Abstract
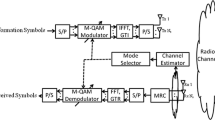
The paper presents a new multiplexing scheme, called convolutional multiplexing (CM), to achieve high diversity gain and high spectrum efficiency for OFDM-based systems. In this scheme, data symbols are spread onto several subcarriers by the convolutional spreader. Spectrum efficiency can be improved by two approaches: high order modulation and multi-code multiplexing. With the best spreading codes searched out, the multi-code multiplexing OFDM-CM system performs better in AWGN channel, but may lose diversity gain in frequency selective fading channels. On the other hand, the single-code spreading OFDM-CM system with high order modulation can achieve the maximum diversity order. Simulation results show that the multi-code convolutional multiplexing perform better than code-division multiplexing (CDM) for OFDM-based systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
3GPP TS 36.212. (2007). Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Multiplexing and channel coding (Release 8).
Anderson J. and Mohan S. (1984). Sequential coding algorithms: A survey and cost analysis. IEEE Transactions on Communications 32(2): 169–176
Bingham J.A.C. (1990). Multicarrier modulation for data transmission: An idea whose time has come. IEEE Communications Magazine 28(5): 5–14
Chouly, A., Brajal, A., & Jourdan, S. (1993). Orthogonal multicarrier techniques applied to direct sequence spread spectrum CDMA systems. In IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference (GLOBECOM’93), Houston, USA (Vol. 3, pp. 1723–1728).
Divsalar D. and Simon M.K. (1988). The design of trellis coded MPSK for fading channels: Performance criteria. IEEE Transactions on Communications 36(9): 1004–1012
ETSI ETS 300 401. (1995). Radio broadcasting systems; digital audio broadcasting (DAB) to mobile, portable and fixed receivers.
ETSI ETS 300 744. (1997). Digital video broadcasting (DVB); frame structure, channel coding and modulation for digital terrestrial television (DVB-T).
Eyuboglu M.V. and Qureshi S.U.H. (1988). Reduced-state sequence estimation with set partitioning and decision feedback. IEEE Transactions on Communications 36(1): 13–20
Fazel, K., & Papke, L. (1993). On the performance of convolutionally coded CDMA-OFDM for mobile communication system. In IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC’93), Yokohama, Japan (pp. 468–472).
Forney G.D. Jr. (1972). Maximum-likelihood sequence estimation of digital sequences in the presence of intersymbol interference. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 18(3): 363–378
Forney G.D. Jr. (1973). The Viterbi algorithm. Proceedings of the IEEE 61(3): 268–278
Hanzo L., Mnster M., Choi B. and Keller T. (2003). OFDM and MC-CDMA for broadband multi-user communications, WLANs and broadcasting. Wiley-IEEE Press, New York
ITU-R M.1225. (1998). Guidelines for evaluation of radio transmission technologies for IMT-2000.
Kaiser S. (2002). OFDM code-division multiplexing in fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Communications 50(8): 1266–1273
Le Floch B., Alard M. and Berrou C. (1995). Coded orthogonal frequency division multiplex. Proceedings of the IEEE 83(6): 982–996
Proakis J.G. (2001). Digital communications (4th ed). McGraw Hill, New York
Sundberg C.-E.W. and Seshadri N. (1993). Coded modulation for fading channels: An overview. European Transactionns on Telecommunications 4(3): 309–323
Ungerboeck G. (1974). Adaptive maximum-likelihood receiver for carrier-modulated data-transmission systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications 22(5): 624–636
van Nee R., Awater G., Morikura M., Takanashi H., Webster M. and Halford K.W. (1999). New high-rate wireless LAN standards. IEEE Communications Magazine 37(12): 82–88
Weinstein S. and Ebert P. (1971). Data transmission by frequency-division multiplexing using the discrete Fourier transform. IEEE Transactions on Communications 19(5): 628–634
Yee, N., Linnartz, J. P., & Fettweis, G. (1993). Multi-carrier CDMA in indoor wireless radio networks. In IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC’93), Yokohama, Japan (pp. 109–113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, W., Li, D. Convolutional Multiplexing for Multicarrier Transmission: System Performance and Code Design. Wireless Pers Commun 49, 545–560 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-008-9576-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-008-9576-0