireless body area network—A review. Research Cell: An International Journal of Engineering Sciences, 17.
Gope, P., & Hwang, T. (2016). BSN-care: A secure IoT-based modern healthcare system using body sensor network. IEEE Sensors Journal, 16(5), 1368–1376.
Li, W., & Song, H. (2016). Art: An attack-resistant trust management scheme for securing vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 17(4), 960–969.
Sawand, A., Djahel, S., Zhang, Z., & Naït-Abdesselam, F. (2015). Toward energy-efficient and trustworthy ehealth monitoring system. China Communications, 12(1), 46–65.
Huang, H., Gong, T., Ye, N., Wang, R., & Dou, Y. (2017). Private and secured medical data transmission and analysis for wireless sensing healthcare system. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 13(3), 1227–1237.
Islam, S. R., Kwak, D., Kabir, M. H., Hossain, M., & Kwak, K.-S. (2015). The internet of things for health care: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access, 3, 678–708.
Wac, K., Bults, R., Van Beijnum, B., Widya, I., Jones, V., Konstantas, D., et al. (2009). Mobile patient monitoring: the mobihealth system. In Annual IEEE international conference on engineering in medicine and biology society (pp. 1238–1241).
Gao, T., Massey, T., Selavo, L., Crawford, D., Chen, B.-R., Lorincz, K., et al. (2007). The advanced health and disaster aid network: A light-weight wireless medical system for triage. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 1(3), 203–216.
Kang, E., Im, Y., & Kim, U. (2007). Remote control multi-agent system for u-healthcare service. Agent and multi-agent systems: Technologies and applications (pp. 636–644).
Shnayder, V., Chen, B.-r., Lorincz, K., Fulford-Jones, T. R., & Welsh, M. (2005). Sensor networks for medical care. Harvard University Technical Report, No. TR-08-05.
Ouchi, K., Suzuki, T., & Doi, M. (2002). Lifeminder: A wearable healthcare support system using user’s context. In Proceedings of 22nd IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems Workshops (pp. 791–792).
Curtis, D., Shih, E., Waterman, J., Guttag, J., Bailey, J., Stair, T., et al. (2008). Physiological signal monitoring in the waiting areas of an emergency room. In Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Body Area Networks (p. 5).
Jiang, S., Cao, Y., Iyengar, S., Kuryloski, P., Jafari, R., Xue, Y., et al. (2008). Carenet: An integrated wireless sensor networking environment for remote healthcare. In Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Body Area Networks (p. 9).
Sheltami, T., Mahmoud, A., & Abu-Amara, M. (2006). Warning and monitoring medical system using sensor networks. In Proceedings of 18th National Computer Conference (NCC18) (pp. 63–68).
Mithril. The next generation research platform for context aware wearable computing. https://www.media.mit.edu/wearables/mithril/index.html. Accessed May 15, 2017.
Falck, T., Espina, J., Ebert, J.-P., & Dietterle, D. (2006). Basuma-the sixth sense for chronically ill patients. In Proceedings of IEEE International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (pp. 4).
Milenković, A., Otto, C., & Jovanov, E. (2006). Wireless sensor networks for personal health monitoring: Issues and an implementation. Computer Communications, 29(13), 2521–2533.
Gyselinckx, B., Vullers, R., Van Hoof, C., Ryckaert, J., Yazicioglu, R. F., Fiorini, P., et al. (2006). Human++: Emerging technology for body area networks. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Very Large Scale Integration (pp. 175–180).
Farella, E., Pieracci, A., Benini, L., Rocchi, L., & Acquaviva, A. (2008). Interfacing human and computer with wireless body area sensor networks: The wimoca solution. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 38(3), 337–363.
Jantunen, I., Laine, H., Huuskonen, P., Trossen, D., & Ermolov, V. (2008). Smart sensor architecture for mobile-terminal-centric ambient intelligence. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 142(1), 352–360.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Punj, R., Kumar, R. Technological aspects of WBANs for health monitoring: a comprehensive review. Wireless Netw 25, 1125–1157 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1694-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1694-3