Abstract
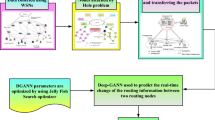
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) contain multiple wireless sensor nodes deployed around the geographical locations. The WSN used in military applications need more security and hence the deployment of trustworthy nodes and links in WSN provides more secure data transmission in Decentralized Military Sensor Networks (DMSNs). Moreover, the DMSNs work with different set of significance constraints including higher security requirements. The design of DMSNs targets surveillance tasks, intruder tracking tasks, army resource maintenance tasks and communication security requirements. Therefore, building a secure and dynamic DMSN against multiple threats is a challenging task. In addition, security principles developed for DMSN cause excessive energy consumption. Moreover, DMSN has completely open distributed architecture without having any base stations. Under this situation, the need for effective and secured data communication can be achieved with the help of a secure routing protocol. Block chains are generally used for making secure financial transactions. However, the routing protocols used in DMSN can support autonomous routing transactions from one node to other node. In this situation, block chain enabled routing procedures can ensure the trustworthiness of any data that is forwarded through different sensor nodes. Hence, a new Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) based Block Chain enabled secured Routing Protocol (GBCRP) is proposed in this paper which authenticates and validates the ongoing routing procedures of DMSN. Moreover, a new intrusion detection system is also proposed in this work using GAN which is deployed in the nodes of the DMSN for enhancing the security of communication. Since block chain based routing protocols do not provide security, the GBCRP works for creating volatile block chains using decentralized authentication principles and effective intrusion detection. The proposed system uses a Fully Decentralized Generative Adversarial Network (FDGAN) for monitoring the secure routing transactions by the development of an intrusion detection system. The results obtained from this work show that the proposed GBCRP providing better secured routing compared to the existing systems with respect to security, energy consumption and routing metrics.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soundararajan, R., Palanisamy, N., Patan, R., Nagasubramanian, G., & Khan, M. S. (2020). Secure and concealed watchdog selection scheme using masked distributed selection approach in wireless sensor networks. IET Communications, 14(6), 948–955.
Rajasoundaran, S., Prabu, A. V., Kumar, G. S., Malla, P. P., & Routray, S. (2021). Secure opportunistic watchdog production in wireless sensor networks: A review. Wireless Personal Communications, 1-25.
Rajasoundaran, S., Prabu, A. V., Subrahmanyam, J. B. V., Rajendran, R., Kumar, G. S., Kiran, S., & Khalaf, O. I. (2021). Secure watchdog selection using intelligent key management in wireless sensor networks. Materials Today: Proceedings
Viswanathan, S., & Kannan, A. (2019). Elliptic key cryptography with beta gamma functions for secure routing in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 25(8), 4903–4914.
Selvi, M., Thangaramya, K., Ganapathy, S., Kulothungan, K., Nehemiah, H. K., & Kannan, A. (2019). An energy aware trust based secure routing algorithm for effective communication in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 105(4), 1475–1490.
Hajisalem, V., & Babaie, S. (2018). A hybrid intrusion detection system based on ABC-AFS algorithm for misuse and anomaly detection. Computer Networks, 136, 37–50.
Stallings, W. (2017). Cryptography and network security principles and practices (7th ed.). Pearson Education.
Dorri, A., Luo, F., Kanhere, S. S., Jurdak, R., & Dong, Z. Y. (2019). SPB: A secure private blockchain-based solution for distributed energy trading. IEEE Communications Magazine, 57(7), 120–126.
Ramezan, G., & Leung, C. (2018). A blockchain-based contractual routing protocol for the internet of things using smart contracts. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2018.
Yang, J., He, S., Yang, Xu., Chen, L., & Ren, Ju. (2019). A trusted routing scheme using blockchain and reinforcement learning for wireless sensor networks. Sensors, 19(4), 970.
She, W., Liu, Qi., Tian, Z., Chen, J.-S., Wang, Bo., & Liu, W. (2019). Blockchain trust model for malicious node detection in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access, 7, 38947–38956.
Lazrag, H., Chehri, A., Saadane, R., & Rahmani, M. D. (2019). A blockchain-based approach for optimal and secure routing in wireless sensor networks and IoT. In 2019 15th International Conference on Signal-Image Technology & Internet-Based Systems (SITIS) (pp. 411-415). IEEE.
Khalid, N. A. (2019). Distributed trust-based routing decision making for WSN. Ph.D diss., Auckland University of Technology.
Ren, Y., Liu, Y., Ji, S., Sangaiah, A. K., & Wang, J. (2018). Incentive mechanism of data storage based on blockchain for wireless sensor networks. Mobile Information Systems, 2018
Busygin, A., Konoplev, A., Kalinin, M., & Zegzhda, D. (2018). Floating genesis block enhancement for blockchain based routing between connected vehicles and software-defined VANET security services. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Security of Information and Networks (pp. 1-2)
Kim, T. H., Goyat, R., Rai, M. K., Kumar, G., Buchanan, W. J., Saha, R., & Thomas, R. (2019). A novel trust evaluation process for secure localization using a decentralized blockchain in wireless sensor networks. IEEE access, 7, 184133–184144.
Yang, Z., Yang, K., Lei, L., Zheng, K., & Leung, V. C. (2018). Blockchain-based decentralized trust management in vehicular networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(2), 1495–1505.
Qu, C., Tao, M., Zhang, J., Hong, X., & Yuan, R. (2018). Blockchain based credibility verification method for IoT entities. Security and Communication Networks, 2018.
Liu, Y., Yu, F. R., Li, X., Ji, H., & Leung, V. C. (2020). Blockchain and machine learning for communications and networking systems. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 22(2), 1392–1431.
Rajeswari, A. R., Kulothungan, K., Ganapathy, S., & Kannan, A. (2019). A trusted fuzzy based stable and secure routing algorithm for effective communication in mobile adhoc networks. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 12(5), 1076–1096.
Logambigai, R., & Kannan, A. (2016). Fuzzy logic based unequal clustering for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks, 22(3), 945–957.
Thangaramya, K., Kulothungan, K., Gandhi, S. I., Selvi, M., Kumar, S. S., & Arputharaj, K. (2020). Intelligent fuzzy rule-based approach with outlier detection for secured routing in WSN. Soft Computing, 24(21), 16483–16497.
Nancy, P., Muthurajkumar, S., Ganapathy, S., Kumar, S. S., Selvi, M., & Arputharaj, K. (2020). Intrusion detection using dynamic feature selection and fuzzy temporal decision tree classification for wireless sensor networks. IET Communications, 14(5), 888–895.
Roshan, S., Miche, Y., Akusok, A., & Lendasse, A. (2018). Adaptive and online network intrusion detection system using clustering and extreme learning machines. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 355(4), 1752–1779.
Manzoor, I., & Kumar, N. (2017). A feature reduced intrusion detection system using ANN classifier. Expert Systems with Applications, 88, 249–257.
Maldonadoa, S., & López, J. (2018). Dealing with high-dimensional class-imbalanced datasets: Embedded feature selection for SVM classification. Applied Soft Computing, 67, 94–105.
Yang, H., Liang, Y., Yuan, J., Yao, Q., Yu, A., & Zhang, J. (2020). Distributed blockchain-based trusted multidomain collaboration for mobile edge computing in 5G and beyond. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 16(11), 7094–7104.
Magdy, Y., Kashkoush, M. S., Azab, M., & Rizk, M. R. (2020). Anonymous blockchain Based Routing For Moving-target Defense Across Federated Clouds. In 2020 IEEE 21st International Conference on High Performance Switching and Routing (HPSR) (pp. 1-7). IEEE
Mubarakali, A. (2021). An Efficient Authentication Scheme Using Blockchain Technology for Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 1-15
Kimbahune, V. V., Deshpande, A. V., & Mahalle, P. N. (2021). Lightweight key management for adaptive addressing in next generation internet. In Research Anthology on Blockchain Technology in Business, Healthcare, Education, and Government (pp. 1890-1914). IGI Global.
Hsiao, S. J., & Sung, W. T. (2021). employing blockchain technology to strengthen security of wireless sensor networks. IEEE Access, 9, 72326–72341.
Revanesh, M., & Sridhar, V. (2021). A trusted distributed routing scheme for wireless sensor networks using blockchain and meta‐heuristics‐based deep learning technique. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, e4259.
Arifeen, M. M., Al Mamun, A., Ahmed, T., Kaiser, M. S., & Mahmud, M. (2021). A blockchain-based scheme for sybil attack detection in underwater wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of International Conference on Trends in Computational and Cognitive Engineering (pp. 467-476). Springer, Singapore.
Mrinal, M., Garg, A., & DuraiswamyMaikandavel, V. (2021). Blockchain secured vehicle tracking using wireless sensor network. Ilkogretim Online, 20(1).
Ran, C., Yan, S., Huang, L., & Zhang, L. (2021). An improved AODV routing security algorithm based on blockchain technology in ad hoc network. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2021(1), 1–16.
Lazrag, H., Chehri, A., Saadane, R., & Rahmani, M. D. (2020). Efficient and secure routing protocol based on Blockchain approach for wireless sensor networks. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, e6144.
Ferrag, M. A., & Maglaras, L. (2019). DeepCoin: A novel deep learning and blockchain-based energy exchange framework for smart grids. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 67(4), 1285–1297.
Mohanta, B. K., Jena, D., Satapathy, U., & Patnaik, S. (2020). Survey on IoT Security: challenges and solution using machine learning, artificial intelligence and blockchain technology. Internet of Things, 11, 100227.
Saha, A. K., & Johnson, D. B. (2004). Modeling mobility for vehicular ad-hoc networks. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM international workshop on Vehicular ad hoc networks (pp. 91-92)
Kuzmin, A., & Znak, E. (2018). Blockchain-base structures for a secure and operate network of semi-autonomous Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. In 2018 IEEE International conference on service operations and logistics, and informatics (SOLI) (pp. 32-37). IEEE.
Banerjee, M., Lee, J., & Choo, K. K. R. (2018). A blockchain future for internet of things security: a position paper. Digital Communications and Networks, 4(3), 149–160.
Xie, J., Yu, F. R., Huang, T., Xie, R., Liu, J., Wang, C., & Liu, Y. (2018). A survey of machine learning techniques applied to software defined networking (SDN): Research issues and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 21(1), 393–430.
Sahay, R., Geethakumari, G., & Mitra, B. (2020). A novel blockchain based framework to secure IoT-LLNs against routing attacks. Computing, 102, 2445–2470.
Mateen, A., Tanveer, J., Khan, N. A., Rehman, M., & Javaid, N. (2019). One step forward: towards a blockchain based trust model for wsns. In International conference on P2P, parallel, grid, cloud and internet computing (pp. 57-69). Springer, Cham
Rahouti, M., Xiong, K., & Ghani, N. (2018). Bitcoin concepts, threats, and machine-learning security solutions. IEEE Access, 6, 67189–67205.
Geepthi, D., & Columbus, C. C. (2020). Network traffic detection for peer-to-peer traffic matrices on bayesian network in WSN. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 1-12
Lee, Y., Rathore, S., Park, J. H., & Park, J. H. (2020). A blockchain-based smart home gateway architecture for preventing data forgery. Human-centric Computing and Information Sciences, 10(1), 1–14.
Singh, M., Aujla, G. S., & Bali, R. S. (2020). A deep learning-based blockchain mechanism for secure internet of drones environment. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 34(2), 83–91.
Renault, É., Mühlethaler, P., & Boumerdassi, S. (Eds.). (2019). Machine Learning for Networking: First International Conference, MLN 2018, Paris, France, November 27–29, 2018, Revised Selected Papers (Vol. 11407). Springer.
Huang, Ru., Ma, L., Zhai, G., He, J., Chu, X., & Yan, H. (2020). Resilient routing mechanism for wireless sensor networks with deep learning link reliability prediction. IEEE Access, 8, 64857–64872.
Aggarwal, P., & Sharma, S. K. (2015). Analysis of KDD dataset attributes-class wise for intrusion detection. Procedia Computer Science, 57, 842–851.
Jhaveri, R. H., & Patel, N. M. (2015). A sequence number based bait detection scheme to thwart grayhole attack in mobile ad hoc networks. Wireless Networks, 21(8), 2781–2798.
Sagar, R., Jhaveri, R., & Borrego, C. (2020). Applications in security and evasions in machine learning: A survey. Electronics, 9(1), 97.
Jhaveri, R. H., Desai, A., Patel, A., & Zhong, Y. (2018). A sequence number prediction based bait detection scheme to mitigate sequence number attacks in MANETs. Security and Communication Networks, 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajasoundaran, S., Kumar, S.V.N.S., Selvi, M. et al. Machine learning based volatile block chain construction for secure routing in decentralized military sensor networks. Wireless Netw 27, 4513–4534 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02748-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02748-2