Abstract
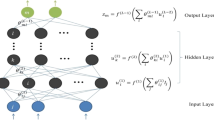
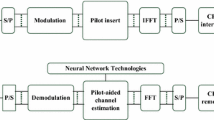
In this paper, a scheme for reducing the peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) primarily and bit error rate simultaneously in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing using feed forward artificial neural network is proposed and analyzed. The proposed scheme switches one or more null-carriers with data subcarriers to offer minimum PAPR and requires no channel side information during transmission. To reduce high computational complexity, a multilayer neural network with Levenberg–Marquardt training algorithm is used. The proposed scheme thus suits to supplement some of other PAPR-reduction methods with low rate hit and complexity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang, T., & Wu, Y. (2008). An overview: Peak-to-average power ratio reduction techniques for OFDM signals. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 54(2), 257–268.
Han, S. H., & Lee, J. H. (2005). An overview of peak-to-average power ratio reduction techniques for multicarrier transmission. IEEE Wireless Communications, 12(2), 56–65.
Marc, D., Behravan, A., Eriksson, T., & Pijoan, J. L. (2008). Evaluation of performance improvement capabilities of PAPR-reducing methods. Wireless Personal Communications, 47(1), 137–147.
Armstrong, J. (2002). Peak-to-average power eduction for OFDM by repeated clipping and frequency domain filtering. IEEE Electronics Letters, 38(8), 246–247.
Cimini, L. J., & Sollenberger, N. R. (2000). Peak-to-average power ratio reduction of an OFDM signal using partial transmit sequences. IEEE Communication Letters, 4(3), 86–88.
Yong, W., Ge, J., Wang, L., & Li, J. (2012). Reduction of PAPR of OFDM signals using nonlinear companding transform. Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-012-0820-2.
Li, C. M., & Cheng, Y. Y. (2013). A low complexity partition dummy sequence insertion PAPR reduction method for the OFDM system. Wireless Personal Communications, 68(3), 949–961.
Davis, J. A., & Jedwab, J. (1999). Peak-to-mean power control in OFDM, Golay complementary sequences, and Reed-Muller codes. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 45(7), 2397–2417.
Yang, K., & Chang, S. (2003). Peak-to-average power control in OFDM using standard arrays of linear block codes. IEEE Communication Letters, 7(4), 174–176.
Ryu, H. G., Lee, J. E., & Park, J. S. (2004). Dummy sequence insertion (DSI) for PAPR reduction in the OFDM communication system. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 50(1), 89–94.
Devlin, C. A., Zhu, A., & Brazil, T. J. (2008). Peak to average power ratio reduction technique for OFDM using pilot tones and unused carriers. In IEEE radio and wireless symposium (pp. 33–36).
Hosokawa, S., Ohno, S., Teo, K. A. D., & Hinamato, T. (2005). Pilot tone design for peak-to-average power ratio reduction in OFDM. In IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (pp. 6014–6017).
Hu, D., Yang, L., Shi, Y., & He, L. (2006). Optimal pilot sequence design for channel estimation in MIMO OFDM systems. IEEE Communications Letters, 10(1), 1–3.
Wen, J. H., Lee, S. H., Huang, Y. F., & Hung, H. L. (2008). A suboptimal PTS algorithm based on particle swarm optimization technique for PAPR reduction in OFDM systems. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 601346, 1–8.
Weng, C. E, Chang, C.W, Chen, C.H, & Hung, H.L. (2012). “Novel low-complexity partial transmit sequences scheme for PAPR reduction in OFDM systems using adaptive differential evolution algorithm,”. Wireless Personal Communications,. doi:10.1007/s11277-012-0836-7.
Lain, J. K., Wu, S. Y., & Yang, P. H. (2011). PAPR reduction of OFDM signals using PTS: A real-valued genetic approach, EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 126, 1–8.
Sohn, I. (2007). RBF neural network based SLM peak-to-average power ratio reduction in OFDM systems. ETRI Journal, 29(3), 402–404.
Wong, K. T., Wang, B., & Chen, J.-C. (2011). OFDM PAPR reduction by switching null subcarriers and data subcarriers. IEEE Electronics Letters, 47(1), 62–63.
Marquardt, D. W. (1963). An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. Journal of the Industry Society Industrial & Applied Mathematics, 11(2), 431–441.
Jabrane, Y., Jimenez, V. P. G., Armeda, A. G., Said, B. E., & Ouahman, A. A. (2010). Reduction of power envelope fluctuations in OFDM signals by using neural networks. IEEE Communication Letters, 14(7), 599–601.
Ohta, M., Ueda, Y., & Tamashita, K. (2006). PAPR reduction of OFDM signal by neural networks without side information and its FPGA implementation. Trans. Inst. Elect. Engnr. Japan, 126, 1296–1303.
Hagan, M. T., Demuth, H. B., & Beale, M. (2011). Neural network design 4th ed. Cengage Learning India Pvt. Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, A., Saxena, R. & Patidar, M. OFDM Link with a Better Performance Using Artificial Neural Network. Wireless Pers Commun 77, 1477–1487 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1593-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1593-y