Abstract
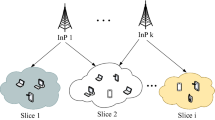
In this paper, we address the interference management problem in non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA)-enabled virtualized wireless networks (VWNs) by using power allocation approaches. Specifically, the power resources of the base station (BS) are shared among different service providers (called the slices), where the maximum tolerant interference is considered for each slice to guarantee their interference isolation. The interference management (IM) problem is formulated aiming to maximize the sum-rate of the system subject to the slice interference isolation, the minimum required rates of the individual users, and the power budget constraints of the whole system. Then, an optimal interference management algorithm (IMA) is proposed to solve the IM problem in a centralized manner at the BS. In addition, a computational-complexity reduced IMA (CCRIMA) is proposed with the implementation in a semi-distributed manner within each slice to obtain a suboptimal IM solution. Simulation results show that the proposed optimal power allocation in IMA achieves a flexible interference management within each slice, while supporting the minimum rate requirements of all users by adjusting the maximum tolerant interference in the slice. Moreover, the proposed CCRIMA can approximate the optimal performance of IMA in terms of the sum-rate of the system with a little computational cost of the computational complexity in each slice.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is obtained on execution of the code and no external data source is involved in the study.
Code availability
Code is being written by the author and no external source is involved for the coding and development.
References
Zhang, H., Liu, N., Chu, X., Long, K., Aghvami, A.-H., & Leung, V. C. M. (2017). Network slicing based 5G and future mobile networks: Mobility, resource management, and challenges. IEEE Communication Magazine, 55(8), 138–145.
Saad, W., Bennis, M., & Chen, M. (2020). A vision of 6G wireless systems: Applications, trends, technologies, and open research problems. IEEE Network, 34(3), 134–142.
Zhang, N., Liu, Y., Farmanbar, H., Chang, T., Hong, M., & Luo, Z. (2017). Network slicing for service-oriented networks under resource constraints. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 35(11), 2512–2521.
Habiba, U., & Hossain, E. (2018). Auction mechanisms for virtualization in 5G cellular networks: basics, trends, and open challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 20(3), 2264–2293.
Yang, K., Yang, N., Ye, N., Jia, M., Gao, Z., & Fan, R. (2019). Non-orthogonal multiple access: achieving sustainable future radio access. IEEE Communications Magazine, 57(2), 116–121.
Shahini, A., & Ansari, N. (2019). NOMA aided narrowband IoT for machine type communications with user clustering. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(4), 7183–7191.
Ali, M. S., Tabassum, H., & Hossain, E. (2016). Dynamic user clustering and power allocation for uplink and downlink non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) systems. IEEE Access, 4, 6325–6343.
Tang, S. Y., Ma, Z., Xiao, M., & Hao, L. (2020). Hybrid transceiver design for beamspace MIMO-NOMA in code-domain for MmWave communication using lens antenna array. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 38(9), 2118–2127.
Wang, K., Liang, W., Yuan, Y., Liu, Y., Ma, Z., & Ding, Z. (2019). User clustering and power allocation for hybrid non-orthogonal multiple access systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 68(12), 12052–12065.
Yang, Z., Xu, W., Pan, C., Pan, Y., & Chen, M. (2017). On the optimality of power allocation for NOMA downlinks with individual QoS constraints. IEEE Communications Letter, 21(7), 1649–1652.
Zhang, Y., Wang, H.-M., Zheng, T.-X., & Yang, Q. (2017). Energy-Efficient transmission design in non-orthogonal multiple access. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66(3), 2852–2857.
Liang, C., & Yu, F. R. (2015). Wireless network virtualization: A survey, some research issues and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 17(1), 358–380.
Tun, Y. K., Ndikumana, A., Pandey, S. R., Han, Z., & Hong, C. S. (2020). Joint radio resource allocation and content caching in heterogeneous virtualized wireless networks. IEEE Access, 8, 36764–36775.
Goswami, D., & Das, S. S. (2020). Iterative sub-band and power allocation in downlink multiband NOMA. IEEE Systems Journal, 14(4), 5199–5209.
Salaün, L., Coupechoux, M., & Chen, C. S. (2020). Joint subcarrier and power allocation in NOMA: optimal and approximate algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 68, 2215–2230.
Wang, X., Chen, R., Xu, Y., & Meng, Q. (2019). Low-complexity power allocation in NOMA systems With IMPERFECT SIC for maximizing weighted sum-rate. IEEE Access, 7, 94238–94253.
Zhu, J., Wang, J., Huang, Y., He, S., You, X., & Yang, L. (2017). On optimal power allocation for downlink non-orthogonal multiple access systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 35(12), 2744–2757.
Fang, F., Wang, K., Ding, Z., & Leung, V. C. M. (2021). Energy-efficient resource allocation for NOMA-MEC networks with imperfect CSI. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 69(5), 3436–3449.
Liu, B., Liu, C., & Peng, M. (2021). Resource allocation for energy-efficient MEC in NOMA-enabled massive IoT networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 39(4), 1015–1027.
Tun, Y. K., Tran, N. H., Ngo, D. T., Pandey, S. R., Han, Z., & Hong, C. S. (2019). Wireless network slicing: Generalized kelly mechanism-based resource allocation. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 37(8), 1794–1807.
Kim, D. H., Ahsan Kazmi, S. M., Ndikumana, A., Manzoor, A., Saad, W., & Hong, C. S. (2020). Distributed radio slice allocation in wireless network virtualization: matching theory meets auctions. IEEE Access, 8, 73494–73507.
Parsaeefard, S., Dawadi, R., Derakhshani, M., & Le-Ngoc, T. (2016). Joint user-association and resource-allocation in virtualized wireless networks. IEEE Access, 4, 2738–2750.
Parsaeefard, S., Jumba, V., Derakhshani, M., & Le-Ngoc, T. (2015). Joint Resource Provisioning and Admission Control in Wireless Virtualized Networks. In 2015 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC) (pp. 2020–2025). IEEE, New Orleans.
Ho, T. M., Tran, N. H., Kazmi, S.M.A., & Hong, C. S. (2017). Dynamic Pricing for Resource Allocation in Wireless Network Virtualization: A Stackelberg Game Approach. In 2017 IEEE International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN) (pp. 429–434). IEEE, Da Nang.
Tun, Y. K., Zaw, C. W., & Hong, C. S. (2017). Downlink power allocation in virtualized wireless networks. In 2017 19th Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS) (pp. 346–349). IEEE, Seoul.
Chang, Z., & Chen, T. (2021). Virtual Resource Allocation for Wireless Virtualized Heterogeneous Network with Hybrid Energy Supply. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, (Early Access).
Tang, L., Shi, Y., Wang, C., & Chen, Q. (2018). Adaptive virtual resource allocation in 5G network slicing using constrained markov decision process. IEEE Access, 6, 61184–61195.
Rezvani, S., Parsaeefard, S., Mokari, N., Mokari, N., Mohammad, R., & Yanikomeroglu, H. (2019). Cooperative multi-bitrate video caching and transcoding in multicarrier NOMA-assisted heterogeneous virtualized MEC networks. IEEE Access, 7, 93511–93536.
Tweed, D., Parsaeefard, S., Derakhshani, M., & Le-Ngoc, T. (2017). Dynamic resource allocation for MC-NOMA VWNs with imperfect SIC. In 2017 IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC) (pp. 1–5). IEEE, Montreal.
Tweed, D., & Le-Ngoc, T. (2018). Dynamic Resource Allocation for Uplink MIMO NOMA VWN with Imperfect SIC. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) (pp. 1–6). IEEE, Kansas.
Mohammad, A., & Ansari, N. (2021). Energy aware latency minimization for network slicing enabled edge computing. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 5(4), 2150–2159.
Mohammad, R., Mokhtari, F., & Ashtiani, F. (2019). Improving tradeoff among downlink rates of service providers in a VWN by using NOMA. IEEE Communication Letters, 23(1), 156–159.
Souto, V., Montejo-Sanchez, S., Rebelatto, J., Souza, R., & Uchoa-Filho, B. (2021). IRS-aided physical layer network slicing for URLLC and eMBB. IEEE Access, 9, 163086–163098.
Wang, Z., Xu, T., Zhou, T., & Hu, H. (2020). Joint Tier Slicing and Power Control for a Novel Multicast System based on NOMA and D2D-Relay. In 2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 1–6). IEEE, Taipei.
Tominaga, E., Alves, H., L´opez, O., Souza, R., & Luiz, J. (2021). Network Slicing for eMBB and mMTC with NOMA and Space Diversity Reception. In 2021 IEEE 93rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2021-Spring) (pp. 1–6). IEEE, Helsinki.
Mohammad, A., & Ansari, N. (2021). Network Slicing for NOMA-Enabled Edge Computing. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, (Early Access).
Mlika, Z., & Cherkaoui, S. (2021). Network slicing with MEC and deep reinforcement learning for the internet of vehicles. IEEE Network, 35(3), 132–138.
Tebe, P., Ntiamoah-Sarpong, K., Tian, W., Li, J., Huang, Y., & Wen, G. (2020). Using 5G network slicing and non-orthogonal multiple access to transmit medical data in a mobile hospital system. IEEE Access, 8, 189163–189178.
Sinaie, M., Ng, D. W. K., & Jorswieck, E. A. (2018). Resource allocation in NOMA virtualized wireless networks under statistical delay constraints. IEEE Wireless Communication Letters, 7(6), 954–957.
Dawadi, R., Parsaeefard, S., Derakhshani, M., & Le-Ngoc, T. (2016). Power-Efficient Resource Allocation in NOMA Virtualized Wireless Networks. In 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 1–6). IEEE, Washington.
Ho, T. M., Tran, N. H., Kazmi, S.M A., Han, Z., & Hong, C. S. (2018). Wireless Network Virtualization with Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access. In 2018 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium (NOMS) (pp. 1–6). IEEE, Taipei.
Rezvani, S., Yamchi, N. M., Javan, M. R., & Jorswieck, E. A. (2021). Resource allocation in virtualized CoMP-NOMA HetNets: multi-connectivity for joint transmission. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 69(6), 4172–4185.
Boyd, S., & Vandenberghe, L. (2004). Convex optimization. Cambridge University Press.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chinese Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grant No. BK20181032, the Major Projects of Natural Sciences of University of Jiangsu Province under Grant No. 20KJB510044b, and the Scientific Research Foundation of Changshu Institute of Technology under Grant No. KYZ2018004Q.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Tao, Y. & Xing, S. Interference management in NOMA-enabled virtualized wireless networks. Wireless Netw 28, 1457–1474 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-022-02911-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-022-02911-3