Abstract
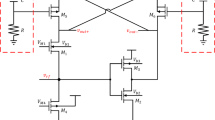
Aiming for the simultaneous realization of constant gain, accurate input and output impedance matching and minimum noise figure (NF) over a wide frequency range, the circuit topology and detailed design of wide broadband low noise amplifier (LNA) are presented in this paper. A novel 2.5–3.1 GHz wide-band LNA with unique characteristics has been presented. Its design and layout are done by TSMC 0.18 \(\upmu \hbox {m}\) technology. Common gate stage has been used to improve input matching. In order to enhance output matching and reduce the noise as well, a buffer stage is utilized. Mid-stages which tend to improve the gain and reverse isolation are exploited. The proposed LNA achieves a power gain of 15.9 dB, a NF of 3.5 dB with an input return loss less than \(-\)11.6, output return loss of \(-\)19.2 to \(-\)19 and reverse isolation of \(-\)38 dB. The LNA consumes 54.6 mW under a supply voltage of 2 V while having some acceptable characteristics.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, Zh., Wang, Z., Zhang, M., Chen, L., Wu, Ch., & Wang, Zh. (2014). A 2.4 GHz ultra-low-power current-reuse CG-LNA with active-boosting technique \(G_m\) boosting technique. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 24(5).
Kao, H. L., & Chang, K. C. (2008). Very low-power CMOS LNA for UWB wireless receivers using current-reused topology, Science-direct2007 Elsevier Ltd. Solid-State Electrochemistry, 52, 8690.
Karimi, Gh R, & Babaei, S. (2012). Sedaghat, ultra low voltage, ultra-low power low noise amplifier for 2 GHz applications. International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 66, 1822.
Saman, A., Jamal Deen, M., & Chih-Hung, Ch. (2007). Design of the input matching network of RF CMOS LNAs for low-power operation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits Systems-I: Regular Papers, 54(3).
Khurram, M., & R. Hasan, S. M. (2011) Novel analysis and optimization of gm-boosted common-gate UWBLNA. Microelectronics Journal, 42, 25364.
Oh, N.-J. (2010). A low-power 3.110.6 GHz ultra-wideband CMOS low-noise amplifier with common-gate input stage. Current Applications and Physics, 11(8792).
Meammar, A., Chye, B. C., Anh, D. M., & Seng, Y. K. (2009). A 3–8 GHz low-noise CMOS amplifier. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 19(4), 245–247.
Chang, J. F., & Lin, Y. S. (2011). 0.99 mW 310 GHz common-gate CMOS UWB LNA using T-match input network and self-body-bias technique. Electronics Letters, 47(11), 658659.
Liu, R. C., Deng, K. L., & Wang, H. (2003). A 0.622 GHz broadband CMOS distributed amplifier. In Proceedings of the IEEE radio frequency integrated circuits (RFIC) symposium (p. 103106), 810.
Park, B., Choi, S., & Hong, S. (2010). A low-noise amplifier with tunable interference rejection for 3.1-to 10.6-GHz UWB systems. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 20(1):40-42.
Jung, J. H., Yun, T. Y., & Choi, J. H. (2006). Ultra-wideband low noise amplifier using a cascode feedback topology. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 48(6), 1102–1104.
Ziabakhsh, S., Alavi-Rad, H., & Yagoub, M. C. E. (2012). A high-gain low-power 214 GHz ultra-wide-band CMOS LNA for wireless receivers. International Journal of Electronics and Communications (AE), 727–731.
Liang, C. P., Rao, P. Z., Huang, T. J., & Chung, S. J. (Feb. 2010). Analysis and design of two low-power ultra-wideband CMOS low-noise amplifiers with out-band rejection. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 58(2), 227–286.
Duan, J., & Wang, Z., Li, Z. (2008). A fully integrated LNA for 3–5 GHz UWB wireless applications in 0.18m CMOS technology. IEEE, 1274–1277.
Lei, Ch., Chunqi, Sh, Runxi, Zh, Ying, R., & Zongsheng, L. (2012). An ultra-wide-band 3.110.6 GHz LNA design in 0.18 um SiGe BiCMOS. International Journal of Electronics Communications (AE), 66, 157–161.
Bevilac, A., & Niknejad, A. M. (2004). An ultra-wideband CMOS LNA for 3.1 to 10.6 GHz wireless receivers. In IEEE Solid-State Circuits Conference (pp. 382–383).
Razavi, B. (1998). RF microelectronics. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-hall.
Rajashekharaiah, M. (2005). Gain control and linearity Improvement for low noise amplifier in 5GHz direct conversion receivers, Master of Science thesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nouri, M., Karimi, G. A Novel 2.5–3.1 GHz Wide-Band Low-Noise Amplifier in 0.18 \(\upmu \hbox {m}\) CMOS. Wireless Pers Commun 79, 1993–2003 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1969-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1969-7