Abstract
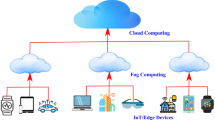
After years of research and discussion on edge technologies, the importance of Fog Computing for the Internet of Things (IoT) is not hidden from anyone. This technology serves at the closest distance to the operating environment and has a multi-layered architecture that penetrates deep into the network. Many resource-constraint and heterogeneous IoT devices send their requests to the Fog. The variety of equipment in this layer is remarkable, but the most important of them is Nano Datacenters. These nodes are located a hop away from the operating environment and provide processing, data storage, and communication services. Fog Nano Datacenters have beneficial features that enhance the ability of developers and researchers to properly design service delivery for IoT real-time applications. In this paper, we tried to introduce them comprehensively, remove ambiguities and describe its services and values. Finally, we presented the challenges and remarks for future research directions in this context.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Fuqaha, A., Guizani, M., Mohammadi, M., Aledhari, M., & Ayyash, M. (2015). Internet of things: A survey on enabling technologies, protocols, and applications. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 17(4), 2347–2376.
Periola, A. (2019). Incorporating diversity in cloud-computing: A novel paradigm and architecture for enhancing the performance of future cloud radio access networks. Wireless Networks, 25(7), 3783–3803.
Wang, Z., Gao, F., & Jin, X. (2020). Optimal deployment of cloudlets based on cost and latency in internet of things networks. Wireless Networks, 26(8), 6077–6093.
Peng, K., Huang, H., Wan, S., & Leung, V.C. (2020). End-edge-cloud collaborative computation offloading for multiple mobile users in heterogeneous edge-server environment. Wireless Networks, pp. 1–12.
Aazam, M., Zeadally, S., & Harras, K. A. (2018). Offloading in fog computing for IOT: Review, enabling technologies, and research opportunities. Future Generation Computer Systems, 87, 278–289.
Luan, T.H., Gao, L., Li, Z., Xiang, Y., & Sun, L. Fog computing: Focusing on mobile users at the edge, CoRR. arXiv:abs/1502.01815.
Yi, S., Li, C., & Li, Q. (2015). A survey of fog computing: Concepts, applications and issues. in Proceedings of the 2015 Workshop on Mobile Big Data, Mobidata ’15, ACM, pp. 37–42.
Jalali, F., Khodadustan, S., Gray, C., Hinton, K., & Suits, F. (2017). Greening iot with fog: A survey. in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Edge Computing (EDGE), pp. 25–31.
Lee, I., & Lee, K. (2015). The internet of things (iot): Applications, investments, and challenges for enterprises. Business Horizons, 58(4), 431–440.
Jalali, F., Hinton, K., Ayre, R., Alpcan, T., & Tucker, R. S. (2016). Fog computing may help to save energy in cloud computing. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 34(5), 1728–1739.
Zhu, C., Leung, V. C. M., Shu, L., & Ngai, E. C. (2015). Green internet of things for smart world. IEEE Access, 3, 2151–2162.
Nguyen, K. T., Laurent, M., & Oualha, N. (2015). Survey on secure communication protocols for the internet of things. Ad Hoc Networks, 32, 17–31.
Centenaro, M., Vangelista, L., Zanella, A., & Zorzi, M. (2016). Long-range communications in unlicensed bands: The rising stars in the iot and smart city scenarios. IEEE Wireless Communications, 23(5), 60–67.
Mahmoud, S., & Mohamad, A. A. H. (2016). A study of efficient power consumptionwireless communication techniques 1 modules for internet of things (iot) applications. Advances in Internet of Things, 06(02), 19–29.
Desai, P., Sheth, A., & Anantharam, P. (2015). Semantic gateway as a service architecture for iot interoperability. in 2015 IEEE International Conference on Mobile Services, pp. 313–319.
Aloi, G., Caliciuri, G., Fortino, G., Gravina, R., Pace, P., Russo, W., & Savaglio, C. (2016). A mobile multi-technology gateway to enable iot interoperability. in 2016 IEEE First International Conference on Internet-of-Things Design and Implementation (IoTDI), pp. 259–264.
Blackstock, M., & Lea, R. (2014). Iot interoperability: A hub-based approach. in 2014 International Conference on the Internet of Things (IOT), pp. 79–84.
Karagiannis, V., Chatzimisios, P., Vazquez-Gallego, F., & Alonso-Zarate, J. (2015). A survey on application layer protocols for the internet of things. Transaction on IoT and Cloud Computing, 03(01), 11–17.
Rahman, T., & Chakraborty, S.K. (2018). Provisioning technical interoperability within zigbee and ble in iot environment. in 2018 2nd International Conference on Electronics, Materials Engineering & Nano-Technology (IEMENTech), IEEE, pp. 1–4.
Thangavel, D., Ma, X., Valera, A., Tan, H., & Tan, C.K. (2014). Performance evaluation of mqtt and coap via a common middleware. in 2014 IEEE Ninth International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing (ISSNIP), pp. 1–6.
Pacini, F., Aderohunmu, F.A., Azzara, A., Petracca, M., & Bocchino, S. (2015). Performance analysis of data serialization formats in m2m wireless sensor networks. in International Conference on Embedded Wireless Systems and Networks.
Petersen, B., Bindner, H., You, S., & Poulsen, B. (2017). Smart grid serialization comparison: Comparision of serialization for distributed control in the context of the internet of things, in. Computing Conference, 2017, 1339–1346.
Sun, X., & Ansari, N. (2016). Edgeiot: Mobile edge computing for the internet of things. IEEE Communications Magazine, 54(12), 22–29.
Mahmud, R., Kotagiri, R., & Buyya, R. (2018). Fog computing: A taxonomy, survey and future directions, pp. 103–130.
M. Satyanarayanan, Chen, Z., Ha, K., Hu, W., Richter, W., & Pillai, P. (2014). Cloudlets: at the leading edge of mobile-cloud convergence. in 6th International Conference on Mobile Computing, Applications and Services, pp. 1–9.
Mao, Y., You, C., Zhang, J., Huang, K., & Letaief, K. B. (2017). A survey on mobile edge computing: The communication perspective. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 19(4), 2322–2358.
Habibi, P., Farhoudi, M., Kazemian, S., Khorsandi, S., & Leon-Garcia, A. (2020). Fog computing: A comprehensive architectural survey. IEEE Access, 8, 69105–69133.
Ren, J., Zhang, D., He, S., Zhang, Y., & Li, T. (2019). A survey on end-edge-cloud orchestrated network computing paradigms: Transparent computing, mobile edge computing, fog computing, and cloudlet. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 52(6), 1–36.
Kaur, K., Dhand, T., Kumar, N., & Zeadally, S. (2017). Container-as-a-service at the edge: Trade-off between energy efficiency and service availability at fog nano data centers. IEEE Wireless Communications, 24(3), 48–56.
Mohan, N., & Kangasharju, J., (2016). Edge-fog cloud: A distributed cloud for internet of things computations. in Cloudification of the Internet of Things (CIoT). IEEE, pp. 1–6.
Aazam, M., & Huh, E. (2014). Fog computing and smart gateway based communication for cloud of things. in 2014 International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud, pp. 464–470.
Bonomi, F., Milito, R., Zhu, J., & Addepalli, S. (2012). Fog computing and its role in the internet of things. in Proceedings of the First Edition of the MCC Workshop on Mobile Cloud Computing, MCC ’12, ACM, pp. 13–16.
Farahzadi, A., Shams, P., Rezazadeh, J., & Farahbakhsh, R. Middleware technologies for cloud of things-a survey, Digital Communications and Networks, Elsevier.
Mach, P., & Becvar, Z. (2017). Mobile edge computing: A survey on architecture and computation offloading. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 19(3), 1628–1656.
Satyanarayanan, M., Lewis, G., Morris, E., Simanta, S., Boleng, J., & Ha, K. (2013). The role of cloudlets in hostile environments. IEEE Pervasive Computing, 12(4), 40–49.
Satyanarayanan, M. (2013). Cloudlets: At the leading edge of cloud-mobile convergence. in Proceedings of the 9th International ACM Sigsoft Conference on Quality of Software Architectures, QoSA ’13, ACM, pp. 1–2.
Brogi, A., & Forti, S. (2017). Qos-aware deployment of iot applications through the fog. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 4(5), 1185–1192.
Skarlat, O., Nardelli, M., Schulte, S., & Dustdar, S. (2017). Towards qos-aware fog service placement. in 2017 IEEE 1st International Conference on Fog and Edge Computing (ICFEC), pp. 89–96.
Yousefpour, A., Ishigaki, G., & Jue, J. P., (2017). Fog computing: Towards minimizing delay in the internet of things. in 2017 IEEE international conference on edge computing (EDGE). IEEE, pp. 17–24.
Firdhous, M., Ghazali, O., & Hassan, S. (2014). Fog computing: Will it be the future of cloud computing?. in The Third International Conference on Informatics and Applications, Vol. 03 pp. 8–15.
La, Q. D., Ngo, M. V., Dinh, T. Q., Quek, T. Q., & Shin, H. (2019). Enabling intelligence in fog computing to achieve energy and latency reduction. Digital Communications and Networks, 5(1), 3–9.
Gia, T.N., Jiang, M., Rahmani, A., Westerlund, T., Liljeberg, P., & Tenhunen, H. (2015). Fog computing in healthcare internet of things: A case study on ecg feature extraction. in 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology; Ubiquitous Computing and Communications, pp. 356–363.
Rezazadeh, J., Moradi, M., & SamadIsmail, A. (2011). Efficient localization via middle-node cooperation in wireless sensor networks. in 2011 International Conference on Electrical, Control and Computer Engineering (INECCE), pp. 410–415.
Madsen, H., Burtschy, B., Albeanu, G., & Popentiu-Vladicescu, F. (2013). Reliability in the utility computing era: Towards reliable fog computing. in 2013 20th International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing (IWSSIP), pp. 43–46.
Klimenko, A.B., & Melnik, E.V. (2020). An experimental study of the fog-computing-based systems reliability. in Computer Science On-line Conference, Springer, pp. 438–449.
Pereira, J., Ricardo, L., Luís, M., Senna, C., & Sargento, S. (2019). Assessing the reliability of fog computing for smart mobility applications in vanets. Future Generation Computer Systems, 94, 317–332.
Donta, P.K., Amgoth, T., & Annavarapu, C.S.R. (2020). An extended aco-based mobile sink path determination in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, pp. 1–16.
Yi, S., Hao, Z., Qin, Z., & Li, Q. (2015). Fog computing: Platform and applications. in 2015 Third IEEE Workshop on Hot Topics in Web Systems and Technologies (HotWeb), pp. 73–78.
Rabay’a, A., Schleicher, E., & Graffi, K. (2019). Fog computing with p2p: Enhancing fog computing bandwidth for iot scenarios. in 2019 International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data (SmartData), IEEE, pp. 82–89.
Rezazadeh, J., Moradi, M., Ismail, A. S., & Dutkiewicz, E. (2014). Superior path planning mechanism for mobile beacon-assisted localization in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 14(9), 3052–3064.
Stojmenovic, I., & Wen, S. (2014). The fog computing paradigm: Scenarios and security issues. in 2014 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems, pp. 1–8.
Yi, S., Li, C., & Li, Q. (2015). A survey of fog computing: concepts, applications and issues. in Proceedings of the 2015 workshop on mobile big data, pp. 37–42.
Donta, P. K., Rao, B. S. P., Amgoth, T., Annavarapu, C. S. R., & Swain, S. (2019). Data collection and path determination strategies for mobile sink in 3d wsns. IEEE Sensors Journal, 20(4), 2224–2233.
Zhang, R., Pan, J., Xie, D., & Wang, F. (2015). Ndcmc: A hybrid data collection approach for large-scale wsns using mobile element and hierarchical clustering. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 3(4), 533–543.
Amgoth, T., & Jana, P. K. (2015). Energy-aware routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 41, 357–367.
Dastjerdi, A., Gupta, H., Calheiros, R., Ghosh, S., & Buyya, R. (2016). Chapter 4 - fog computing: Principles, architectures, and applications. In R. Buyya & A. V. Dastjerdi (Eds.), Internet of Things (pp. 61–75). Burlington: Morgan Kaufmann.
Zhang, H., Xiao, Y., Bu, S., Niyato, D., Yu, R., & Han, Z. (2016). Fog computing in multi-tier data center networks: A hierarchical game approach. in 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), pp. 1–6.
Stojmenovic, I. (2014). Fog computing: A cloud to the ground support for smart things and machine-to-machine networks. in 2014 Australasian Telecommunication Networks and Applications Conference (ATNAC), pp. 117–122.
Bellavista, P., & Zanni, A. (2017). Feasibility of fog computing deployment based on docker containerization over raspberrypi. in Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Distributed Computing and Networking, ICDCN ’17, ACM, pp. 16:1–16:10.
van Kempen, A., Crivat, T., Trubert, B., Roy, D., & Pierre, G. (2017). Mec-conpaas: An experimental single-board based mobile edge cloud. in 2017 5th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Cloud Computing, Services, and Engineering (MobileCloud), pp. 17–24.
Rezazadeh, J., Moradi, M., Ismail, A. S., & Dutkiewicz, E. (2015). Impact of static trajectories on localization in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Network, 21(3), 809–827.
Hou, X., Li, Y., Chen, M., Wu, D., Jin, D., & Chen, S. (2016). Vehicular fog computing: A viewpoint of vehicles as the infrastructures. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 65(6), 3860–3873.
Rezazadeh, J., Moradi, M., & Ismail, A. S. (2012). Message-efficient localization in mobile wireless sensor networks. Journal of Communication and Computer, 9(3), 340–344.
Sarkar, S., & Misra, S. (2016). Theoretical modelling of fog computing: A green computing paradigm to support iot applications. IET Networks, 5(2), 23–29.
Ye, D., Wu, M., Tang, S., & Yu, R. (2016). Scalable fog computing with service offloading in bus networks. in 2016 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Cyber Security and Cloud Computing (CSCloud), pp. 247–251.
Okafor, K., Achumba, I., Chukwudebe, G. & Gordon, O. (2017). Leveraging fog computing for scalable iot datacenter using spine- leaf network topology. Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering.
Lashkari, B., Rezazadeh, J., Farahbakhsh, R., & Sandrasegaran, K. (2019). Crowdsourcing and sensing for indoor localization in iot: A review. IEEE Sensors Journal, 19(7), 2408–2434.
Cao, Y., Hou, P., Brown, D., Wang, J., & Chen, S. (2015). Distributed analytics and edge intelligence: Pervasive health monitoring at the era of fog computing. in Proceedings of the 2015 Workshop on Mobile Big Data, Mobidata ’15, ACM, pp. 43–48.
Tang, B., Chen, Z., Hefferman, G., Wei, T., He, H., & Yang, Q. (2015). A hierarchical distributed fog computing architecture for big data analysis in smart cities. in Proceedings of the ASE BigData & SocialInformatics 2015, ASE BD&SI ’15, ACM, pp. 28:1–28:6.
Li, S., Maddah-Ali, M. A., & Avestimehr, A. S. (2017). Coding for distributed fog computing. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(4), 34–40.
Datta, S. K., Bonnet, C., & Haerri, J. (2015). Fog computing architecture to enable consumer centric internet of things services. in 2015 International Symposium on Consumer Electronics (ISCE), pp. 1–2.
Al Faruque, M. A., & Vatanparvar, K. (2016). Energy management-as-a-service over fog computing platform. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 3(2), 161–169.
Aazam, M., & Huh, E. (2015). Fog computing micro datacenter based dynamic resource estimation and pricing model for iot. in 2015 IEEE 29th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications, pp. 687–694.
Hosseinzadeh Sahraei, S., Riahi Kashani, M. M., Rezazadeh, J., & Farahbakhsh, R. (2019). Efficient job scheduling in cloud computing based on genetic algorithm. International Journal of Communication Networks and Distributed Systems, 22(4), 447–467.
Wu, T., Wu, F., Redouté, J., & Yuce, M. R. (2017). An autonomous wireless body area network implementation towards iot connected healthcare applications. IEEE Access, 5, 11413–11422.
Pereira, C., Rodrigues, J., Pinto, A., Rocha, P., Santiago, F., Sousa, J., & Aguiar, A. (2016). Smartphones as m2m gateways in smart cities iot applications. in 2016 23rd International Conference on Telecommunications (ICT), pp. 1–7.
Li, S., Da Xu, L., & Zhao, S. (2015). The internet of things: A survey. Information Systems Frontiers, 17(2), 243–259.
Bardyn, J., Melly, T., Seller, O., & Sornin, N. (2016). Iot: The era of lpwan is starting now. in ESSCIRC Conference 2016: 42nd European Solid-State Circuits Conference, pp. 25–30.
Petersen, B., Bindner, H., Poulsen, B., & You, S. (2017). Smart grid communication comparison: Distributed control middleware and serialization comparison for the internet of things. in 2017 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference Europe (ISGT-Europe), pp. 1–6.
Lanza, J., Sanchez, L., Gomez, D., Elsaleh, T., Steinke, R., & Cirillo, F. A proof-of-concept for semantically interoperable federation of iot experimentation facilities. Sensors, vol. 16, no. 7.
Yassein, M. B., Shatnawi, M. Q., & Al-zoubi, D. (2016). Application layer protocols for the internet of things: A survey. in 2016 International Conference on Engineering MIS (ICEMIS), pp. 1–4.
Mijovic, S., Shehu, E., & Buratti, C. (2016). Comparing application layer protocols for the internet of things via experimentation. in 2016 IEEE 2nd International Forum on Research and Technologies for Society and Industry Leveraging a better tomorrow (RTSI), pp. 1–5.
Rezazadeh, J., Moradi, M., Sandrasegaran, K., & Farahbakhsh, R. (2019). Transmission power adjustment scheme for mobile beacon-assisted sensor localization. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 15(5), 2859–2869.
Kausha, K., Kaur, T., & Kaur, J. Zigbee based wireless sensor networks. in International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies(IJCSIT).
Obaid, T., Rashed, H., Abou-Elnour, A., Rehan, M., Saleh, M., & Tarique, M. (2014). Zigbee technology and its application in wireless home automation systems: A survey. in International Journal of Computer Networks and Communications.
[link]. https://z-wave.sigmadesigns.com
Ahson, S., & Ilyas, M. (2017). Rfid Handbook: Applications, Technology, Security, and Privacy. Hoboken: CRC Press.
Zhang, D., Huang, H., & Jo, M. (2015). Future rfid technology and applications: visions and challenges. in Telecommunication Systems, Vol. 58, pp. 193–194.
Rezazadeh, J., Subramanian, R., Sandrasegaran, K., Kong, X., Moradi, M., & Khodamoradi, F. (2018). Novel ibeacon placement for indoor positioning in iot. IEEE Sensors Journal, 18(24), 10240–10247.
Raza, S., Misra, P., He, Z., & Voigt, T. (2015). Bluetooth smart: An enabling technology for the internet of things. in 2015 IEEE 11th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob), pp. 155–162.
Raza, S., Misra, P., He, Z., & Voigt, T. (2017). Building the internet of things with bluetooth smart. Ad Hoc Networks, 57, 19–31 special Issue on Internet of Things and Smart Cities: security, privacy and new technologies.
Matheus, L. E. M., Vieira, A. B., Vieira, L. F., Vieira, M. A., & Gnawali, O. (2019). Visible light communication: Concepts, applications and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 21(4), 3204–3237.
Finnegan, J., & Brown, S. (2018). A comparative survey of lpwa networking. arXiv:1802.04222.
Adelantado, F., Vilajosana, X., Tuset-Peiro, P., Martinez, B., Melia-Segui, J., & Watteyne, T. (2017). Understanding the limits of lorawan. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(9), 34–40.
[link]. http://waviot.com
Chen, M., Miao, Y., Hao, Y., & Hwang, K. (2017). Narrow band internet of things. IEEE Access, 5, 20557–20577.
Wang, Y. E., Lin, X., Adhikary, A., Grovlen, A., Sui, Y., Blankenship, Y., Bergman, J., & Razaghi, H. S. (2017). A primer on 3g pp narrowband internet of things. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(3), 117–123.
Sjstrm, D. (2017). Unlicensed and licensed low-power wide area networks: Exploring the candidates for massive iot.
[link]. https://www.qualcomm.com
Ge, S., Chun, S., Kim, H., & Park, J. (2016). Design and implementation of interoperable iot healthcare system based on international standards. in 2016 13th IEEE Annual Consumer Communications Networking Conference (CCNC), pp. 119–124.
[link]. https://www.w3.org/XML/
Moazzami, M., Xing, G., Mashima, D., Chen, W., & Herberg, U. (2016). Spot: A smartphone-based platform to tackle heterogeneity in smart-home iot systems. in 2016 IEEE 3rd World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), pp. 514–519.
Huang, J.-Y., Hong, W.-C., Tsai, P.-S., & Liao, I.-E. (2017). A model for aggregation and filtering on encrypted xml streams in fog computing. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 13(5), 1550147717704158.
[link]. https://buildbot.tools.ietf.org
Hussain, A., & Wu, W. (2017). Sustainable interoperability and data integration for the iot-based information systems. in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom), pp. 824–829.
Datta, S.K., & Bonnet, C. (2016). Describing things in the internet of things: From core link format to semantic based descriptions. in 2016 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW), pp. 1–2.
[link]. http://yaml.org/
Wang, S., Hou, Y., Gao, F., & Ma, S. (2016). Ontology-based resource description model for internet of things. in 2016 International Conference on Cyber-Enabled Distributed Computing and Knowledge Discovery (CyberC), pp. 105–108.
Lucky, M. N., Cremaschi, M., Lodigiani, B., Menolascina, A., & De Paoli, F. (2016). Enriching api descriptions by adding api profiles through semantic annotation. In Q. Z. Sheng, E. Stroulia, S. Tata, & S. Bhiri (Eds.), Service-Oriented Computing (pp. 780–794). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Johnston, S.J., Apetroaie-Cristea, M., Scott, M., & Cox, S.J. (2016). Applicability of commodity, low cost, single board computers for internet of things devices. in 2016 IEEE 3rd World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), pp. 141–146.
[link]. http://thrift.apache.org/
Babovic, Z. B., Protic, J., & Milutinovic, V. (2016). Web performance evaluation for internet of things applications. IEEE Access, 4, 6974–6992.
Suthakar, U., Magnoni, L., Smith, D. R., Khan, A., & Andreeva, J. (2016). An efficient strategy for the collection and storage of large volumes of data for computation. Journal of Big Data, 3(1), 21.
[link]. https://msgpack.org/index.html
[link]. https://www.prismtech.com
[link]. http://cbor.io/
[link]. https://tools.ietf.org/
Pöhls, H.C., & Petschkuhn, B. (2017). Towards compactly encoded signed iot messages. in 2017 IEEE 22nd International Workshop on Computer Aided Modeling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD), pp. 1–6.
Peralta, G., Iglesias-Urkia, M., Barcelo, M., Gomez, R., Moran, A., & Bilbao, J., (2017). Fog computing based efficient iot scheme for the industry 4.0. in 2017 IEEE International Workshop of Electronics, Control, Measurement. Signals and their Application to Mechatronics (ECMSM), pp. 1–6.
Singh, M., Rajan, M. A., Shivraj, V. L., & Balamuralidhar, P. (2015). Secure mqtt for internet of things (iot). in 2015 Fifth International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies, pp. 746–751.
Kim, S., Choi, H., & Rhee, W. (2015). Iot home gateway for auto-configuration and management of mqtt devices. in 2015 IEEE Conference on Wireless Sensors (ICWiSe), pp. 12–17.
Govindan, K., & Azad, A.P. (2015). End-to-end service assurance in iot mqtt-sn. in 2015 12th Annual IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC), pp. 290–296.
[link]. https://www.amqp.org/
Bhimani, P., & Panchal, G. (2018). Message delivery guarantee and status update of clients based on iot-amqp. In Y.-C. Hu, S. Tiwari, K. K. Mishra, & M. C. Trivedi (Eds.), Intelligent Communication and Computational Technologies (pp. 15–22). Singapore: Springer Singapore.
Happ, D., Karowski, N., Menzel, T., Handziski, V., & Wolisz, A. (2017). Meeting iot platform requirements with open pub/sub solutions. Annals of Telecommunications, 72(1), 41–52.
Luzuriaga, J.E., Perez, M., Boronat, P., Cano, J.C., Calafate, C., & Manzoni, P. (2015). A comparative evaluation of amqp and mqtt protocols over unstable and mobile networks. in 2015 12th Annual IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC), pp. 931–936.
Shi, H., Chen, N., & Deters, R. (2015). Combining mobile and fog computing: Using coap to link mobile device clouds with fog computing. in 2015 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Data Intensive Systems, pp. 564–571.
Castro, M., Jara, A. J., & Skarmeta, A. F. (2016). Enabling end-to-end coap-based communications for the web of things. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 59, 230–236.
Cirani, S., Ferrari, G., Iotti, N., & Picone, M. (2015). The iot hub: a fog node for seamless management of heterogeneous connected smart objects. in 2015 12th Annual IEEE International Conference on Sensing, Communication, and Networking - Workshops (SECON Workshops), pp. 1–6.
Capossele, A., Cervo, V., De Cicco, G., & Petrioli, C. (2015). Security as a coap resource: An optimized dtls implementation for the iot. in 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), pp. 549–554.
[link]. https://www.websocket.org/
Kayal, P., & Perros, H. (2017). A comparison of iot application layer protocols through a smart parking implementation. in 2017 20th Conference on Innovations in Clouds, Internet and Networks (ICIN), pp. 331–336.
Mun, D., Dinh, M.L., & Kwon, Y. (2016). An assessment of internet of things protocols for resource-constrained applications. in 2016 IEEE 40th Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Vol. 1, pp. 555–560.
Conzon, D., Bolognesi, T., Brizzi, P., Lotito, A., Tomasi, R., & Spirito, M.A. (2012). The virtus middleware: An xmpp based architecture for secure iot communications. in 2012 21st International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN), pp. 1–6.
Kirsche, M., & Klauck, R. (2012). Unify to bridge gaps: Bringing xmpp into the internet of things. in 2012 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops, pp. 455–458.
[link]. https://xmpp.org/
Peniak, P., & Franekova, M. (2015). Open communication protocols for integration of embedded systems within industry 4. in 2015 International Conference on Applied Electronics (AE), pp. 181–184.
Al-Fuqaha, A., Khreishah, A., Guizani, M., Rayes, A., & Mohammadi, M. (2015). Toward better horizontal integration among iot services. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(9), 72–79.
[link]. http://portals.omg.org/dds/
[link]. https://stomp.github.io/
Hintjens, P. (2013). Toward better horizontal integration among iot services, O’Reilly Media,
[link]. http://zeromq.org/
Faraj, O., Megías, D., Ahmad, A.-M., & Garcia-Alfaro, J. (2020). Taxonomy and challenges in machine learning-based approaches to detect attacks in the internet of things. in Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security, pp. 1–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farahzadi, A., Farahsary, P.S. & Rezazadeh, J. A survey on IoT fog nano datacenters. Wireless Netw 28, 173–207 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02829-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02829-2