Abstract
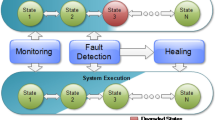
The self-adaptation of software systems is a complex process that depends on several factors that can change during the system operational lifetime. But, Today’s workflow management systems are only applicable in a secure and safe manner if the business process to be supported is well-structured and there is no need for ad hoc deviations at runtime. Hence, it is necessary to define mechanisms for providing a self-adaptive system the capability of reconfiguration during run-time the process that controls its adaptation. In this paper, we provide rapid dynamic reconfiguration using the workflow based on goal-scenario as the basis to set up strategies in accordance with the adaptive judgment. Also, we provide a sophisticated approach which fosters learning from past process changes by process variants through the order matrix. We present a formal foundation for the support of dynamic structural workflow changes of running. Our approach uses estimates based goal-scenario to determine which remaining parts of running workflows are affected by the external environment and is able to predictively perform suitable adaptation. This helps to ensure that necessary adaptation are performed in time with minimal user interaction which is especially valuable in change of external environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rinderle, S., Reichert, M., & Dadam, P. (2004). Correctness criteria for dynamic changes in workflow systems—A survey. Data and Knowledge Engineering, 50, 9–34.
Reichert, M., Rinderle, S., & Dadam, P. (2003). “On the common support of workflow type and instance changes under correctness constraints”, in: CoopIS’03, LNCS (Vol. 2888, pp. 407–425). Italy: Catania.
Baek, S. J., Ko, J. W., & Song, Y. J. (2011). Design of goal-scenario based diagnosis agent for business activity monitoring. In ICISA (International Conference on Information Science and Applications), pp. 1–7, (2011).
Garlan, D. & Schmerl, B. (2002). Model-based adaptation for self-healing systems. In ACM SIGSOFT workshop on self-healing systems (WOSS’02), pp. 18–19, (2002).
Lee, K. D., Nam, M. Y., Chung, K. Y., Lee, Y. H., & Kang, U. G. (2013). Context and profile based cascade classifier for efficient people detection and safety care system. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 63(1), 27–44.
Song, C. W., Chung, K. Y., Jung, J. J., Rim, K. W., & Lee, J. H. (2011). Localized approximation method using inertial compensation in WSNs. Information—An International Interdisciplinary Journal, 14(11), 3591–3600.
Jung, Y. G., Han, M. S., Chung, K. Y., & Lee, S. J. (2011). A study of a valid frequency range using correlation analysis of throat signal. Information-An International Interdisciplinary Journal, 14(11), 3791–3799.
S. W. Cheng et al. Architecture-based self-adaptation in the presence of multiple objectives, In Proc. of the ICSE SEAMS’06, pp. 2–8, (2006).
Georgas, J. C., & Talylor, R. N. (2004). Towards a knowledge based approach to architectural adaptation management. In Proceedings of the WOSS’04, pp. 59–63.
Chung, K. Y. (2013). Effect of facial makeup style recommendation on visual sensibility. Multimedia Tools and Applications. doi:10.1007/s11042-013-1355-6.
Song, C. W., Lee, D., Chung, K. Y., Rim, K. W., & Lee, J. H. (2013). Interactive middleware architecture for lifelog based context awareness. Multimedia Tools and Applications. doi:10.1007/s11042-013-1362-7.
Kim, J. H., & Chung, K. Y. (2013). Ontology-based healthcare context information model to implement ubiquitous environment. Multimedia Tools and Applications,. doi:10.1007/s11042-011-0919-6.
Kim, J. H., Lee, D., & Chung, K. Y. (2013). Item recommendation based on context-aware model for personalized u-healthcare service Multimedia Tools and Applications. doi:10.1007/s11042-011-0920-0.
Kim, S. H., & Chung, K. Y. (2013). 3D Simulator for stability analysis of finite slope causing plane activity. Multimedia Tools and Applications. doi:10.1007/s11042-013-1356-5.
Chung, K. Y., Yoo, J., & Kim, K. J. (2013). Recent trends on mobile computing and future networks. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing. doi:10.1007/s00779-013-0682-y.
Weber, B., Reichert, M., & Rinderle-Ma, S. (2008). Change Pattern and changes support features-enhancing flexibility in process-aware information systems. Data and Knowledge Engineering, 66(3), 438–466.
Aalst, W. M. P. V. D., Weske, M., Wirtz, G. (2003). Advanced topics in workflow management: Issues, requirements, and solutions. International Journal of Integrated Design and Process Science, 7(3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baek, SJ., Han, JS. & Chung, KY. Dynamic Reconfiguration Based on Goal-Scenario by Adaptation Strategy. Wireless Pers Commun 73, 309–318 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1239-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1239-0