Abstract
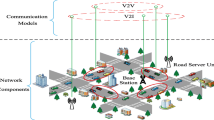
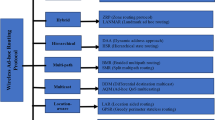
Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks (VANETs) are now considered as a way to realize active safety, by providing the position information of each other or the possible danger warning by wireless vehicular communications. Multi-hop data delivery in VANETs is a challenging task, since it encounters rapid changes in network topology and frequent fragmentation in the network. Because of these characteristics, routing algorithms based on greedy forwarding are known to be very suitable for VANETs. The design and implementation of efficient and scalable routing protocols for VANETs is a challenging task due to high dynamics and mobility constraints. In this paper, we have worked on a routing protocol over VANETs to efficiently broadcast the information for the sake of active safety applications, such as the positions and the directions of the vehicles. Therefore, we have explained a position-based routing protocol called directional-location aided routing (D-LAR) with (1) location-aided routing utilizes location information using GPS to limit the area for discovering a new route to a smaller request zone and (2) directional routing having direction closest to the line drawn between source and destination. D-LAR protocol is a greedy based approach to forward packet to the node present in request zone part of sender’s transmission range as a most suitable next-hop node. Further, we have justified the feasibility of D-LAR routing protocol for VANETs. Through analytical analysis we have also given the relationship among the average number of hop counts, link lifetime, and path throughput metrics for the protocol. Finally, simulation results show that the proposed formulation can be used to evaluate path throughput accurately in the network.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moustafa, H., & Zhang, Y. (2009). Vehicular networks: Techniques, standards, and applications. Boca Raton London, New York: CRC Press.
Guo, J., & Balon, N. (2006). Vehicular ad-hoc networks and dedicated short-range communication. Dearborn: University of Michigan.
Xi, S., & Xia-miao, L. et al. (2010). Study of the feasibility of VANET and its routing protocols. IEEE, WiCOM, 08, 1–4.
Lee, K. C., Lee, U., & Gerla, M. (2010). Survey of routing protocols in vehicular ad hoc networks. In M. Watfa (Ed.), Advances in vehicular ad-hoc networks: Developments and challenges (pp. 149–170). USA: IGI Global.
Yamaguchi, H., Sun, W., & Higashino, T. (2010). Geographic routing on vehicular ad hoc networks. In Advances in vehicular ad-hoc networks: Developments and challenges. USA: IGI Global.
Boukerche, A., Oliveira, H. A. B. F., Nakamura, E. F., & Loureiro, A. A. F. (2008). Vehicular ad-hoc networks: A new challenge for localization-based systems. Computer Communication. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Dommety, G., & Jain, R. (1996). Potential networking applications of global positioning systems (GPS). Technical Report TR-24. Columbus: Ohio State University.
Young-BaeKo, Vaidya, N. H. et al., (1998). Location-aided routing (LAR) in mobile ad-hoc networks. ACM/IEEE, MOBICOM’98, 66–75.
Stojmenovic, I., Ruhil, A. P., Lobiyal, D. K., et al. (2006). Voronoi diagram and convex hull based geocasting and routing in wireless networks. Wireless communications and mobile computing special issue on ad-hoc wireless networks (pp. 247–258). New York: Wiley.
Kranakis, E., Singh, H., & Urrutia, J. et al., (1999). Compass routing on geometric networks. In Proceedings of the 11th Canadian conference on computational geometry (CCCG’99).
Johnson, D. B., Maltz, D. A., et al. (1996). Dynamic source routing in ad-Hoc wireless networks. Mobile computing (pp. 153–181). Dordrecht: Kluwer.
Raw, R. S., Das, S., Singh, N., & Kumar, S., et al. (2012). Feasibility evaluation of VANET using directional-location aided routing (D-LAR) protocol. International Journal of Computer Science Issues, 9(5), No. 3, 404–410.
Wang, N., Chen, J., Huang, Y., & Wang, S., et al. (2002). A greedy location-aided routing protocol for mobile ad-hoc networks. In WSEAS international conference on applied computer and applied computational science (pp. 175–180).
RITES. (2010). Urban environmental engineering household survey, Delhi. http://www.scribd.com/doc/36200890/Delhi-Metro
Xi, S., & Xia-Miao, L., et al., (2008). Study of the feasibility of VANET and its routing protocols. In IEEE 4th international conference on wireless communications, networking and mobile computing (WOCOM) (pp. 1–4).
Raw, R. S., Das, S., et al. (2011). Performance analysis of P-GEDIR protocol for vehicular ad-hoc network in urban traffic environments. Wireless Personal Communications, 68(1), 65–78.
Nasipuri, A., Castañeda, R., et al. (2001). Performance of multipath routing for on-demand protocols in mobile ad-hoc networks. Mobile Networks and Applications, 6, 339–349.
Heusse, M., Rousseau, F., Berger-Sabbatel, G., & Duda, A. (2003). Performance anomaly of 802.11b. IEEE, INFOCOM, 2, 836–843.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raw, R.S., Lobiyal, D.K., Das, S. et al. Analytical Evaluation of Directional-Location Aided Routing Protocol for VANETs. Wireless Pers Commun 82, 1877–1891 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2320-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2320-7