Abstract
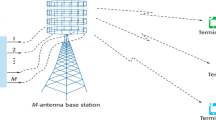
Multi-user single-carrier multiple-input multiple-output (MU SC-MIMO) multiplexing can increase the uplink capacity of a cellular system without expanding the signal bandwidth. It is practically important to make clear an extent to which the MU SC-MIMO multiplexing combined with frequency-domain equalization (FDE) and transmit power control (TPC) can increase the uplink capacity in the presence of the co-channel interference (CCI). Since the theoretical analysis is quite difficult, we resort to the computer simulation to investigate the uplink capacity. In this paper, frequency-domain zero-forcing detection (ZFD) and frequency-domain minimum mean square error detection (MMSED) are considered for MU signal detection. It is shown that ZFD and MMSED provide almost the same uplink capacity and that an advantage of fast TPC over slow TPC diminishes. As a result, MU SC-MIMO using computationally efficient ZFD can be used together with slow TPC instead of using MMSED. With 8 receive antennas and slow TPC, MU SC-MIMO multiplexing using ZFD can achieve about 1.5 times higher uplink capacity than SU SC-SIMO diversity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi F. (2001) Wireless past and future-evolving mobile communications systems. IEICE Transactions Fundamentals of Electronics 84(A1): 55–60
Proakis J. G. (2001) Digital communications. McGraw-Hill, New york
Falconer D., Ariyavistakul S. L., Benyamin-Seeyer A., Eidson B. (2002) Frequency domain equalization for single-carrier broadband wireless systems. IEEE Communication Magazine 40(4): 58–66
Adachi F., Garg D., Takaoka S., Takeda K. (2005) Broadband CDMA techniques, Special Issue on Modulation, Coding and Signal Processing. IEEE Wireless communications Magazine 12(2): 8–18
Jakes, W. C., Jr. (eds) (1974) Microwave mobile communications. John Wiley & Sons, New york
Gesbert D., Kountouris M., Heath R. W. Jr., Chae C. B., Salzer T. (2007) Shifting the MIMO paradigm: From single user to multiuser communications. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 24(5): 36–46
Spencer Q. H., Peel C. B., Swindlehurst A. L., Haardt M. (2004) An introduction to the multi-user MIMO downlink. IEEE Communications Magazine 42(10): 60–67
Suard B., Xu G., Liu H., Kailath T. (1998) Uplink channel capacity of space-division-multiple-access schemes. IEEE Transactions Information Theory 44(4): 1468–1476
Sfar S., Murch R. D., Letaief K. B. (2003) Layered space-time multiuser detection over wireless uplink systems. IEEE Transactions Wireless communications 2(4): 653–668
Ekstrom H., Furuskar A., Karlsson J., Meyer M., Parkvall S., Torsner J., Wahlqvist M. (2006) Technical solutions for the 3G long-term evolution. IEEE Communications Magazine 44(3): 38–45
Guo, L., & Huang, Y. (2005). A Multi-user SC-FDE-MIMO system for frequency-selective channels. In Thirty-Ninth Asilomar conference on signals, systems and computers, pp. 1593–1597.
Vandenameele, P., der Perre, L.V., Gyselinckx, B., Engels, M., Moonen, M., & Man, H.D. (2000). A single-carrier frequency-domain SDMA basestation. In Proceedings IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, pp. 3714–3717.
Coon, J.P., & Beach, M.A. (2002). An investigation of MIMO single-carrier frequency domain MMSE equalization. In: Proceedings London communications simposium, pp. 237–240.
Rappaport T. S. (1996) Wireless communications. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Dohi, T., Sawahashi, M., & Adachi, F. (1995). Performance of SIR based power control in the presence of non-uniform traffic distribution. In Fourth IEEE international conference on universal personal communications, pp. 334–338.
Kaltakis D., Katranaras E., Imran M. A., Tzaras C. (2009) Information theoretic capacity of Gaussian cellular multiple-access MIMO fading channel. IET Communications 3(7): 1201–1207
Aktas D., Bacha M. N., Evans J. S., Hanly S. V. (2006) Scaling results on the sum capacity of cellular networks with MIMO links. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 52(7): 3264–3274
Chatzinotas S., Imran M., Hoshyar R. (2009) On the multicell processing capacity of the cellular MIMO uplink channel in correlated rayleigh fading environment. IEEE Transactions on Wireless communications 8(7): 3704–3715
Jian, L., Kortke, A., & Keusgen, W. (2009). Antenna diversity schemes for uplink frequency-domain multiuser detection in CP-assisted DS-CDMA systems. In IEEE international conference on communications, pp. 1–5.
El-Sallabi, H., Baum, D. S., Zetterberg, P., Kyosti, P., Rautiainen, T., & Schneider, C. (2006). Wideband spatial channel model for MIMO systems at 5 GHz in indoor and outdoor environments. In IEEE 63rd vehicular technology conference, 6, pp. 7–10.
Skentos, N. D., Kanatas, A. G., & Constantinou, P. (2006). Multipath parameter results for short range urban propagation environments. In IEEE international conference on wireless and mobile computing, networking and communications, pp. 413–418.
Huang, H., & Valenzuela, R. A. (2005). Fundamental simulated performance of downlink fixed wireless cellular networks with multiple antennas. In IEEE 16th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications, pp. 161–165.
Huang H., Trivellato M., Hottinen A., Shafi M., Smith P., Valenzuela R. (2009) Increasing downlink cellular throughput with limited network MIMO coordination. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 8(6): 2983–2989
Adachi F., Sao T. (2003) Joint antenna diversity and frequency-domain equalization for multi-rate MC-CDMA. IEICE Transactions Communications E86-B(11): 3217–3224
Chen, C., & Wang, L. (2005). On the performance of the zero-forcing receiver operating in the multiuser MIMO system with reduced noise enhancement effect. In Proceedings IEEE global telecommunications conference, pp. 1294–1298.
Gore D. A., Heath R. W., Paulraj A. J. (2002) Transmit selection in spatial multiplexing systems. IEEE Communications Letters 6(11): 491–493
Winters J. H., Salz J., Gitlin R. D. (1994) The impact of antenna diversity on the capacity of wireless communication systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications 42(2/3/4): 1740–1751
Bauch, G., Bach Andersen, J., Guthy, C., Herdin, M., Nielsen, J., Nossek, J. A., Tejera, P., & Utschick, W. (2007). Multiuser MIMO channel measurements and performance in a large office environment. In IEEE wireless communications and networking conference, pp. 1900–1905.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiba, T., Takeda, K., Takeda, K. et al. Uplink Capacity of A Cellular System Using Multi-user Single-carrier MIMO Multiplexing Combined with Frequency-domain Equalization and Transmit Power Control. Wireless Pers Commun 58, 455–468 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-010-0130-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-010-0130-5