Abstract
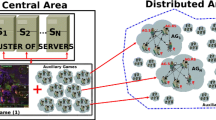
Massively multi-player online role-playing games (MMORPGs) follows a client-server model that has the numerous gaming users with many interactions at the same virtual world, massive loading that result in delays, resource shortages, and other such problems occur. Also, faced with high resource demand variability and with misfit resource renting policies, the current practices is to overprovision for each game tens of owned data. Existing load balancing schemes for distributed virtual environments and multiplayer games try to balance the workload among servers by transferring some workload of an overloaded server to other servers. While load balancing algorithms can minimize the average response time of the system, they may also result in frequent client migrations, which may damage the interactivity of an online games. To solve this, many developers devote research to load-balancing servers, yet due to steady and dynamic map divisions, such research is unreliable. Many developers propose algorithms to distribute the load on the server nodes, but the load is usually defined as the number of players on each server, what is not an ideal results. So, we propose a gaming user-oriented load balancing scheme for the load balancing of MMORPGs servers in this paper. This scheme shows effectiveness at dealing with hot-spots and other gatherings of gaming users at specific servers compared to previous methods.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, D., & Shirmohammadi. S. (2008). A microcell oriented load balancing model for collaborative virtual environments. In Proceeding of the IEEE conference on virtual environments, human computer interfaces and measurement systems, VECIMS (pp. 86–91).
Barraca, J., Matos, A., & Aguiar, R. (2011). User centric community cloud. Wireless Personal Communications, 58, 31–48.
Kim, H.-Y. (2012). An efficient access control scheme for online gaming server, proceeding of the computer science and convergence. lecture notes in. Electrical Engineering, 114(1), 259–267.
White, W. M., Koch, C., Gupta, N., Gehrke, J., & Demers, A. J. (2007). Database research opportunities in computer games. SIGMOD Record, 36(3), 7–13.
Bartle, R. (2003). Designing virtual worlds. Indianapolis: New Riders Games.
Karve, A., Kimbrel, T., Pacifici, G., Spreitzer, M., Steinder, M., Sviridenko, M., et al. (2006). Dynamic placement for clustered web applications. In Proceedings Conference World Wide Web (WWW) (pp. 595–604).
Zhang, Y., Zhang, K., et al. (2008). An adaptive threshold load balancing scheme for the end-to-end recognifigurable system. Wireless Personal Communications, 46, 47–65.
Koutsorodi, A. A., Adamopoulou, E. F., et al. (2007). Service configuration and user profile in 4G terminals. Wireless Personal Communications, 43, 1303–1321.
Bezerra, C. E. B., & Geyer, C. F. R. (2009). A load balancing scheme for massively multiplayer online games. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 45(1), 263–289.
Zamboni, M. A., & Ferretti, S. (2005). Interactivity maintenance event synchronization in massive multiplayer online games, Technical, Report UBLCS-2005-05.
Nae, V., & Losup, A. (2011). Dynamic resource provisioning in massively multiplayer online games. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 22(3), 380–395.
Grande, R. E. D., & Boukerche, A. (2009). Dynamic partitioning of distributed virtual simulations for reducing communication load. IEEE international workshop on: Haptic audio visual environments and games (pp. 176–181).
Duong, T. N. B., & Zhou, S. (2003). A dynamic load sharing algorithm for massively multiplayer online games. The 11th IEEE internatinal conference on network ICON (pp. 131–136).
Grosu, D., & Chronopoulos, A. T. (2004). Algorithmic mechanism design for load balancing in distributed systems. Part B: Cybernetic, IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics, 34(1), 77–84.
Andrade, G., & Corruble, V. (2005). Challenge-Sensitive action selection an application to game balancing. In IEEE/WIC/ACM international conference on, intelligent agent technology (pp. 194–200).
Jinzhonh, W. A. N. G., & Zhigang, Y. U. E. (2010). A finding less-load server algorithm based on mmog and analysis. International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation (ICICTA), 1, 96–99.
Huang, G., Ye, M., & Cheng, L. (2004). Modeling system performance in MMORPG, Global telecommunications conference workshops. IEEE (pp. 512–518).
Nae, V., Prodan, R., & Fahringer, T. (2010). Cost-efficient hosting and load balancing of massively multiplayer online games. In IEEE/ACM 11th internatinal conference on GridComputing CGRID (pp. 9–16).
Quax, P., Cleuren, J., Vanmontfort, W., & Lamotte, W. (2011). Empirical evaluation of the efficiency of spatial subdivision schemes and load balancing strategies for networked games. In Proceeding of 20th internatinal conference on computer communications and networks (ICCN) (pp. 1–6).
Lee, K., & Lee, D. (2003). A Scalable dynamic load distribution scheme for multi-server distributed virtual environment system with highly-skewed user distribution. In Proceedings of the ACM symposium on virtual reality software and technology (pp. 160–168). New York.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the MKE (The Ministry of Knowledge Economy), NHN Corp., under IT/SW Creative research program supervised by the NIPA (National IT Industry Promotion Agency) (NIPA-2012-H0506-12-101)). This Research was supported by the Sookmyung Women’s University Research Grants (1–1303-0109)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HY., Park, HJ. An Efficient Gaming User Oriented Load Balancing Scheme for MMORPGs. Wireless Pers Commun 73, 289–297 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1237-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1237-2