Abstract
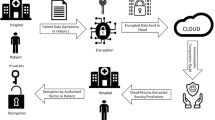
With the popularity of cloud computing, how to securely authenticate a user while not releasing user’s sensitive information becomes a challenge. In this paper, we introduce a slight homomorphic signature, which is suitable to implement an access controlling service in cloud computing. In slight homomorphic signature, each user in cloud computing who have a set of identity attributes, firstly computes a full signature on all his identity attributes, and sends it to a semi-trusted access controlling server. The access controlling server verifies the full signature for all identity attributes. After then, if the user wants to require a cloud service, which may have a special requirement on one of the identity attributes, the user only needs to securely send the cloud service’s name to the access controlling server. The access controlling server which does not know the secret key can compute a partial signature on this special identity attribute, and then sends it to the cloud server for authentication. In the paper, we give a formal secure definition of this slight homomorphic signature, and construct a scheme from Boneh–Boyen signature. We prove that our scheme is secure under q-SDH problem with a weak adversary.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Teamviewer is one of the top 15 consumer cloud services, which is a great screen sharing and ”GoToMyPC” style service. The service works PC to PC, Mac to Mac, and PC to Mac as well. If used in a commercial setting, license fees are a one-time charge and range from 7,500 to 2,700 for corporate accounts.
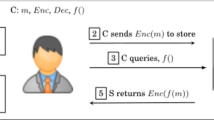
Since the client side usually has limited resource, the heavy operations in the computation of full signatures can be forwarded to other servers.
References
Ateniese, G. et al. (2005). Sanitizable signatures. In Proceedings of ESORICS’05.
Bellare, M., & Neven, G. (2005). Transitive signatures: New schemes and proofs. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 51, 2133–2151.
Bertino, E., Paci, F., Ferrini, R., & Shang N. (2009) Privacy-preserving digital identity management for cloud computing. IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin, 32(1), 21–27.
Boneh, D., & Boyen, X. (2008). Short signatures without random oracles and the sdh assumption in bilinear groups. Journal of Cryptology, 21, 149–177.
Boneh, D., & Freeman, D. (2010). Linearly homomorphic signatures over binary fields and new tools for lattice-based signatures. In Proceedings of the 13th international conference on practice and theory in public key cryptography(PKC’10).
Boneh, D., & Freeman, D. (2011). Homomorphic signatures for polynomial functions. In Proceedings of Eurocrypt 2011.
Boneh, D., Freeman, D., Katz, J., & Waters, B. (2009). Signing a linear subspace: Signature schemes for network coding. In Proceedings of the 12th international conference on practice and theory in public key cryptography(PKC’09).
Boneh, D., Lynn, B., & Shacham, H. (2004). Short signatures from the weil pairing. Journal of Cryptology, 17(4), 297–319.
Brzuska, C. et al. (2009). Security of sanitizable signatures revisited. In Proceedings of the 12th international conference on practice and theory in public key cryptography(PKC’09).
Brzuska, C. et al. (2010). Unlinkability of sanitizable signatures. In Proceedings of the 13th international conference on practice and theory in public key cryptography(PKC’10).
Gennaro, R. et al. (2010). Secure network coding over the integers. In Proceedings of the 13th international conference on practice and theory in public key cryptography(PKC’10).
Gentry, C. (2009). A fully homomorphic encryption scheme.
Hatano, Y. et al. (2008). Efficient signature schemes supporting redaction, pseudonymization, and data deidentification. In Proceedings of ASIACCS’08.
Hevia, A., & Micciancio, D. (2002). The provable security of graph-based one-time signatures and extensions to algebraic signature schemes. In Proceedings of ASIACRYPT’02.
Johnson, R., Molnar, D., Song, D., Wagner, D. (2002). Homomorphic signature schemes. In Proceedings of the 2th cryptographers’ track at the RSA conference on topics in cryptology.
Miyazaki, K., Hanaoka, G., & Imai, H. (2006). Digitally signed document sanitizing scheme based on bilinear maps. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM symposium on information, computer and communications security.
Neven, G. (2008). A simple transitive signature scheme for directed trees. Theoretical Computer Science, 396(1–3), 277–282.
Ranchal, R. et al. (2010). Protection of identity information in cloud computing without trusted third party. In Proceedings the 29th IEEE international symposium on reliable distributed systems (SRDS’10).
Shahandashti, S. F., Salmasizadeh, M., & Mohajeri, J. (2005) A provably secure short transitive signature scheme from bilinear group pairs. In Proceedings of the 4th international conference on security in communication networks.
Smart, N. P., & Vercauteren, F. (2010). Fully homomorphic encryption with relatively small key and ciphertext sizes. In Proceedings of the 13th international conference on practice and theory in public key cryptography(PKC’10).
van Dijk, M. et al. (2010). Fully homomorphic encryption over the integers. In Proceedings of the 13th international conference on practice and theory in public key cryptography(PKC’10).
Wei, L., Coull, S. E., & Reiter, M. K. (2011). Bounded vector signatures and their applications. In Proceedings of ASIACCS’11.
Yi, X. (2007). Directed transitive signature scheme. In Proceedings of the 7th cryptographers’ track at the RSA conference on topics in cryptology.
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No.61272422, 61202353, the Open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Information Security under Grant No. BK212004, and Program for Excellent Talents in Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications under Grant No.NY209014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Sha, K. & Lv, W. Slight Homomorphic Signature for Access Controlling in Cloud Computing. Wireless Pers Commun 73, 51–61 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0977-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0977-8