Abstract
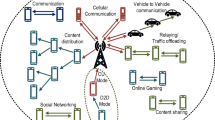
D2D (device-to-device) communication is one of the developments of 5G networks (5th generation mobile networks) that reduce mobile traffic load, reduce energy consumption and effectively use the available electrical radio spectrum. An increase in the number of mobile devices might, in theory, promote D2D communications to 5G networks; however, in practice, the D2D communications technologies, such as Wi-Fi Ad-Hoc, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Direct, are not available or require human interaction. To overcome these limitations, a middleware based on Wi-Fi infrastructure mode, which establishes connections and performs data exchange without human interaction, is presented. Practical proofs of the concept demonstrate that the middleware enables transparent D2D communications for 5G applications.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agiwal, M., Roy, A., & Saxena, N. (2016). Next generation 5G wireless networks: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 18, 1617–1655.
Palattella, M., Dohler, M., Grieco, A., Rizzo, G., Torsner, J., Engel, T., et al. (2016). Internet of things in the 5G era: Enablers, architecture and business models. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 34, 510–527.
Soldani, D., & Manzalini, A. (2015). Horizon 2020 and beyond: on the 5G operating system for a true digital society. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 10, 32–42.
Panwar, N., Sharma, S., & Singh, A. K. (2016). A survey on 5G: The next generation of mobile communication. Physical Communication, 18, 64–84.
Wang, Y., Wei, L., Vasilakos, A. V., & Jin, Q. (2017). Device-to-device based mobile social networking in proximity (msnp) on smartphones: Framework, challenges and prototype. Future Generation Computer Systems, 74, 241–253.
Ho, Q. D., Tweed, D., & Le-Ngoc, T. (2017). IEEE 802.11/Wi-Fi medium access control: An overview. In Long term evolution in unlicensed bands. Springerbriefs in electrical and computer engineering. Cham: Springer.
Zuo, J., Wang, Y., Jin, Q., & Ma, J. (2015). Hychat: A hybrid interactive chat system for mobile social networking in proximity. In 2015 IEEE International Conference on Smart City/SocialCom/SustainCom (SmartCity).
Arnaboldi, V., Conti, M., & Delmastro, F. (2014). Cameo: A novel context-aware middleware for opportunistic mobile social networks. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 11, 148–167.
WPAN Task Group 1 (TG1). (2017). IEEE standard 802.15.1—part 15.1: Wireless medium access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications for wireless personal area networks (WPANS).
El Alami, M., Benamar, N., Younis, M., & Shahin, A. A. (2017) A framework for hotspot support using Wi-Fi direct based device-to-device links. In 13th international wireless communications and mobile computing conference (IWCMC).
Alliance, W.-F. (2016). Wi-fi peer-to-peer (p2p) technical specification, version 1.7, alliance technical committee p2p task group.
Saha, D., & Mukherjee, A. (2003). Pervasive computing: A paradigm for the 21st century. Computer, 36, 25–31.
Nordström, E., Rohner, C., & Gunningberg, P. (2014). Haggle: Opportunistic mobile content sharing using search. Computer Communications, 48, 121–132.
Dubois, D. J., Bando, Y., Watanabe, K., & Holtzman, H. (2013). Shair: Extensible middleware for mobile peer-to-peer resource sharing. In Proceedings of the 2013 9th joint meeting on foundations of software engineering.
Turkes, O., Scholten, H., & Havinga, P. J. (2016). Cocoon: A lightweight opportunistic networking middleware for community-oriented smart mobile applications. Computer Networks, 111, 93–108.
Turkes, O., Scholten, H., & Havinga, P. J. (2016). Opportunistic beacon networks: Information dissemination via wireless network identifiers. In 2016 IEEE international conference on pervasive computing and communication workshops (PerCom workshops).
Pavone, M. (2016). Autonomous mobility-on-demand systems for future urban mobility. In Autonomous driving, pp. 387–404.
Zhang, X., Yang, Z., Sun, W., Liu, Y., Tang, S., Xing, K., et al. (2016). Incentives for mobile crowd sensing: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 18, 54–67.
Dahlman, E., Parkvall, S., & Skold, J. (2016). 4G, LTE-advanced Pro and the Road to 5G. Cambridge: Academic Press.
OpenSignal, I. (2010). Global state of mobile networks (February 2017).
For Network, E. U. A., & (ENISA), I. S. (2017). Annual incident reports 2016. In Analysis of article 13a annual incident reports in the telecom sector.
Gebhart, G., & Kohno, T. (2017) Internet censorship in Thailand: User practices and potential threats. In 2017 IEEE European symposium on security and privacy (EuroS&P).
Neokosmidis, I., Rokkas, T., Parker, M. C., Koczian, G., Walker, S. D., Siddiqui, M. S., et al. (2017). Assessment of socio-techno-economic factors affecting the market adoption and evolution of 5G networks: Evidence from the 5G-PPP CHARIMA project. Telematics and Informatics, 34, 572–589.
Index, C. V. N. (2016). Global mobile data traffic forecast update, 2015–2020 white paper. link: http://goo. gl/ylTuVx.
Akyildiz, I. F., Nie, S., Lin, S.-C., & Chandrasekaran, M. (2016). 5G roadmap: 10 Key enabling technologies. Computer Networks, 106, 17–48.
Ahmed, E., Yaqoob, I., Gani, A., Imran, M., & Guizani, M. (2016). Internet-of-things-based smart environments: State of the art, taxonomy, and open research challenges. IEEE Wireless Communications, 23, 10–16.
Poularakis, K., Iosifidis, G., Sourlas, V., & Tassiulas, L. (2016). Exploiting caching and multicast for 5G wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 15, 2995–3007.
Buzzi, S., Chih-Lin, I., Klein, T. E., Poor, H. V., Yang, C., & Zappone, A. (2016). A survey of energy-efficient techniques for 5G networks and challenges ahead. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 34(4), 697–709.
Wang, T., Li, P., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Guo, T., & Cao, Y. (2017). A comprehensive survey on mobile data offloading in heterogeneous network. Wireless Networks, pp. 1–12.
Saifullah, A., Xu, Y., Lu, C., & Chen, Y. (2015). End-to-end communication delay analysis in industrial wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 64, 1361–1374.
Yilmaz, O. N., Li, Z., Valkealahti, K., Uusitalo, M. A., Moisio, M., Lundén, P., & Wijting, C. (2014). Smart mobility management for D2D communications in 5G networks. In 2014 IEEE wireless communications and networking conference workshops.
Aydin, O., Jorswieck, E. A., Aziz, D., & Zappone, A. (2017). Energy-spectral efficiency trade-offs in 5G multi-operator networks with heterogeneous constraints. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 16, 5869–5881.
Biswash, S. K., Ziviani, A., Jain, R., Lin, J.-C., & Rodrigues, J. J. (2017). Device-to-device communication in 5G networks. Mobile Networks and Applications, 22, 995–997.
Ding, G., Wang, J., Wu, Q., Yao, Y.-D., Song, F., & Tsiftsis, T. A. (2016). Cellular-base-station-assisted device-to-device communications in TV white space. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 34, 107–121.
Asadi, A., & Mancuso, V. (2017). Network-assisted outband D2D-clustering in 5G cellular networks: Theory and practice. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 16, 2246–2259.
Meshgi, H., Zhao, D., & Zheng, R. (2017). Optimal resource allocation in multicast device-to-device communications underlaying LTE networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66, 8357–8371.
Karakus, C., & Diggavi, S. (2017). Enhancing multiuser MIMO through opportunistic D2D cooperation. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 16, 5616–5629.
Zou, Y., Zhu, J., Wang, X., & Hanzo, L. (2016). A survey on wireless security: Technical challenges, recent advances, and future trends. Proceedings of the IEEE, 104, 1727–1765.
Constantinescu, M., Onur, E., Durmus, Y., Nikou, S., De Reuver, M., Bouwman, H., et al. (2014). Mobile tethering: Overview, perspectives and challengess. Info, 16, 40–53.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge support from the Brazilian research agencies (CNPq) and (Capes), the Research Foundation of the State of Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), and the Federal University of Ouro Preto (UFOP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garrocho, C.T.B., da Silva, M.J. & Oliveira, R.A.R. D2D pervasive communication system with out-of-band control autonomous to 5G networks. Wireless Netw 26, 373–386 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1820-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1820-2