Abstract
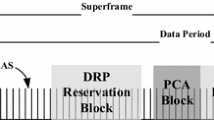
Ultra wideband (UWB) technology has emerged as a solution for the wireless interface between medical sensors and a personal server in future telemedicine systems. The WiMedia Alliance has specified a distributed medium access control protocol based on UWB for high-rate wireless personal area networks. The legacy WiMedia standard must statically reserve an additional transmission time of 30 %, since transmission time is limited to network environment in wireless network. When channel environment is deteriorating badly, the additional reservation may not have enough time. Because the legacy WiMedia standard must wait the next reservation period if sending device does not transmit data frames in the current reservation period, the transmission delay occurs. Also, in a good channel environment, the additional reservation time results in a waste of performance. Therefore, there is a need to provide the reliability of data transmission as sending device predicts channel environment in WiMedia network and reserves the distributed reservation protocol (DRP) reservation duration considering the estimated channel environment. In this paper, we propose a novel resource reservation scheme considering channel environment in WiMedia network. The simulation results show that proposed protocol can enhance the throughput and delay performance and improve energy efficiency by minimizing the idle period of DRP reservation block.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Access category
- AVRS:
-
Average RSSI
- BP:
-
Beacon period
- BER:
-
Bit error rate
- CSI:
-
Channel state information
- CSMA/CA:
-
Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance
- DEP:
-
Distance estimation response
- DER:
-
Distance estimation request
- D-MAC:
-
Distributed medium access control
- DRP:
-
Distributed reservation protocol
- DTP:
-
Data transfer period
- IE:
-
Information element
- LBRS:
-
Lower bound RSSI
- MAS:
-
Medium access slot
- PCA:
-
Prioritized contention access
- PER:
-
Packet error rate
- RSSI:
-
Received strength signal indication
- TDMA:
-
Time division multiplexing access
- UBRS:
-
Upper bound RSSI
- UWB:
-
Ultra wide-band
- WPAN:
-
Wireless personal area network
References
WiMedia MAC Release Spec. 1.5. Distributed medium access control (MAC) for wireless networks, October 5, 2009. http://www.wimedia.org/en/index/asp.
IEEE 802.15.3. Wireless medium access control and physical layer specification for high rate wireless personal area networks, 2003. http://standards.ieee.org/reading/ieee/std/lanman/restricted/802.15.3-2003.pdf.
del Prado Pavon, J., Sai Shankar, N., Gaddam, V., Challapali, K., & Chou, C.-T. (2006). The MBOA–WiMedia specification for ultra wideband distributed networks. Communications Magazine, IEEE, 44(6), 128–134.
Zhang, R., Ruby, R., Pan, J., Cai, L., & Shen, X. (2010). A hybrid reservation/contention-based MAC for video streaming over wireless networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 28(3), 389–398.
Kim, J.-W., Huh, Y., Lee, Y. W., Maeng, S. Y., Park, S. H., Hur, K., et al. (2013). A contention based medium access scheme for energy saving in WiMiedia networks. Advanced Science and Technology Letters, 28, 116–120.
Go, K.-C., Kim, J.-H., Oh, S.-H., Moon, K.-D., & Lee, K.-I. (2009). Resource allocation algorithm considering a priority of service classes for WiMedia UWB system. In Proceedings of ICUIMC 2009 (pp. 298–301), January, 2009.
Daneshi, M., Pan, J., & Ganti, S. (2010). Towards an efficient reservation algorithm for distributed reservation protocols. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM (pp. 1–9), March, 2010.
Xu, Y., Guan, Q., Zhang, J., Wei, G., Ding, Q., & Zhang, H. (2008). Service interval based channel time allocation in wireless UWB networks. In Proceedings of IEEE ICCS (pp. 1550–1554).
Daneshi, M., Pan, J., & Ganti, S. (2010). Distributed reservation algorithms for video streaming over UWB-based home networks. In IEEE consumer and communications networking conference (pp. 250–259).
Kuo, W.-K., & Wu, C.-Y. (2009). Supporting real-time VBR video transport on WiMedia-based wireless personal area networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(4), 1965–1971.
Kim, K.-I. (March 2012). Adjusting transmission power for real-time communications in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Information and Communication Convergence Engineering, 10(1), 21–26.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2009-0093828) and in part by the MSIP (Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning), Korea, under the C-ITRC (Convergence Information Technology Research Center) support program (NIPA-2014-H0401-14-1009) supervised by the NIPA (National IT Industry Promotion Agency).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JW., Hur, K. & Lee, SR. Channel State Information Based Distributed Reservation Protocol for Energy Efficiency in WiMedia Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 80, 769–784 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-2040-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-2040-4