Abstract
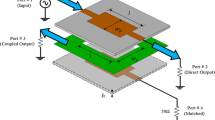
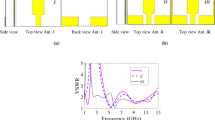
A design of compact and inexpensive two-layer ultra-wideband (UWB) \(4~\times ~4\) butler matrix beam-forming network employing trapezoidal-shaped microstrip-slot technique is presented in this paper. The proposed design uses multi-layer technology that allows having compact size and broad bandwidth. The proposed \(4\times 4\) butler matrix configuration consists of four couplers and two phase shifters without using crossovers. Both couplers and phase shifters use trapezoidal-shaped broadside coupled patches and a rectangular slot created in a common ground plane of two Rogers duroid RT5880 dielectric substrates. The simulations and experimental results show a good performance in terms of transmission magnitudes and phases with good return losses and isolation characteristics across the entire UWB frequency range. To demonstrate the functionality of the designed butler matrix, four identical tapered slot antenna (TSA) elements are connected to four output ports of the butler matrix and the radiation pattern characteristics are simulated, presented and discussed.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beamforming boosts the range and capacity of WiMAX networks, white paper of Fujitsu Microelectronics America Inc (2008).
Blass, J. (1960). Multidirectional antenna—A new approach to stacked beams. IRE international convention record (Vol. 8, pp. 48–50). IEEE.
Lo, Y. T., & Lee, S. W. (1988). Antenna handbook: Theory, applications and design. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Rotman, W., & Turner, R. (1963). Wide-angle microwave lens for line source applications. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 11(6), 623–632.
Butler, J. (1961). Beam-forming matrix simplifies design of electronically scanned antennas. Electronic Design, 9(8), 170–173.
Nedil, M., Denidni, T. A., & Talbi, L. (2006). Novel Butler matrix using CPW multilayer technology. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 54(1), 499–507.
Ibrahim, S. Z., & Bialkowski, M. E. (2009). Wideband Butler matrix in microstrip-slot technology. Asia Pacific Microwave conference 2009, APMC 2009 (pp. 2104–2107). IEEE.
Haraz, O. M., & Sebak, A. R. (2013). Two-layer butterfly-shaped microstrip \(4\times 4\) Butler matrix for ultra-wideband beam-forming applications. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wideband (ICUWB) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Pozar, D. M. (2009). Microwave engineering. Newyork: Wiley.
Tanaka, T., Tsunoda, K., & Aikawa, M. (1988). New slot-coupled directional couplers between double-sided substrate microstrip lines, and their applications. IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, 1988 (pp. 579–582). IEEE.
Abbosh, A. M., & Bialkowski, M. E. (2007). Design of compact directional couplers for UWB applications. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 55(2), 189–194.
Abbosh, A. M. (2008). Broadband quadrature coupler with slotted ground plane. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 50(2), 328–331.
Nedil, M., & Denidni, T. A. (2008). Analysis and design of an ultra wideband directional coupler. Progress in Electromagnetics Research B, 1, 291–305.
Ahmed, O. M., Sebak, A. R., & Denidni, T. A. (2012). A novel butterfly-shaped multilayer backward microstrip hybrid coupler for ultrawideband applications. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 54(10), 2231–2237.
Ansoft Corporation, HFSS, v10, Ansoft Corp., (2007).
CST Microwave Studio, ver. 2008, Computer simulation technology, Framingham, MA. (2008).
Schaubert, D. H., Kollberg, E. L., Korzeniowski, T., Thungren, T., Johansson, J., & Yngvesson, K. S. (1985). Endfire tapered slot antennas on dielectric substrates. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 33(12), 1392–1400.
Hilberg, W. (1969). From approximations to exact relations for characteristic impedances. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 17(5), 259–265.
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and by King AbdulAziz City for Science and Technology (KACST) Technology Innovation Center in RFTONICS hosted at King Saud University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haraz, O.M., Sebak, AR. & Alshebeili, S.A. Ultra-Wideband \(4\times 4\) Butler Matrix Employing Trapezoidal-Shaped Microstrip-Slot Technique. Wireless Pers Commun 82, 709–721 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-2248-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-2248-3